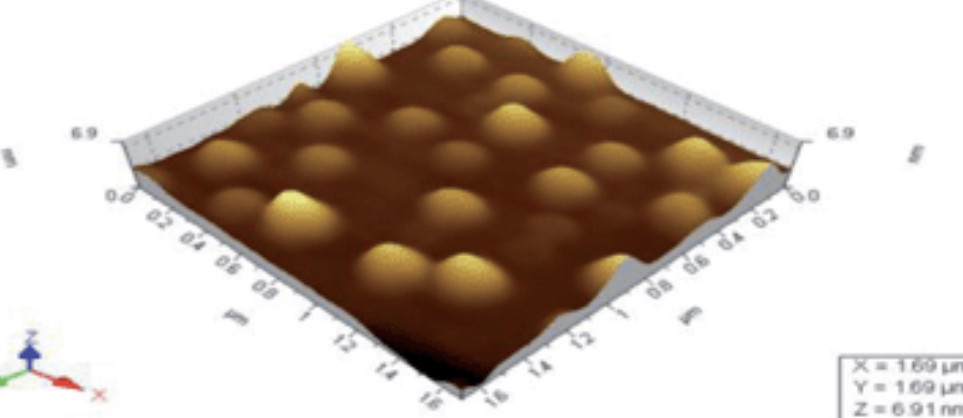
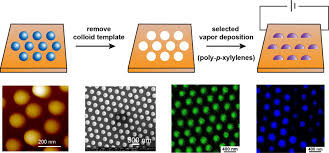
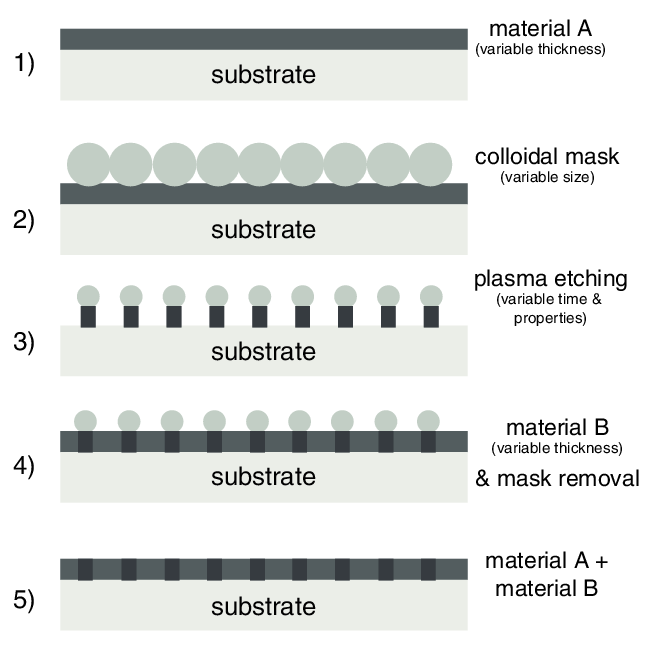
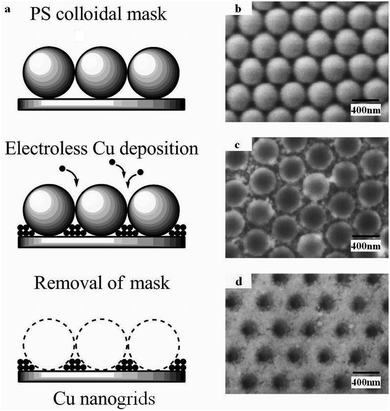
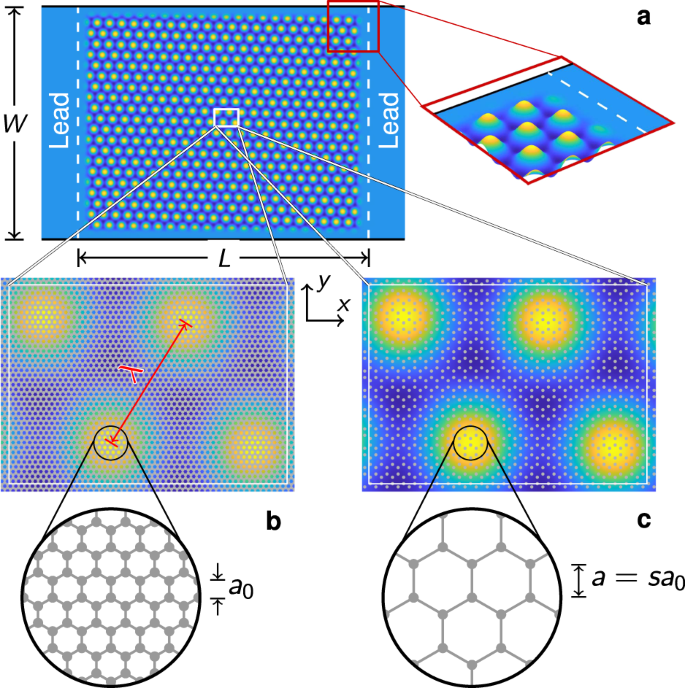
Electrostatic superlattices have been known to significantly modify the electronic structure of low-dimensional materials. Studies of graphene superlattices were triggered by the discovery of moiré patterns in van der Waals stacks of graphene and hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) layers a few years ago. Very recently, gate-controllable superlattices using spatially modulated gate oxides have been achieved, allowing for Dirac band structure engineering of graphene.
Despite these rapid experimental progresses, technical advances in quantum transport simulations for large-scale graphene superlattices have been relatively limited. Here, we show that transport experiments for both graphene/hBN moiré superlattices and gate-controllable superlattices can be well reproduced by transport simulations based on a scalable tight-binding model. Our finding paves the way to tuning-parameter-free quantum transport simulations for graphene superlattices, providing reliable guides for understanding and predicting novel electric properties of complex graphene superlattice devices.
Pure blooded Patriot...Sarcastic and Blunt. My opinions are mine and if you don't like what I have to say...go somewhere else.
Interesting...I keep thinking 'anti-gravity'....Not an expert or even claiming to be close to one....but this is very intereting
An aerosol is a suspension of fine solid particles or liquid droplets in air or another gas.
Optical tweezers (originally called single-beam gradient force trap) are scientific instruments that use a highly focused laser beam to hold and move the microscopic and sub-microscopic objects like atoms, nanoparticles and droplets, in a manner similar to tweezers.
Harmonics generation in water droplets of 20 m m typical radius, induced by femtosecond laser pulses at 800 nm. (a) Experimental arrangement. A droplet generator is synchronized with a femtosecond laser so that each droplet is illuminated by a single laser pulse (b) SHG: 800 nm - 400 nm, (c) SFG: 400 nm + 800 nm - 266 nm, and (d) THG: 800 nm - 266 nm (Fig. 1(d) from ref. 45).
Acoustic levitation is a method for suspending matter in air against gravity using acoustic radiation pressure from high intensity sound waves. It works on the same principles as acoustic tweezers by harnessing acoustic radiation forces.