The chalice
late Middle English: from Old French gobelet, diminutive of gobel ‘cup’, of unknown origin.
French and English: metonymic occupational name for a maker or seller of goblets and tankards, from Old French gobel 'drinking vessel', 'cup' (apparently from Celtic gob 'mouth').
gobble (third-person singular simple present gobbles, present participle gobbling, simple past and past participle gobbled)
(transitive, intransitive) Of a turkey, to make its characteristic vocalisation; also, used of certain other birds.
(transitive, intransitive) To make the sound of a turkey.
gobbledegook (usually uncountable, plural gobbledegooks)
Alternative form of gobbledygook
Gibberish, also called jibber-jabber or gobbledygook, is speech that is (or appears to be) nonsense. It may include speech sounds that are not actual words, or language games and specialized jargon that seems nonsensical to outsiders.
"Gibberish" is also used as an imprecation to denigrate or tar ideas or opinions the user disagrees with or finds irksome, a rough equivalent of "nonsense", "folderol", or "claptrap". The implication is that the criticized expression or proposition lacks substance or congruence, as opposed to simply being a differing view.
The related word jibber-jabber refers to rapid talk that is difficult to understand.
"such sentiments are just pious claptrap"
What is optical dipole trap?
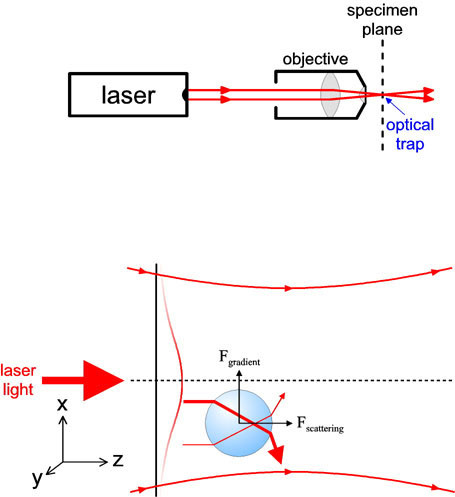
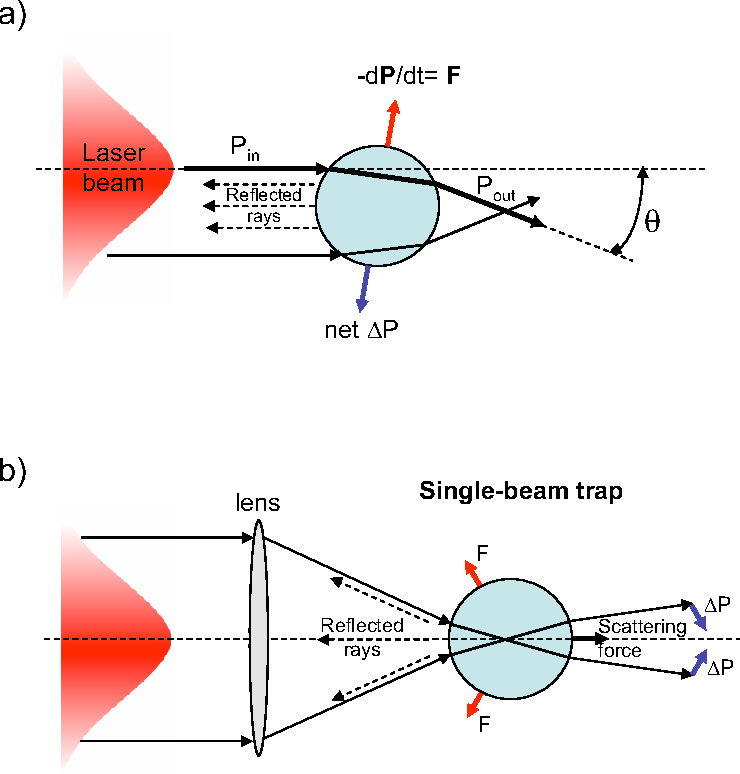
Optical tweezers (originally called single-beam gradient force trap) are scientific instruments that use a highly focused laser beam to hold and move the microscopic and sub-microscopic objects like atoms, nanoparticles and droplets, in a manner similar to tweezers.
An optical trap is formed by tightly focusing a laser beam with an objective lens of high numerical aperture (NA). A dielectric particle near the focus will experience a force due to the transfer of momentum from the scattering of incident photons. ... For most conventional situations, the scattering force dominates.
In optical levitation a laser is used to produce a beam of light directed towards a small (comparable to the size of the laser beam) object. The laser beam will exert a force on the object due to the radiation pressure which can oppose gravity and cause an the object to levitate.
star
/stɑː/
Origin
Old English steorra, of Germanic origin; related to Dutch ster, German Stern, from an Indo-European root shared by Latin stella and Greek astēr .