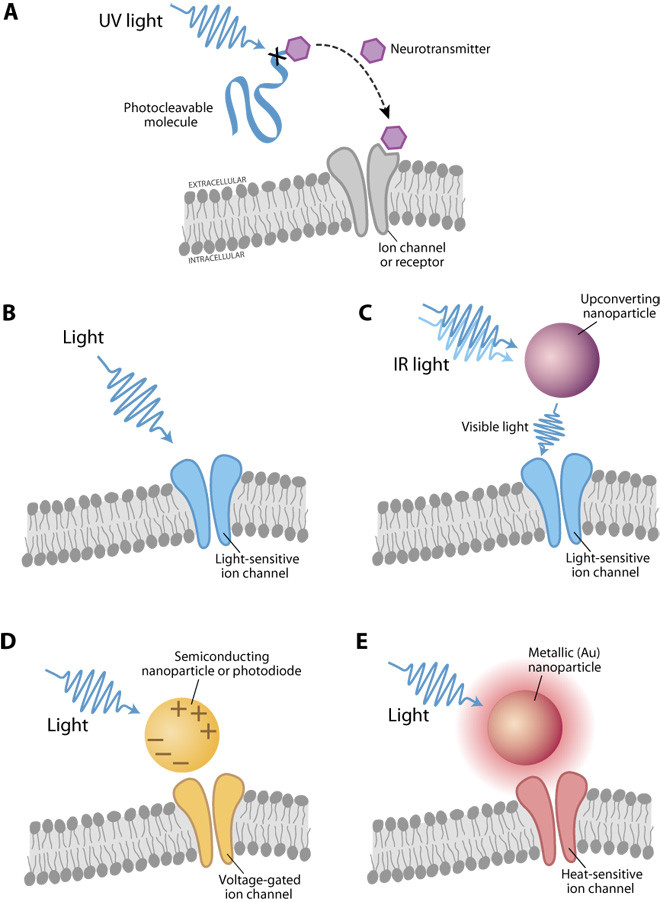
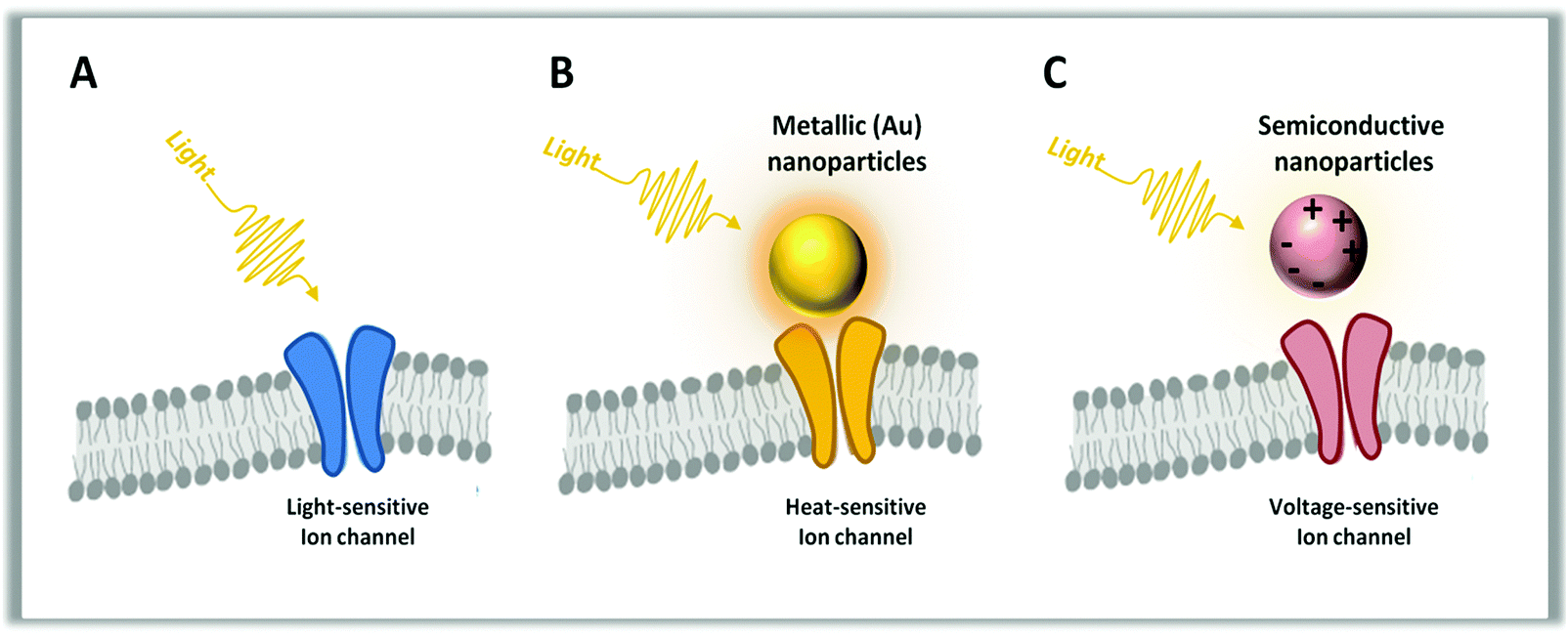
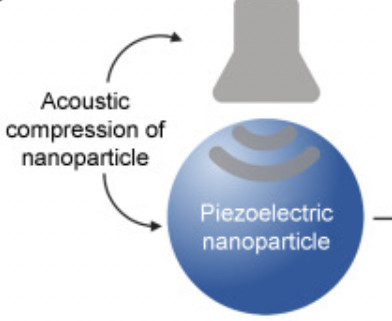
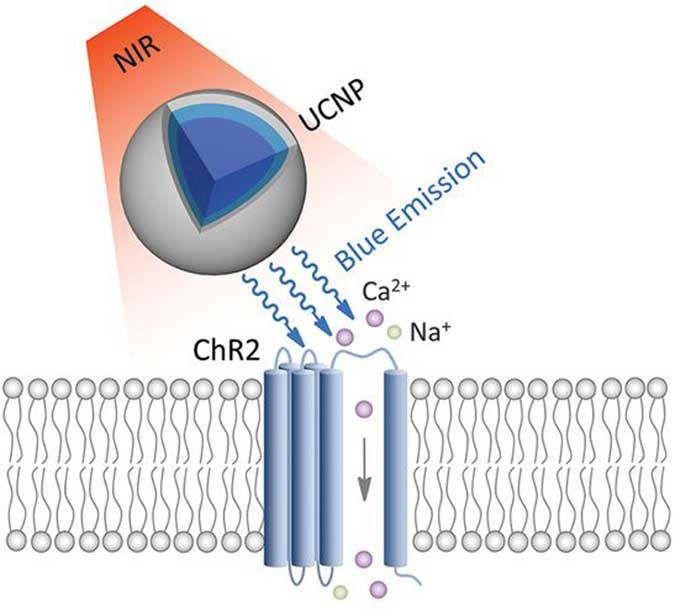
It’s Shifted/At the PRECIPICE💥⚠️WWG1WGA the way to the finish line🏁 👉In The Right Lane for GOD & Country🙌🏻JESUS/TRUMP/AWAKE PATRIOT/STC
This is extremely familiar. Where would i have seen this previously? 🤔
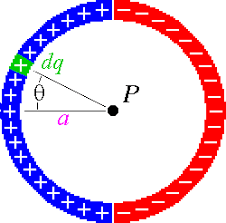
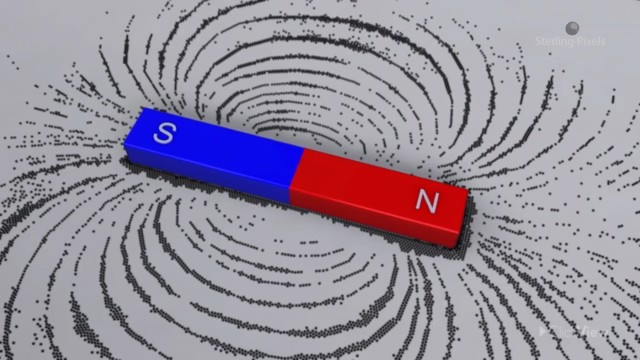
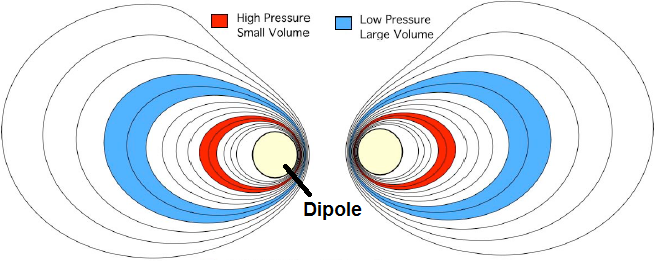
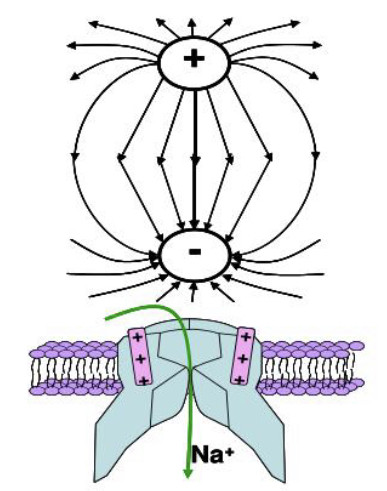
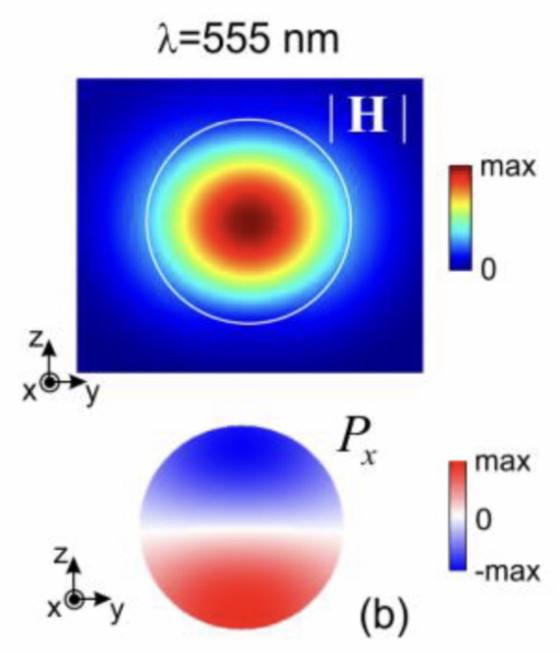
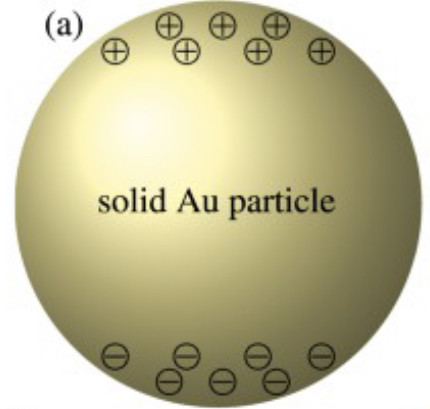
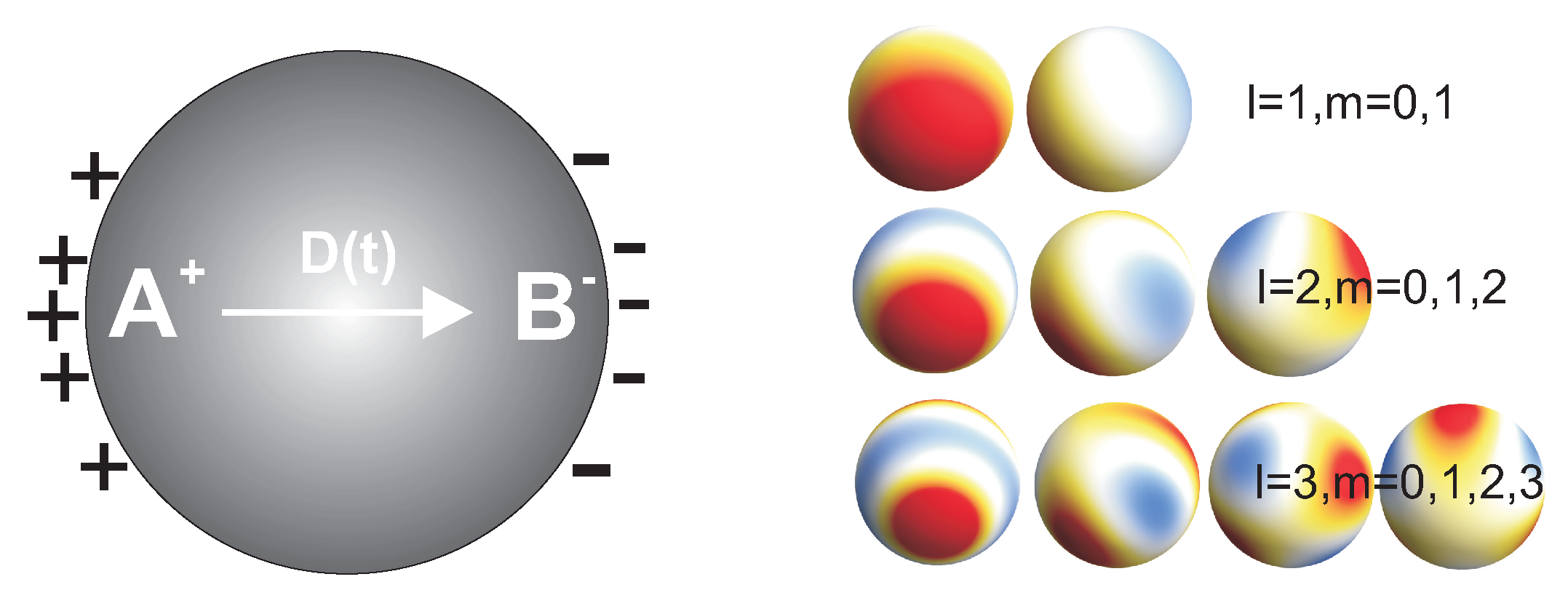
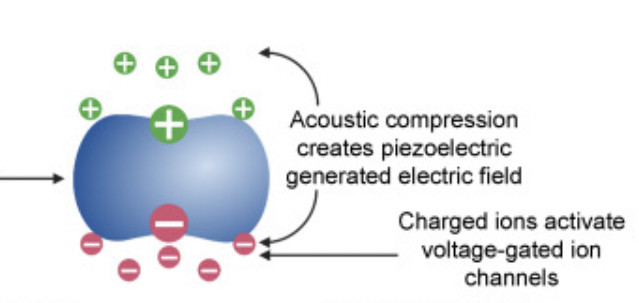
Valence electrons are still attached to an atom. They are the outermost electrons that determine chemical properties, and may be part of chemical bonds. A free electron is an atom that is not attached to any atom and is free to move anywhere.
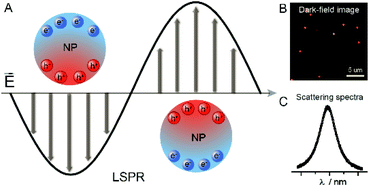
Radical, also called Free Radical, in chemistry, molecule that contains at least one unpaired electron. Most molecules contain even numbers of electrons, and the covalent chemical bonds holding the atoms together within a molecule normally consist of pairs of electrons jointly shared by the atoms linked by the bond.
At high concentrations, however, free radicals can be hazardous to the body and damage all major components of cells, including DNA, proteins, and cell membranes. The damage to cells caused by free radicals, especially the damage to DNA, may play a role in the development of cancer and other health conditions (1, 2).
Many autistic children share a chronic flaw in the body's natural defenses against oxygen free radicals -- corrosive molecules in the body that can severely damage developing brain cells, scientists said Saturday in San Diego.
Indirect markers are consistent with greater oxidative stress in autism. They include greater free-radical production, impaired energetics and cholinergics, and higher excitotoxic markers. Brain and gut, both abnormal in autism, are particularly sensitive to oxidative injury. Higher red-cell lipid peroxides and urinary isoprostanes in autism signify greater oxidative damage to biomolecules.
A preliminary study found accelerated lipofuscin deposition--consistent with oxidative injury to autistic brain in cortical areas serving language and communication. Double-blind, placebo-controlled trials of potent antioxidants--vitamin C or carnosine--significantly improved autistic behavior. Benefits from these and other nutritional interventions may be due to reduction of oxidative stress. Understanding the role of oxidative stress may help illuminate the pathophysiology of autism, its environmental and genetic influences, new treatments, and prevention.
Objectives: Upon completion of this article, participants should be able to: 1. Be aware of laboratory and clinical evidence of greater oxidative stress in autism. 2. Understand how gut, brain, nutritional, and toxic status in autism are consistent with greater oxidative stress. 3. Describe how anti-oxidant nutrients are used in the contemporary treatment of autism.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15624347/
Oxidative stress in autism - PubMed
Upon completion of this article, participants should be able to: 1. Be aware of laboratory and clinical evidence of greater oxidative stress in autism. 2. Understand how gut, brain, nutritional, and toxic status in autism are consistent with greater oxidative stress. 3. Describe how anti-oxidant nut..
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15624347/