🇺🇸 All posts are in service to The Republic, not the corporation, of the United States of America.
SERCO, finally! "The Biggest Company You Never Heard Of". My Sandy Hook research lead to me down this trail. Have a look-see at what camera's they have access to.
I'm a True Blue AUSSIE just here doing my part in The Great Awakening
Isn't Prince William involved in SERCO?
Our Sectors | What We Do | EPC Resilience
We have supported many of the most significant industries and organisations in the UK and across the world. Find out more from our case studies here.
https://www.epcresilience.com/what-we-do/our-sectors?categories=;Serco bags £322m contract extension for Test and Trace, is still struggling to share data with local authorities • The Register
Look who's having a good pandemic
https://www.theregister.com/AMP/2021/06/28/serco_bags_a_322m_contract/Mass Spectrometry of Nanoparticles is Different | SpringerLink
Secondary ion mass spectrometry, SIMS, is a method of choice for the characterization of nanoparticles, NPs. For NPs with large surface-to-volume ratios, h
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13361-015-1151-9A smartphone can be used in a remarkably simple and inexpensive way to teach your students about absorption spectroscopy and Beer's Law. In short, light reflected off of colored construction paper is passed through a sample and detected by an RGB application on a smartphone.
The researchers engineered quantum dot barcoded microbeads and a secondary label to search for antibodies against COVID-19 antigen in the patient's blood. Finding the antibodies leads to a change in microbead emission color.
The beads are then loaded into the device, 'activated' with a laser, and the signal is imaged using a smartphone camera. An app is designed to process the image to identify the bead's emission change. Lastly, the data are interpreted and transmitted remotely across the world for data collection and decision making.
"The beauty of the system is that everything is integrated into one portable unit." said Zhang.
This technology, by which quantum dot microbead detection can measure minuscule amounts of key biomarkers in blood, has been in development for the past 10 years.
Self-assembling of graphene oxide on carbon quantum dot loaded liposomes - ScienceDirect
This paper describes the design of stimuli-sensitive theranostic nanoparticles, composed of reduced graphene oxide (rGO) self-assembled on thermosensi…
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0928493119305703The synthesized GQD by using ionic liquid were evaluated by spectroscopic (DLS, PL, XRD and Raman spectroscopy) and Transmission electron microscopic analysis (TEM).
An ionic liquid (IL) is a salt in the liquid state. In some contexts, the term has been restricted to salts whose melting point is below some arbitrary temperature, such as 100 °C (212 °F). While ordinary liquids such as water and gasoline are predominantly made of electrically neutral molecules, ionic liquids are largely made of ions.
Ionic liquids have many potential applications. They are powerful solvents and can be used as electrolytes. Salts that are liquid at near-ambient temperature are important for electric battery applications, and have been considered as sealants due to their very low vapor pressure.
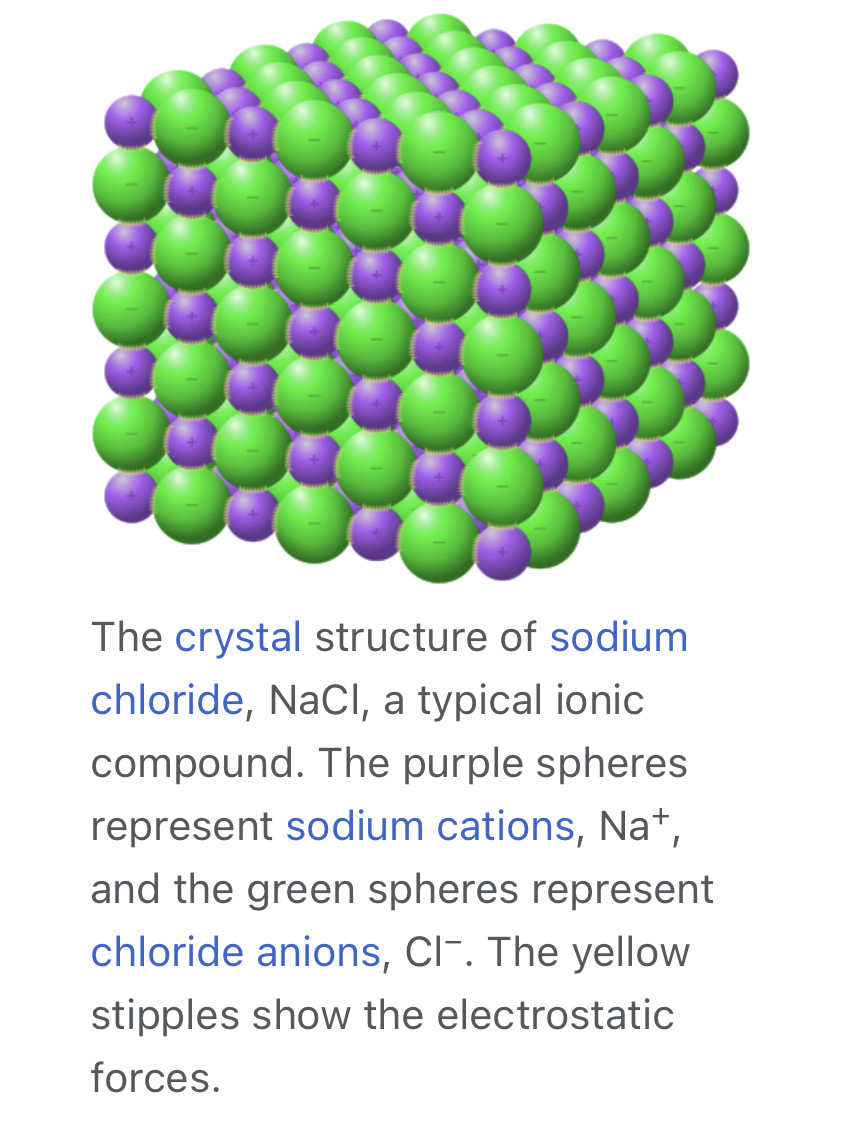
Any salt that melts without decomposing or vaporizing usually yields an ionic liquid. Sodium chloride (NaCl), for example, melts at 801 °C (1,474 °F) into a liquid that consists largely of sodium cations (Na+
) and chloride anions (Cl−
). Conversely, when an ionic liquid is cooled, it often forms an ionic solid—which may be either crystalline or glassy.
An ionic crystal is a crystalline ionic compound. They are solids consisting of ions bound together by their electrostatic attraction into a regular lattice. Examples of such crystals are the alkali halides, including potassium fluoride, potassium chloride, potassium bromide, potassium iodide, sodium fluoride.[1] NaCl has a 6:6 co-ordination. The properties of NaCl reflect the strong interactions that exist between the ions. It is a good conductor of electricity when molten, but very poor in the solid state. When fused the mobile ions carry charge through the liquid.[2] They are characterized by strong absorption of infrared radiation and have planes along which they cleave easily. The exact arrangement of ions in an ionic lattice varies according to the size of the ions in the solid.[3]
Electrostatic forces are non-contact forces; they pull or push on objects without touching them. Rubbing some materials together can result in something called 'charge' being moved from one surface to the other. Charged objects pull on other uncharged objects and may either push or pull on other charged objects.
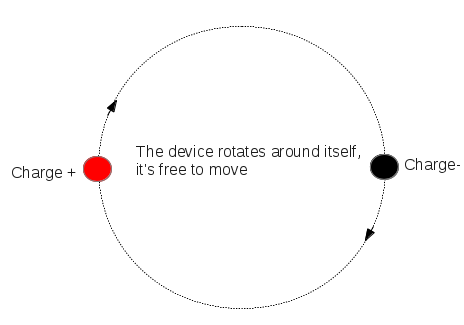
An electric dipole is defined as a couple of opposite charges “q” and “–q” separated by a distance “d”. By default, the direction of electric dipoles in space is always from negative charge “-q” to positive charge “q”. The midpoint “q” and “–q” is called the centre of the dipole.
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that involves the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, or between two atoms with sharply different electronegativities,[1] and is the primary interaction occurring in ionic compounds. It is one of the main types of bonding along with covalent bonding and metallic bonding. Ions are atoms (or groups of atoms) with an electrostatic charge. Atoms that gain electrons make negatively charged ions (called anions). Atoms that lose electrons make positively charged ions (called cations). This transfer of electrons is known as electrovalence in contrast to covalence. In the simplest case, the cation is a metal atom and the anion is a nonmetal atom, but these ions can be of a more complex nature, e.g. molecular ions like NH+
4 or SO2−
4. In simpler words, an ionic bond results from the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal in order to obtain a full valence shell for both atoms.