First Love
1 John 4:19 We love him, because he first loved us.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xfrsSoBkigM&ab_channel=jay-aie
4:04 > 44
This image seems to be following me like the 44's do.🧐
very cool image AWE = A VV E ?
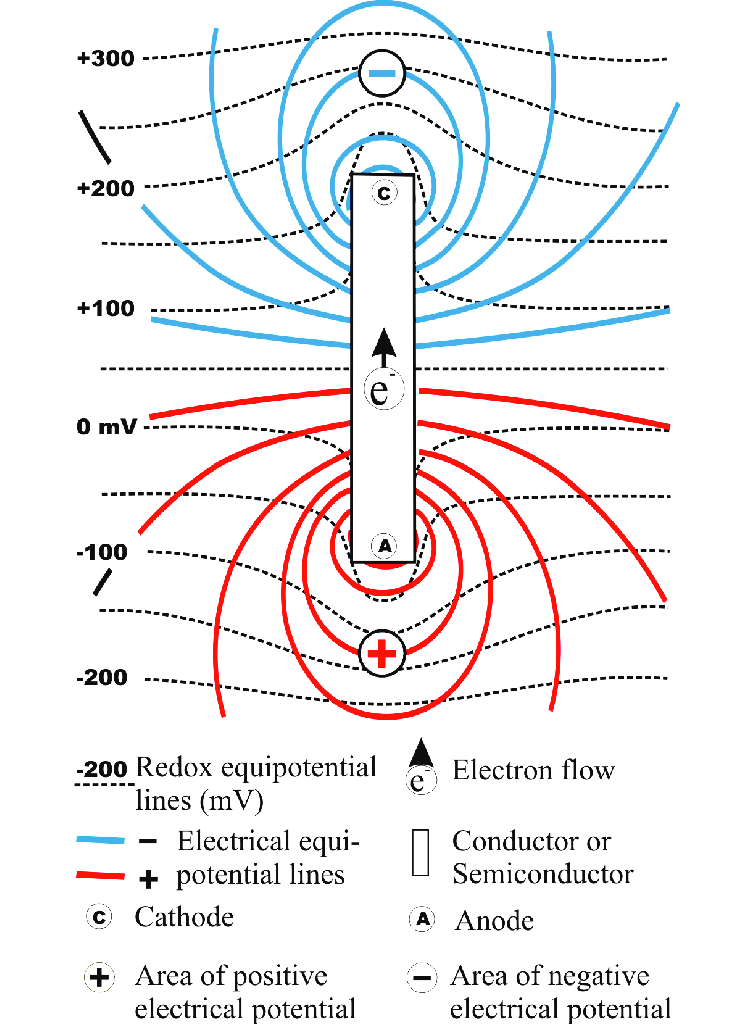
In the summer of 1889, Tesla traveled to the 1889 Exposition Universelle in Paris and learned of Heinrich Hertz's 1886–1888 experiments that proved the existence of electromagnetic radiation, including radio waves.[100] Tesla found this new discovery "refreshing" and decided to explore it more fully.
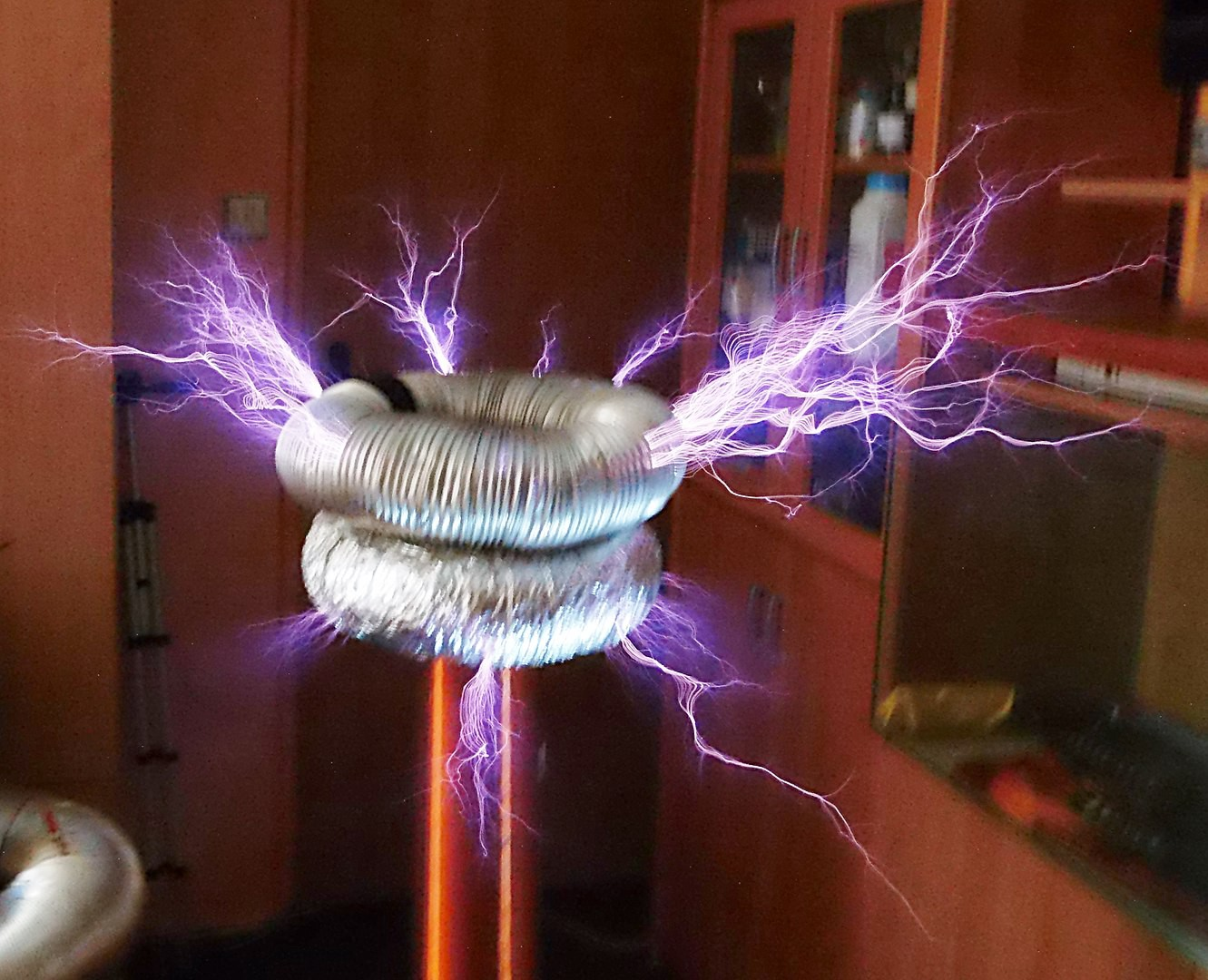
In repeating, and then expanding on, these experiments, Tesla tried powering a Ruhmkorff coil with a high speed alternator he had been developing as part of an improved arc lighting system but found that the high-frequency current overheated the iron core and melted the insulation between the primary and secondary windings in the coil. To fix this problem Tesla came up with his "oscillating transformer", with an air gap instead of insulating material between the primary and secondary windings and an iron core that could be moved to different positions in or out of the coil.[101] Later called the Tesla coil, it would be used to produce high-voltage, low-current, high frequency alternating-current electricity.[102] He would use this resonant transformer circuit in his later wireless power work.[103][104]
Wireless power transfer (WPT), wireless power transmission, wireless energy transmission (WET), or electromagnetic power transfer is the transmission of electrical energy without wires as a physical link. In a wireless power transmission system, a transmitter device, driven by electric power from a power source, generates a time-varying electromagnetic field, which transmits power across space to a receiver device, which extracts power from the field and supplies it to an electrical load. The technology of wireless power transmission can eliminate the use of the wires and batteries, thus increasing the mobility, convenience, and safety of an electronic device for all users.[2] Wireless power transfer is useful to power electrical devices where interconnecting wires are inconvenient, hazardous, or are not possible.
Wireless power techniques mainly fall into two categories, near field and far-field.[3] In near field or non-radiative techniques, power is transferred over short distances by magnetic fields using inductive coupling between coils of wire, or by electric fields using capacitive coupling between metal electrodes.[4][5][6][7] Inductive coupling is the most widely used wireless technology; its applications include charging handheld devices like phones and electric toothbrushes, RFID tags, induction cooking, and wirelessly charging or continuous wireless power transfer in implantable medical devices like artificial cardiac pacemakers, or electric vehicles.