Nanoparticles that are used in vaccines transfer electrons using resonance energy transfer that produces free radicals that creates an imbalance to antioxidants causing oxidative stress ultimately leading to the cause of cancer.
Blunt to the point of abrasive..I shoot from the hip.. AM directed by the heart .. tempered by the 🧠
fenbendiazole... there is a clinical trial for giablastima by john hopkins thst is looking very good.. its about the stucture of the INNERWALLS OF CELLS.. they didnt know cells have innerwalls.. I was in human consumtion form for paradites under the name of “ Vermox” gave to my kids 4 worms ...I take it every 6 months as a preventative( im over 65) Mac ... u dhould check into the workings of that in cells .. id be hapoy to follow it
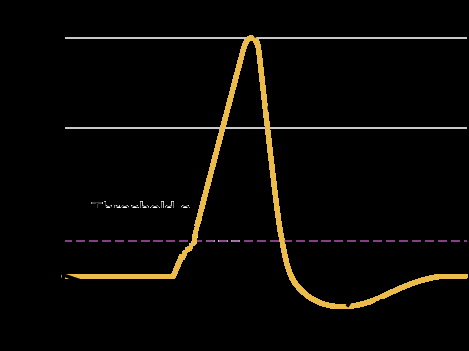
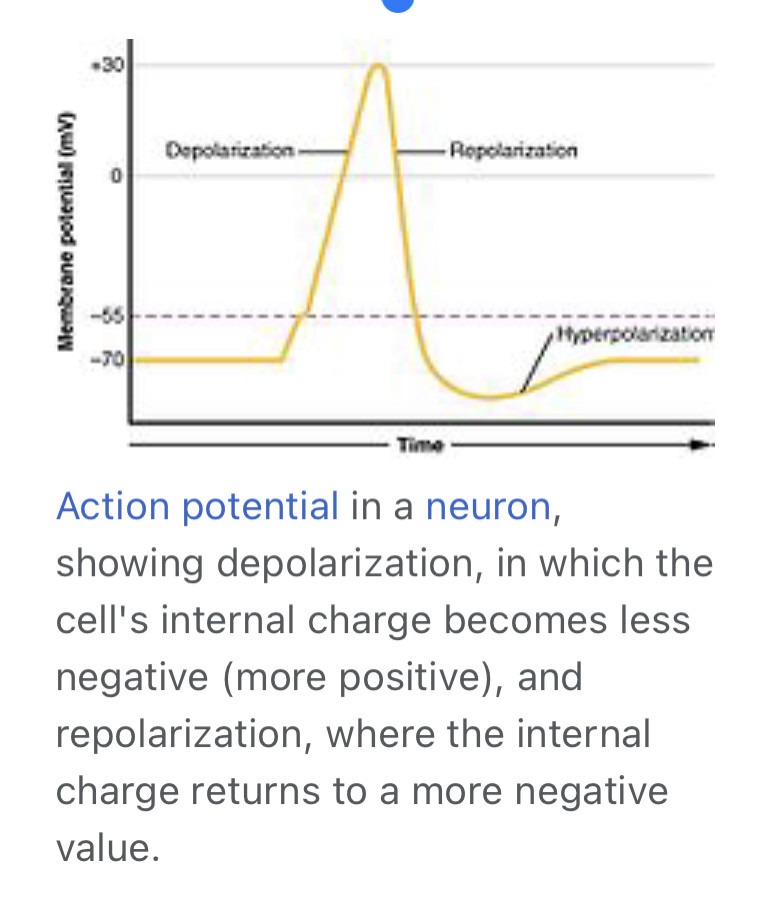
Hyperpolarization is when the membrane potential becomes more negative at a particular spot on the neuron's membrane, while depolarization is when the membrane potential becomes less negative (more positive). ... The opening of channels that let positive ions flow into the cell can cause depolarization.
At very low photon energies most metals have a very large and negative dielectric function. For the response of a metal nanoparticle to an external field in this limit, this means that the particular choice of metal does not matter and the localized surface plasmon energy mainly depends on the shape and size of the particle. Here, we present a theoretical framework to describe this situation and unearth the interplay between the depolarization factor of the problem at hand and the dielectric function of the particle. Available experimental results compare favorably with our theoretical framework.
The paper presents examples of strong depolarization in oriented crystals from the data collected by the polarimetric prototype of the Weather Surveillance Radar-1988 Doppler (WSR-88D) and a theoretical model that explains the results of measurements. It is shown that the sign and magnitude of the ZDR and ΦDP signatures strongly depend on the orientation of crystals and a system differential phase on transmission.
https://journals.ametsoc.org/view/journals/atot/24/7/jtech2034_1.xml
what is the meaning of depolarization?
1 : the process of depolarizing something or the state of being depolarized. 2 physiology : loss of the difference in charge between the inside and outside of the plasma membrane of a muscle or nerve cell due to a change in permeability and migration of sodium ions to the interior …
In biology, depolarization (British English: Depolarisation) is a change within a cell, during which the cell undergoes a shift in electric charge distribution, resulting in less negative charge inside the cell compared to the outside. Depolarization is essential to the function of many cells, communication between cells, and the overall physiology of an organism.
The change in charge typically occurs due to an influx of sodium ions into a cell, although it can be mediated by an influx of any kind of cation or efflux of any kind of anion. The opposite of a depolarization is called a hyperpolarization.
Usage of the term "depolarization" in biology differs from its use in physics, where it refers to situations in which any form of polarity ( i.e. the presence of any electrical charge, whether positive or negative) changes to a value of zero.
Depolarization is sometimes referred to as "hypopolarization".
What is meant by the relaxation time during polarization?
The time it takes ions in the EDL to return to the equilibrium after the polarizing current is cut off is the relaxation time.
T1 relaxation, also known as spin lattice or longitudinal relaxation is the time constant used to describe when ~63% of the magnetization has recovered to equilibrium. The T1 of a given spin is dictated by field fluctuations (both magnetic and electric) that occur in the sample.
And bless your heart. 🙏🏻❤️
Relaxometry refers to the study and/or measurement of relaxation variables in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. In NMR, nuclear magnetic moments are used to measure specific physical and chemical properties of materials.
Relaxation of the nuclear spin system is crucial for all NMR applications. The relaxation rate depends strongly on the mobility (fluctuations, diffusion) of the microscopic environment and the strength of the applied magnetic field. As a rule of thumb, strong magnetic fields lead to increased sensitivity on fast dynamics while low fields lead to increased sensitivity on slow dynamics. Thus, the relaxation rate as a function of the magnetic field strength is a fingerprint of the microscopic dynamics.[1]
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field
When the paramagnetic material is placed in a magnetic field, the magnetic moments of the atoms align along the direction of the applied magnetic field forming a weak net magnetic moment. These materials do not retain magnetic moment when the magnetic field is removed.