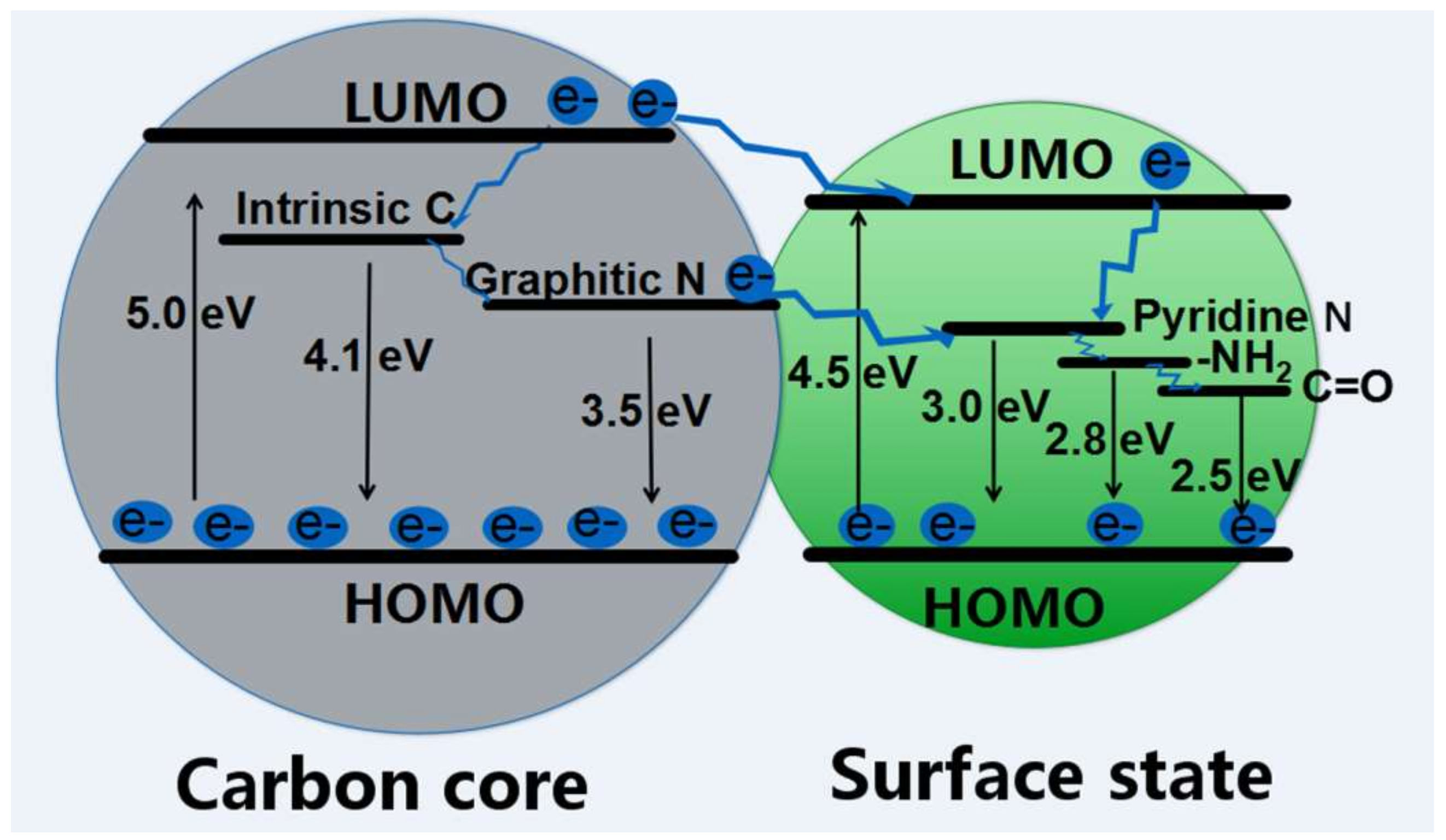
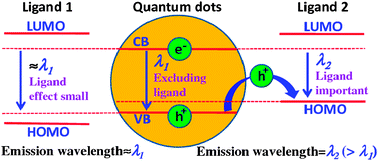
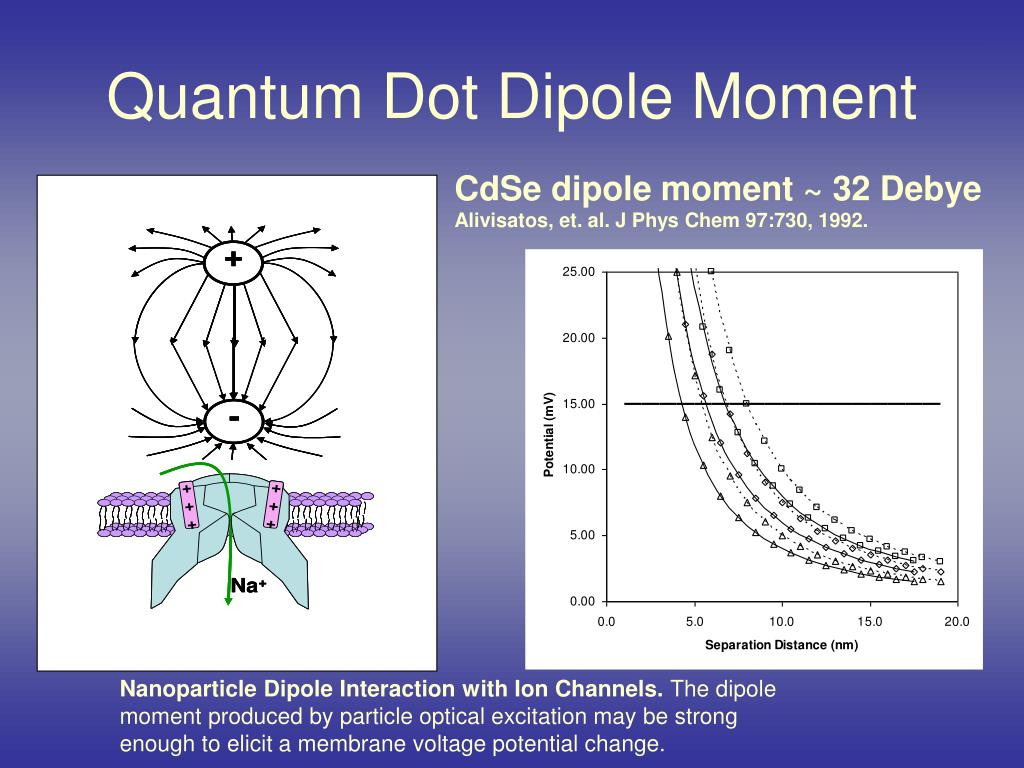
Have they locked up Joe Biden for cheating yet?
What about the corrupt Hillary Clinton?
Or even Prince Andrew?
If not why not because nobody is above the law.
Recently retired, no longer affiliated with any party. Constitutional patriot listening for God’s word
Blind justice will reign, after the storm
During a cytokine storm, various inflammatory cytokines are produced at a much higher rate than normal. This overproduction of cytokines causes positive feedback on other immune cells to occur, which allows for more immune cells to be recruited to the site of injury that can lead to organ damage.
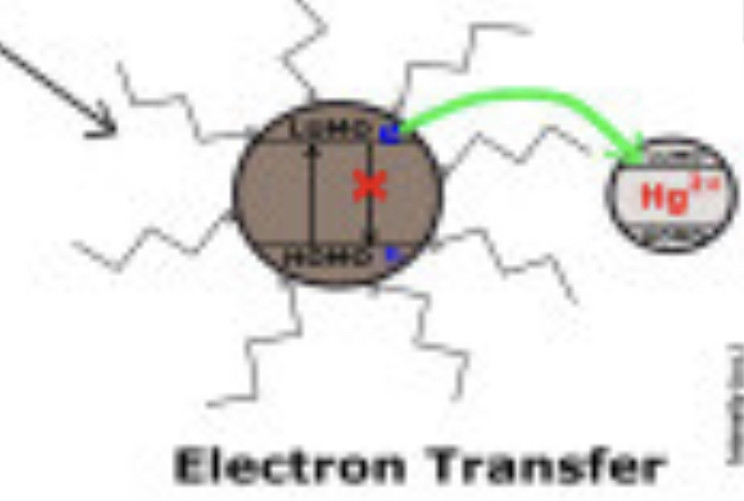
The mammalian mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC) includes complexes I‑IV, as well as the electron transporters ubiquinone and cytochrome c. There are two electron transport pathways in the ETC: Complex I/III/IV, with NADH as the substrate and complex II/III/IV, with succinic acid as the substrate. The electron flow is coupled with the generation of a proton gradient across the inner membrane and the energy accumulated in the proton gradient is used by complex V (ATP synthase) to produce ATP.
The first part of this review briefly introduces the structure and function of complexes I‑IV and ATP synthase, including the specific electron transfer process in each complex. Some electrons are directly transferred to O2 to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the ETC. The second part of this review discusses the sites of ROS generation in each ETC complex, including sites IF and IQ in complex I, site IIF in complex II and site IIIQo in complex III, and the physiological and pathological regulation of ROS. As signaling molecules, ROS play an important role in cell proliferation, hypoxia adaptation and cell fate determination, but excessive ROS can cause irreversible cell damage and even cell death.
The occurrence and development of a number of diseases are closely related to ROS overproduction. Finally, proton leak and uncoupling proteins (UCPS) are discussed. Proton leak consists of basal proton leak and induced proton leak. Induced proton leak is precisely regulated and induced by UCPs. A total of five UCPs (UCP1‑5) have been identified in mammalian cells. UCP1 mainly plays a role in the maintenance of body temperature in a cold environment through non‑shivering thermogenesis. The core role of UCP2‑5 is to reduce oxidative stress under certain conditions, therefore exerting cytoprotective effects. All diseases involving oxidative stress are associated with UCPs.
"Some electrons are directly transferred to O2 to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the ETC."
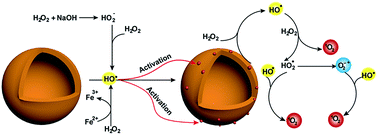
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation is of intense interest because of its crucial role in many fields. Here we demonstrate that MoS2-QDs exhibit a promising capability for the generation of reactive oxygen species, which leads to enhanced chemiluminescence. We discovered that the unique performance is due to hydroxyl radical activation increasing the active catalytic sites on molybdenum sulphide quantum dots (MoS2-QDs). The reactive oxygen species, such as hydroxyl radicals (˙OH), superoxide radicals (˙O2−) and singlet oxygen (1O2) have been efficiently generated from H2O2 solution in alkaline conditions. In particular, the maximum ˙OH yield was enhanced significantly (9.18 times) compared to the Fe(II)/H2O2 Fenton system under neutral conditions. These findings not only enrich our understanding of the fascinating performance of MoS2 QDs, but also provide a new pathway for ROS generation in all kinds of pH
"compared to the Fe(II)/H2O2 Fenton system under neutral conditions."
Ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (USPIO) are being developed for several biomedical applications including drug delivery and imaging. However, little is known about their possible adverse effects on thrombosis and cardiac oxidative and DNA damage.
The results show that the IONP-induced oxidative stress was concentration-dependent in nature, with significant (P < 0.05) increase in ROS levels, lipid peroxidation level as well as depletion of antioxidant enzymes and glutathione. Moreover, we observed morphological changes in the cell after intracellular uptake and localization of nanoparticles in cells. From the findings of the study, it may be concluded that IONPs induce ROS-mediated cytotoxicity in lymphocytes.
Cytokines perform pleiotropic functions to mediate and regulate the immune response and are generally recognized as biomarkers of immunotoxicity. While the specificity and validity of certain cytokines as markers of adverse immune response has been established for chemicals, small and macromolecular drugs, research on their applicability for predicting and monitoring the immunotoxicity of engineered nanomaterials is still ongoing.. .
A N
O N G O I N G
C O N C L U S I O N
a judgement or decision reached by reasoning.
"each research group came to a similar conclusion"
Hear now my reasoning, and hearken to the pleadings of my lips.
🕯
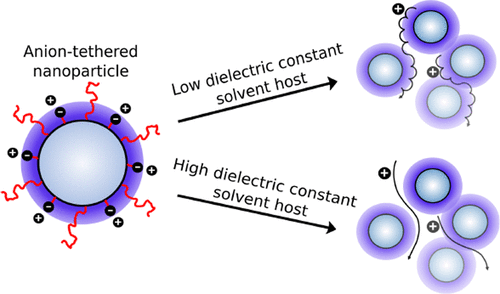
Recent studies have demonstrated the potential of nanoparticle-based single-ion conductors as battery electrolytes. In this work, we introduce a coarse-grained multiscale simulation approach to identify the mechanisms underlying the ion mobilities in such systems and to clarify the influence of key design parameters on conductivity. Our results suggest that for the experimentally studied electrolyte systems, the dominant pathway for cation transport is along the surface of nanoparticles, in the vicinity of nanoparticle-tethered anions. At low nanoparticle concentrations, the connectivity of cationic surface transport pathways and conductivity increase with nanoparticle loading.
However, cation mobilities are reduced when nanoparticles are in close vicinity, causing conductivity to decrease for sufficiently high particle loadings. We discuss the impacts of cation and anion choice as well as solvent polarity within this picture and suggest means to enhance ionic conductivities in single-ion conducting electrolytes based on nanoparticle salts.
tether (plural tethers)
a rope, cable etc. that holds something in place whilst allowing some movement
(nautical, sailing) a strong rope or line that connects a sailor's safety harness to the boat's jackstay
(by extension) the limit of one's abilities, resources etc.
From Middle English tether, teder, from Old English *tēoder and/or Old Norse tjóðr ( > Danish tøjr); both from Proto-Germanic *teudrą (“rope; cord; shaft”), of uncertain origin. Perhaps from Proto-Indo-European *dewtro-, from Proto-Indo-European *dew- (“to tie”), or from Proto-Indo-European *dewk- (“to pull”). Cognate with North German Tüder (“tether for binding the cattle”).
tether (third-person singular simple present tethers, present participle tethering, simple past and past participle tethered)
tether (third-person singular simple present tethers, present participle tethering, simple past and past participle tethered)
to restrict something with a tether.
(Internet) to connect a cellular smartphone to another personal computer in order to give it access to a hotspot.
to connect something to something else