8:08 minute video
MSNBC hit piece on JUAN O SAVIN & “Qanon”
#2832
WE ARE THE NEWS NOW
In most of his 2022 videos 🏎 Juan is ALWAYS DRIVING
sometimes crisscrossing the country several times in a week.
Why?
He’s tirelessly working to restore the Republic of the USA
where it counts: IN THE ELECTIONS
especially the 👉 SECRETARY OF STATE position
in 18 States 👈
#2602
PANIC IS GOOD!
FAKE NEWS attacks..
BADGE OF HONOR.
OVER THE TARGET.
_______
VIDEO 🎥 originally posted on ULTRAMcAfee
re-posted by Q The Storm Rider
Katie Phang, MSNBC
“We used to sit there & roll our eyes
& laugh about the fact of this ‘Qanon’
& how completely FRINGE it is.
Let’s be frank — it’s now no longer fringe…
Is ‘Qanon’ actually part of the Republican Party now?”
Will Sommer, DAILY BEAST
“I think Qanon has succeeded in finding a home
within the GOP”
_______
#4881
There is 'Q'. 1
There are 'Anons'. 2
There is no 'Qanon'. 3
🤠 Bravo Juan. You got em shaking in their boots 🎉
Knowing who really we are🙏✨ True Consciousness Creates Harmonic Circulation. 🌎💞☯️💞◯=♾☺️ Armor of Source Almighty🙏✨
Official McAfee Channel :
https://t.me/OfficialMcAfeeChannel
Official McAfee Chat :
https://t.me/McafeeAfterlife
* 2 pics *
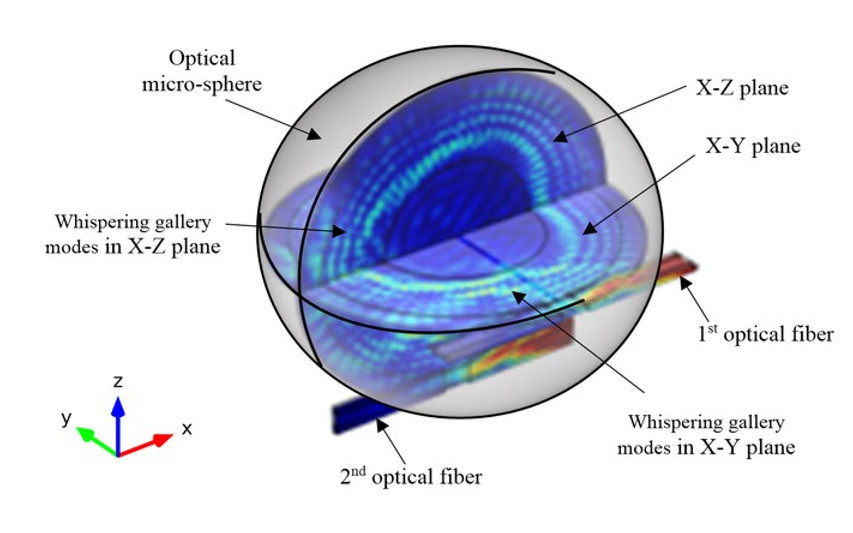
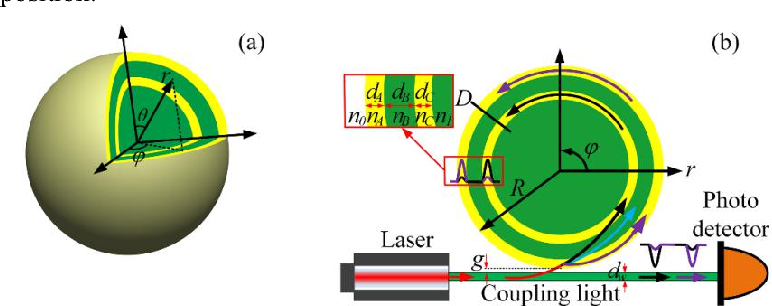
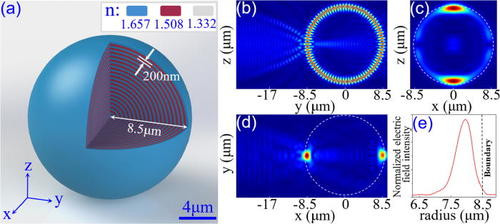
Microresonators are micrometre-scale structures for confining light. Light is reflected internally at the edges of the resonator. This creates a series of standing-wave optical modes, or resonances, similar to those that can exist on a vibrating guitar string.
An optical microcavity or microresonator is a structure formed by reflecting faces on the two sides of a spacer layer or optical medium, or by wrapping a waveguide in a circular fashion to form a ring. The former type is a standing wave cavity, and the latter is a traveling wave cavity. The name microcavity stems from the fact that it is often only a few micrometers thick, the spacer layer sometimes even in the nanometer range. As with common lasers, this forms an optical cavity or optical resonator, allowing a standing wave to form inside the spacer layer or a traveling wave that goes around in the ring.
The fundamental difference between a conventional optical cavity and microcavities is the effects that arise from the small dimensions of the system, but their operational principle can often be understood in the same way as for larger optical resonators. Quantum effects of the light's electromagnetic field can be observed.[1] For example, the spontaneous emission rate and behaviour of atoms is altered by such a microcavity, a phenomenon that is referred to as inhibited spontaneous emission.[2] One can imagine this as the situation that no photon is emitted, if the environment is a box that is too small to hold it. This leads to an altered emission spectrum, which is significantly narrowed.