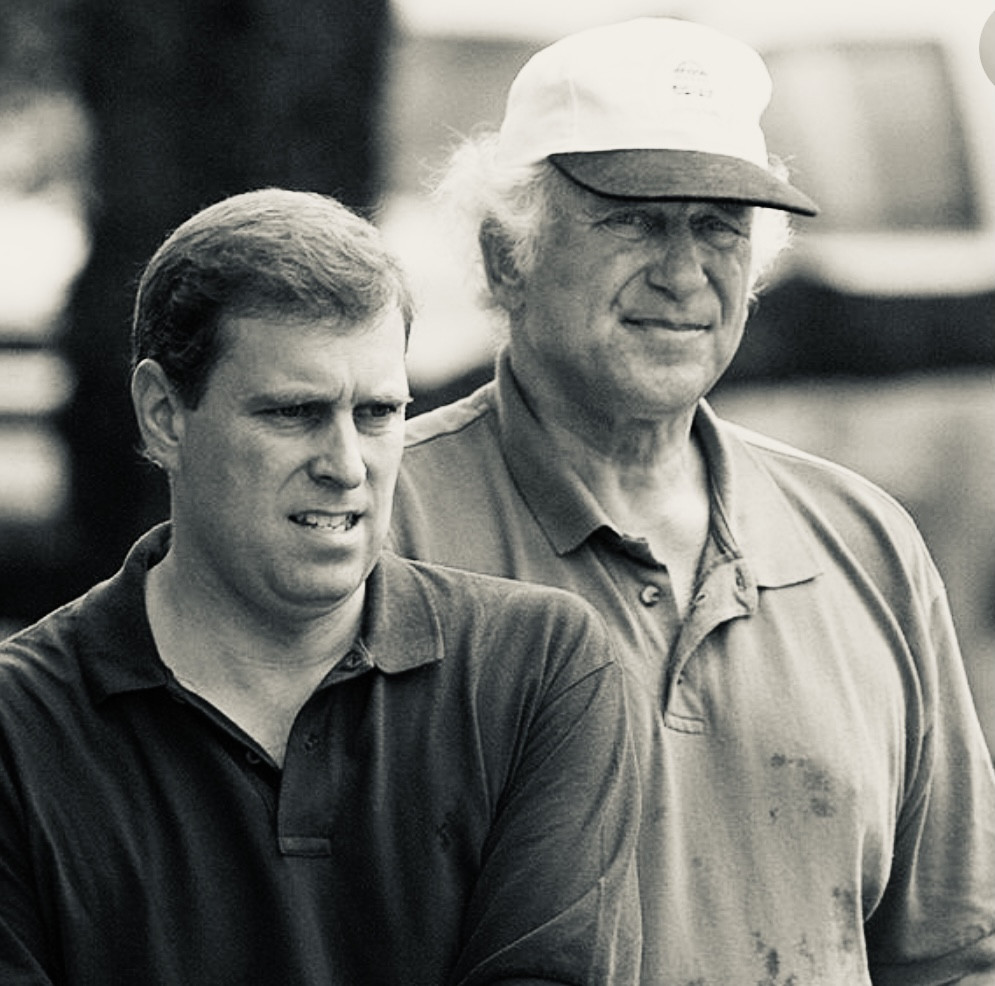
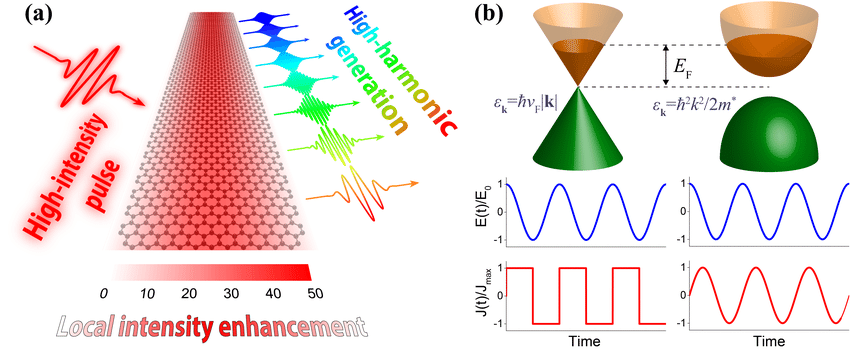
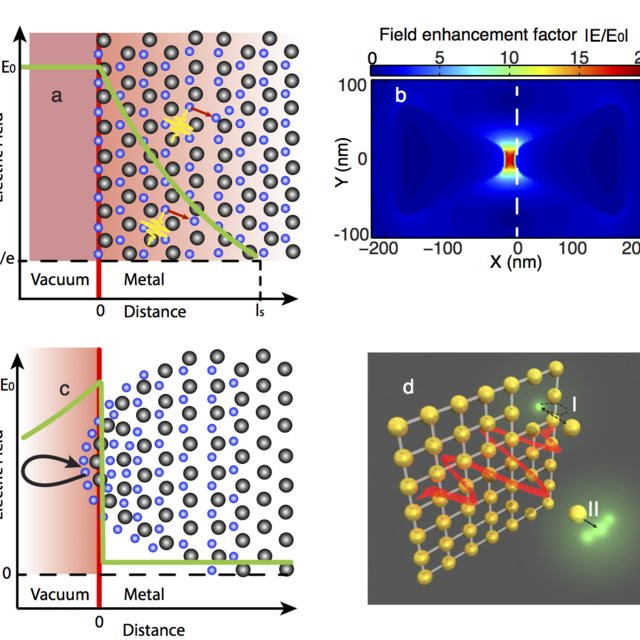
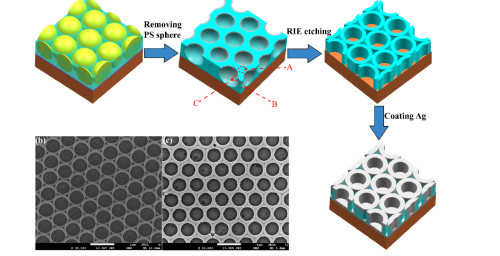
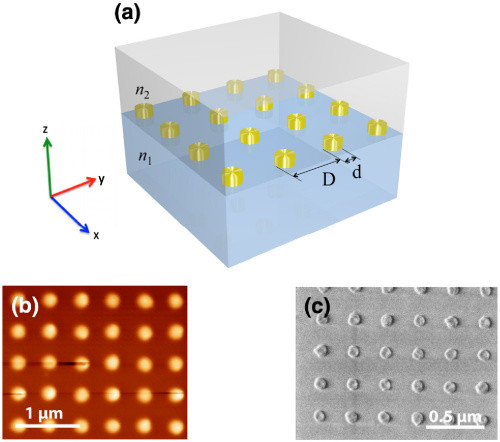
Who is that with Andrew? Never forget a face but just.can’t.place.it.
oh, and i meant @ Not theMacAnon? Yes?
Throughout his career, Evelyn de Rothschild has been actively involved in a number of other organisations in both the private and public sectors and has held the following business positions:
Chairman - The Economist (1972–1989)
Chairman - British Merchant Banking & Securities House Association (1985–1989)
Deputy Chairman - Milton Keynes Development Corporation (1971–1984)
Chairman - United Racecourses (1977–1994)
Director - De Beers Consolidated Mines (1977–1994)
Director - IBM United Kingdom Holdings Limited (1972–1995)
Evelyn de Rothschild also served as a Director of the newspaper group owned by Lord Beaverbrook. Years later, he served for a time as a Director of Lord Black's Daily Telegraph newspaper. An owner of thoroughbred racehorses, he is a former chairman of United Racecourses.
In 1967 Sir Evelyn created the Eranda Foundation to support social welfare, promote the arts and to encourage research into medicine and education.
Sir Evelyn serves as Queen Elizabeth II's financial adviser[citation needed]. He has been a Governor of the London School of Economics and Political Science as well as an active patron of the arts and supporter of a number of charities.
The Rothschilds were reported to have spent a night of their honeymoon at the Clinton White House. Indeed, Lady de Rothschild was so involved with Hillary’s presidential campaign that she had little time to devote to R Chocolate.
lend
/lɛnd/
1.
grant to (someone) the use of (something) on the understanding that it will be returned.
loan
give someone the loan of
let someone use
let someone have the use of
advance
sub
Opposite:
borrow
withhold
allow (a person or organization) the use of (a sum of money) under an agreement to pay it back later, typically with interest.
"no one would lend him the money"
gerund or present participle: lending
A LENDING
ding
/dɪŋ/
verb
verb: ding; 3rd person present: dings; past tense: dinged; past participle: dinged; gerund or present participle: dinging
make a ringing sound.
"cash registers were dinging softly"
exclamation: ding
used to imitate a metallic ringing sound resembling a bell.
sound
/saʊnd/
Origin
Middle English soun, from Anglo-Norman French soun (noun), suner (verb), from Latin sonus . The form with -d was established in the 16th century.
sonus
conditional of soni
Ido
Verb
sonus
conditional of sonar
Latin
Etymology
From sonō (“make a noise, sound”).
Keywords
Ultrasound Sonocrystallization Sonofragmentation Sonochemistry Cavitation Nucleation
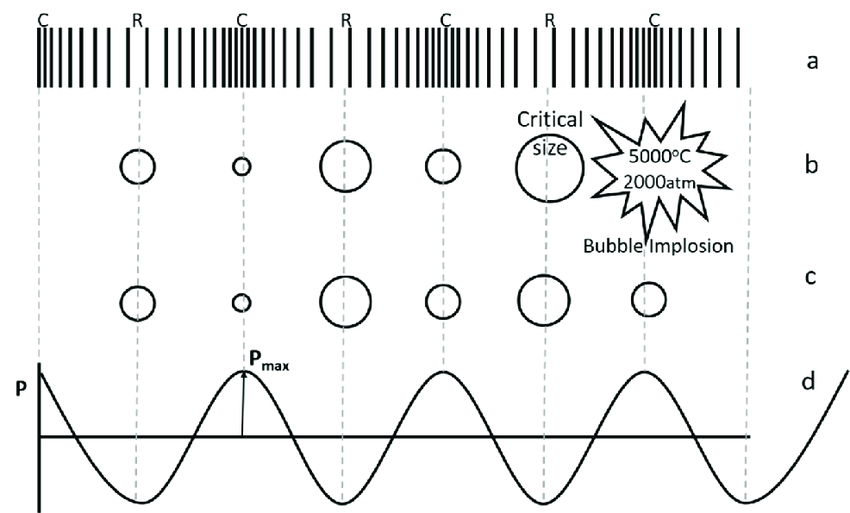
An economic bubble is a situation in which asset prices are much higher than the underlying fundamentals can reasonably justify. Bubbles are sometimes caused by unlikely and overly optimistic projections about the future. It could also be described as prices which strongly exceed the asset's intrinsic value.
Bubbles are sometimes referred to as a speculative bubble, a financial bubble, or a speculative mania.
In the early stages of a bubble, many investors do not notice the bubble for what it is. People notice the prices are going up and often think it is justified. Therefore bubbles are often conclusively identified only in retrospect, after the bubble has already popped and prices have crashed.
late Middle English: from Latin depressio(n- ), from deprimere ‘press down’ (see depress).
compression
/kəmˈprɛʃ(ə)n/
noun: compression; plural noun: compressions
the action of compressing or being compressed.
the reduction in volume (causing an increase in pressure) of the fuel mixture in an internal combustion engine before ignition.
Origin
late Middle English: via Old French from Latin compressio(n- ), from comprimere ‘press together’ (see compress).
Compression- a region in a longitudinal (sound) wave where the particles are closest together. Rarefaction- a region in a longitudinal (sound) wave where the particles are furthest apart.
Because of the longitudinal motion of the air particles, there are regions in the air where the air particles are compressed together and other regions where the air particles are spread apart. These regions are known as compressions and rarefactions respectively.
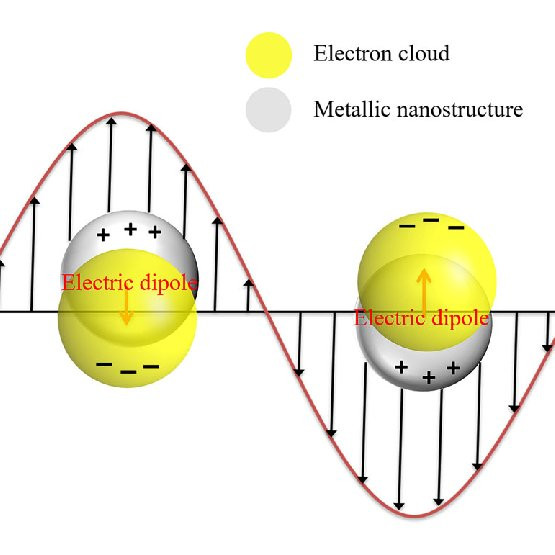
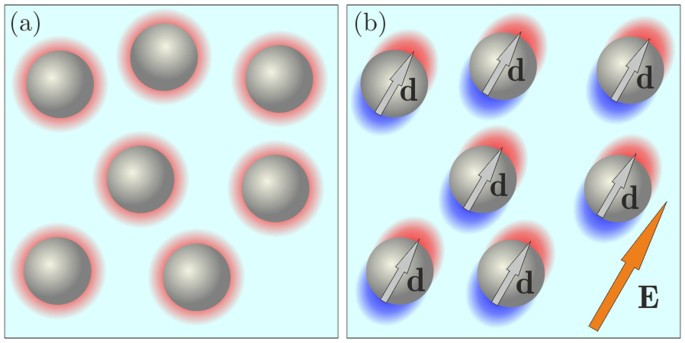
Piezomagnetism is a phenomenon observed in some antiferromagnetic and ferrimagnetic crystals. It is characterized by a linear coupling between the system's magnetic polarization and mechanical strain. In a piezomagnetic material, one may induce a spontaneous magnetic moment by applying physical stress, or a physical deformation by applying a magnetic field.
https://youtu.be/bacBKKgc4Uo
Commercial banks create money, in the form of bank deposits, by making new loans. When a bank makes a loan, for example to someone taking out a mortgage to buy a house, it does not typically do so by giving them thousands of pounds worth of banknotes. Instead, it credits their bank account with a bank deposit of the size of the mortgage. At that moment, new money is created. For this reason, some economists have referred to bank deposits as ‘fountain pen money’, created at the stroke of bankers’ pens when they approve loans.(1)
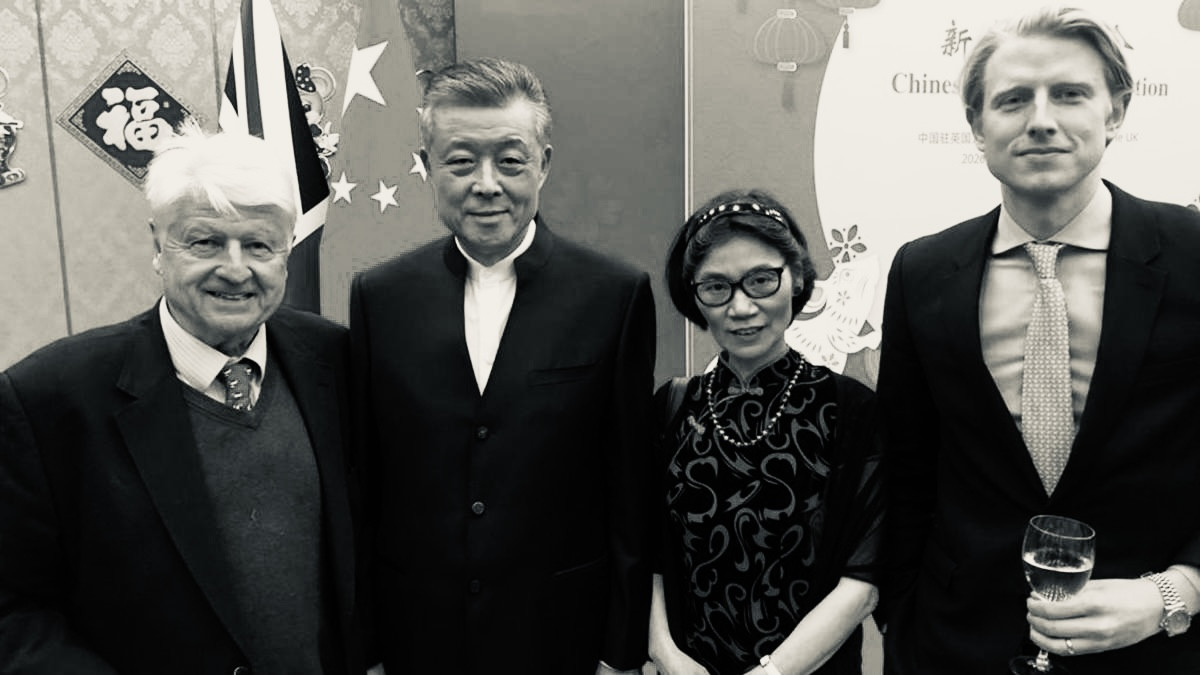
Stanley Johnson, 80, has “what the French would call a préjugé favorable towards China” and considers it “vital at this moment that we speak face to face”, especially in the run-up to COP26. “It is such a large country that if China doesn’t meet [net zero by] 2050, it’s hard to see how the world does.”
Max Johnson, 36, the youngest of Stanley’s six children, who was...
An echo is a sound that is repeated because the sound waves are reflected back. Sound waves can bounce off smooth, hard objects in the same way as a rubber ball bounces off the ground. ... That is why echoes can be heard in a canyon, cave, or mountain range.
With climate change, extreme heat events are on the rise.
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA. The segments of DNA transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins are said to produce messenger RNA. Other segments of DNA are copied into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs.
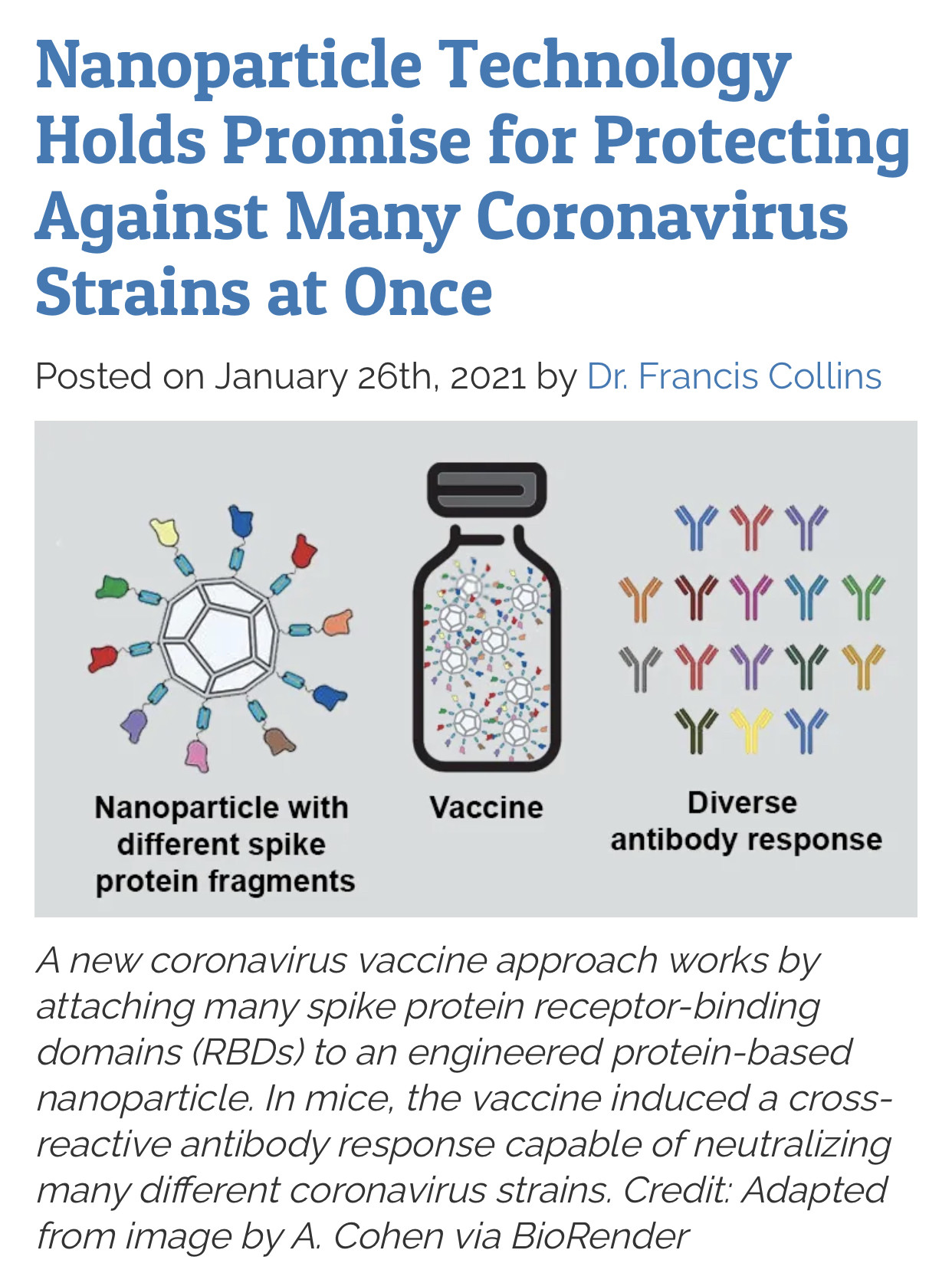
An mRNA vaccine is a type of vaccine that uses a copy of a molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA) to produce an immune response. The vaccine delivers molecules of antigen-encoding mRNA into immune cells, which use the designed mRNA as a blueprint to build foreign protein that would normally be produced by a pathogen (such as a virus) or by a cancer cell. These protein molecules stimulate an adaptive immune response that teaches the body to identify and destroy the corresponding pathogen or cancer cells. The mRNA is delivered by a co-formulation of the RNA encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles that protect the RNA strands and help their absorption into the cells.
An immune response is a reaction which occurs within an organism for the purpose of defending against foreign invaders.
Harvard researchers share views on future, ethics of gene editing – Harvard Gazette
Harvard researchers and others share their views on the issues involved in gene editing.
https://news.harvard.edu/gazette/story/2019/01/perspectives-on-gene-editing/A criticism of eugenics policies is that, regardless of whether negative or positive policies are used, they are susceptible to abuse because the genetic selection criteria are determined by whichever group has political power at the time. Furthermore, many criticize negative eugenics in particular as a violation of basic human rights, seen since 1968's Proclamation of Tehran as including the right to reproduce. Another criticism is that eugenics policies eventually lead to a loss of genetic diversity, thereby resulting in inbreeding depression due to a loss of genetic variation. Yet another criticism of contemporary eugenics policies is that they propose to permanently and artificially disrupt millions of years of evolution, and that attempting to create genetic lines "clean" of "disorders" can have far-reaching ancillary downstream effects in the genetic ecology, including negative effects on immunity and on species resilience.
Researchers from the OHSU Casey Eye Institute in Portland, Oregon, have broken new ground in science, medicine, and surgery — the first gene editing procedure in a living person.
For the first time, scientists are altering DNA in a living human. With more research the study could lead to the development of procedures that can help to correct other genetic disorders.
Hiker-Kayaker-Bicyclist-Paddleboarder (⊙﹏⊙✿) life➭the way I see it, posted here ☯︎_0️⃣social.creditz
oh the "state" of oregon has been editing DNA for decades now (indirectly) = very few "leos" *ever* in that state - socialist mindset, since the free bus ride political wars waaaaay back in the day - and alll the demonrats & demonrat political officials dealing street drugs for years and years and years - i would say since the logging industry ended and the clinton regime shut down fish hatcheries via the american heritage rivers act. they ruined my beloved oregon. Oh also, whatever the bottom line monetary factor there is to any municiple building project has to have (i mean forced) an ADDITIONAL percentage of the project value allocated for public art to be added. i used to think it was kewl until the crack addicts took office - and then i realized what CREEPING socialism looks like. i wish i could go home.
At a Glance
Dysfunction and death of retinal cells, and consequent vision loss, can be inhibited by direct electrical stimulation of vulnerable cells in the visual pathway
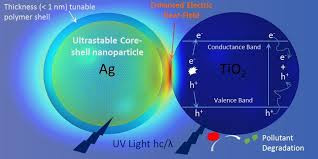
We achieve this effect not by invasive, bulky implants that generate unnatural visual stimuli, but by intravitreal injection of a colloidal suspension of nanoparticle devices that support natural vision
These “quantum dots” diffuse into the retina where they transduce visible light energy into electricity, thereby triggering action potentials in adjacent neural cells and preserving function
Our initial field of focus is retinitis pigmentosa; we are following encouraging Phase I results with a controlled, 15-patient clinical trial, expected to be complete by the end of 2020.
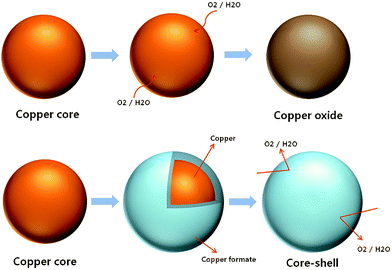
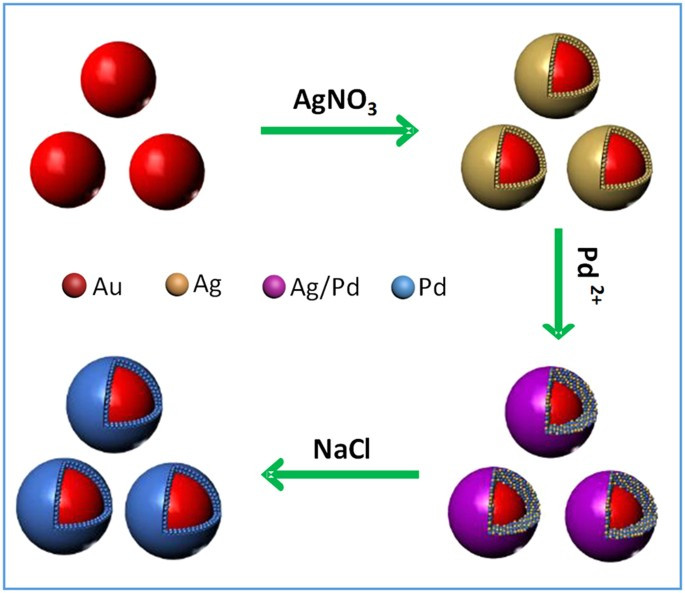
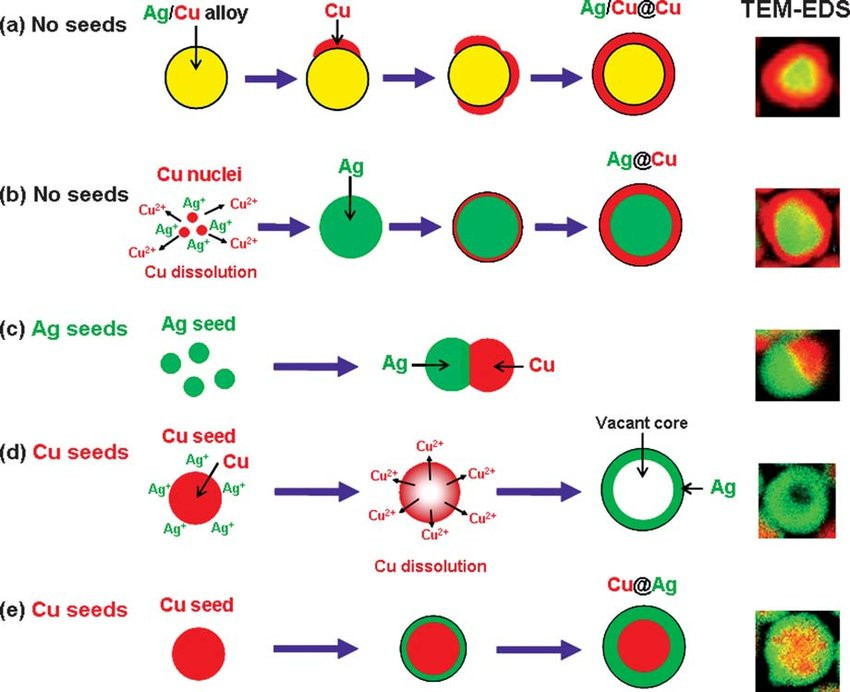
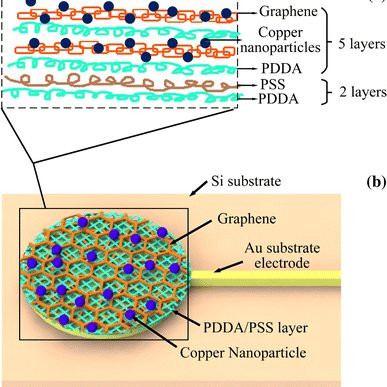
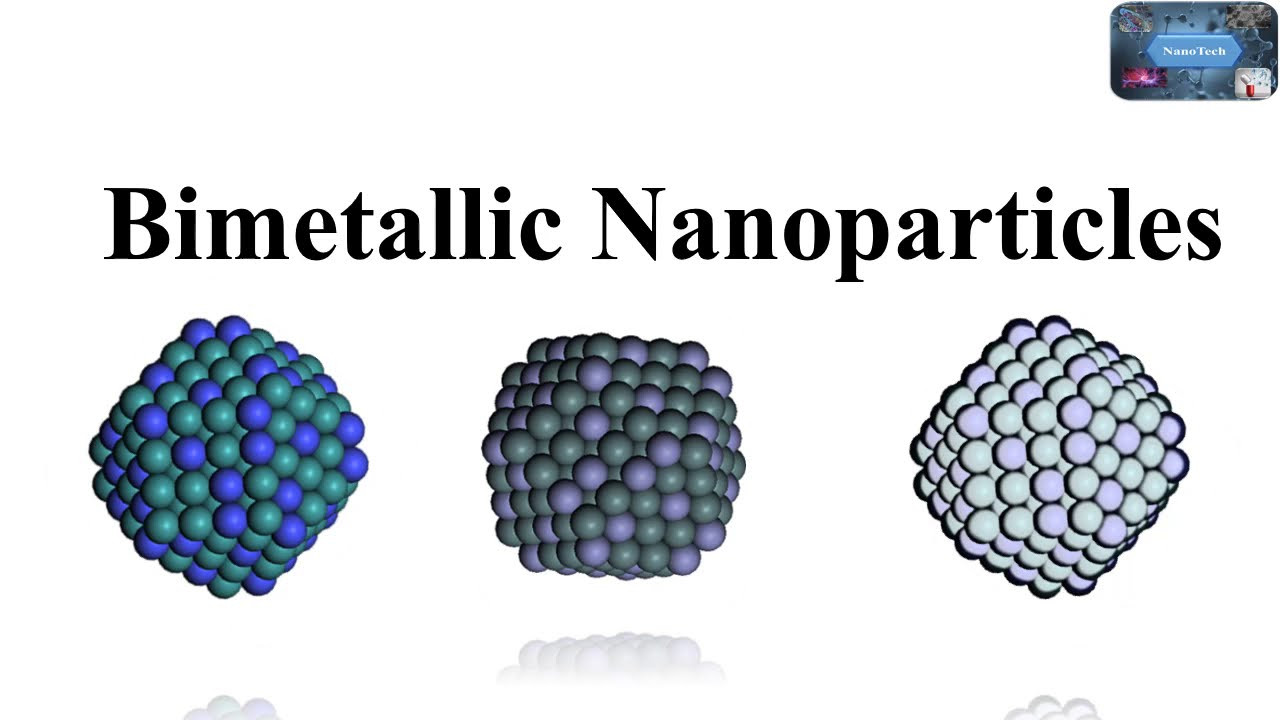
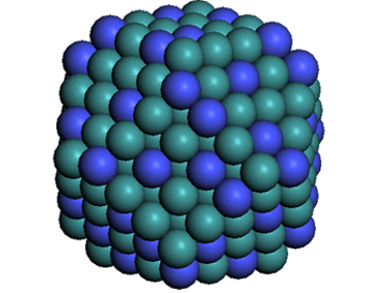
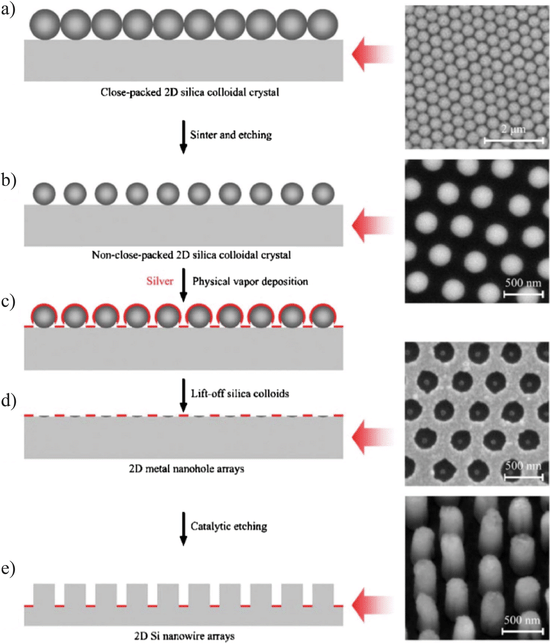
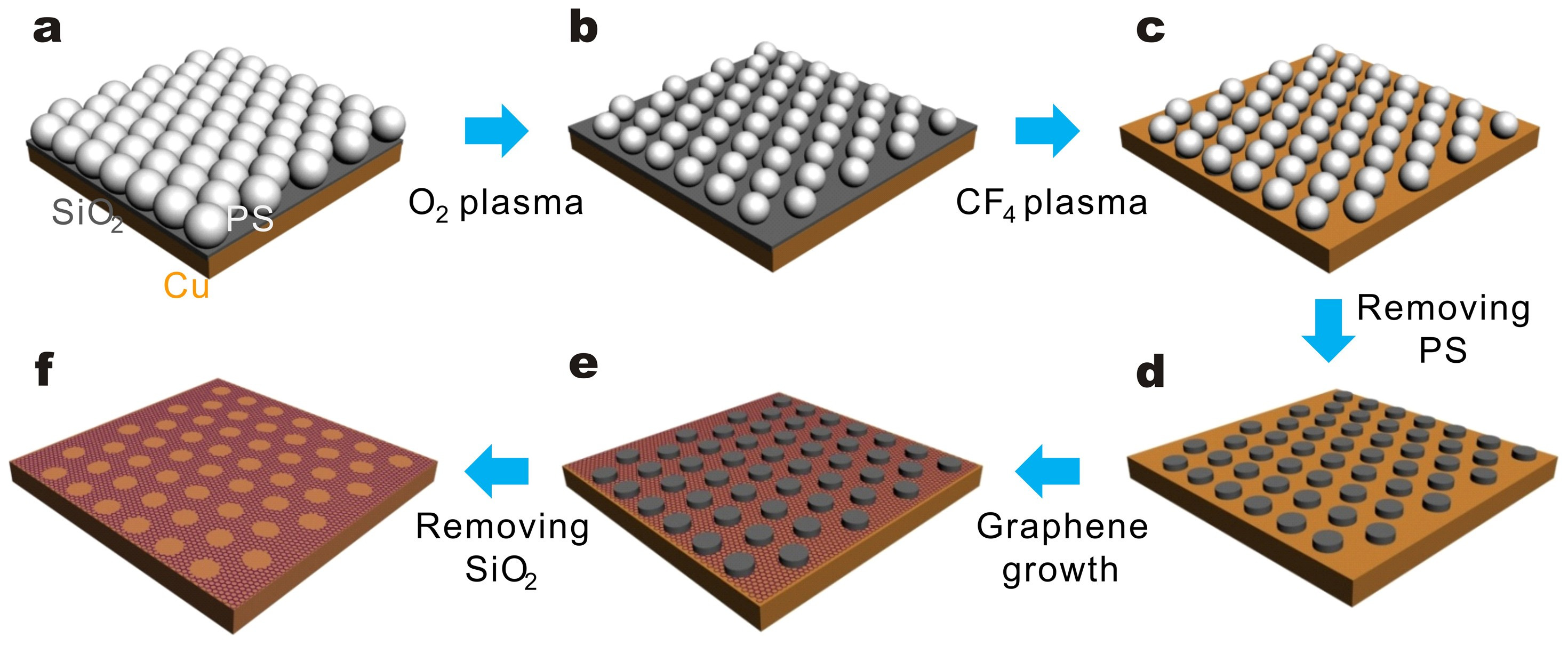
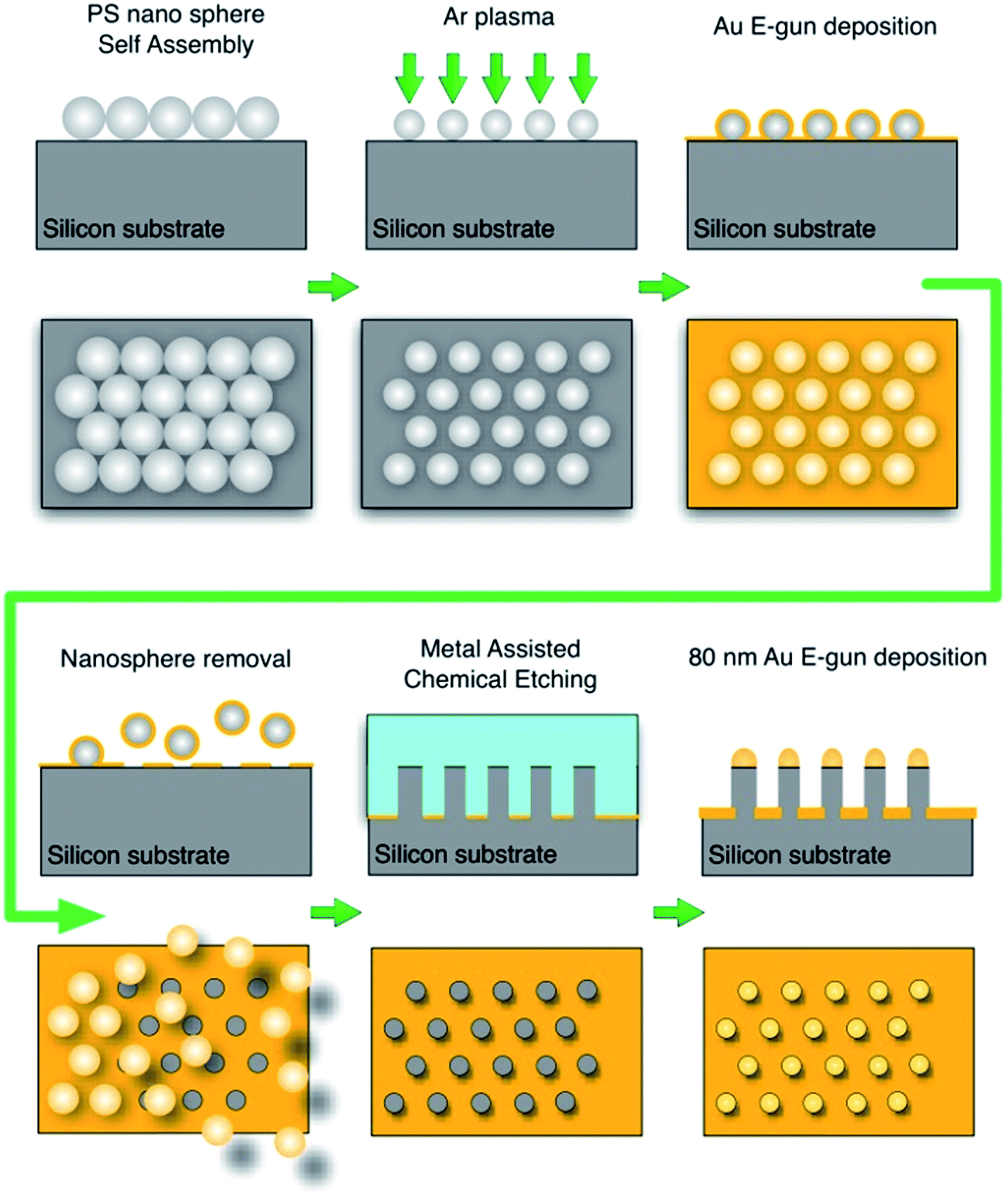
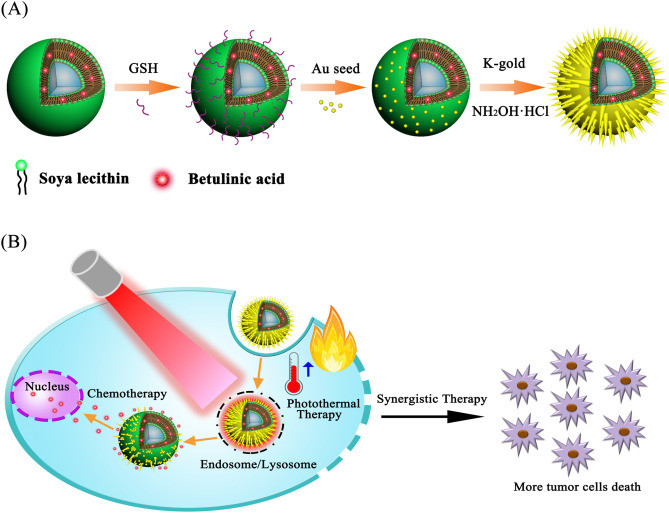
Previous studies were conducted on the effect of the size and shape of colloidal particles on catalysis and the effect of the stabilizer on the activity. In this chapter, we discuss the homogeneous and heterogeneous colloidal nanocatalysts used in the reactions of liquid phase hydrogenation reactions, electron transfer reactions, electrocatalysis, fuel cells, and cross-coupling reactions. Moreover, the effect of the size and shape of colloidal nanoparticles upon each reaction will also be reviewed and presented.
Ions. Radicals. An ion is an atom of an element or a group of atoms of different elements that behave as a single unit. Radical is the atom of an element or a group of atoms of different elements that has at least one unpaired electron. Ion has positive and negative charge on it.
photoelectric effect, phenomenon in which electrically charged particles are released from or within a material when it absorbs electromagnetic radiation. The effect is often defined as the ejection of electrons from a metal plate when light falls on it.
From Middle English or, oor, blend of Old English ōra (“ore, unwrought metal”) and ār (“brass, copper, bronze”), the first a derivate of ear (“earth”), the second from Proto-Germanic *aiz (cognates Old Norse eir (“brass, copper”), German ehern (“of metal, of iron”), Gothic 𐌰𐌹𐌶 (aiz, “ore”)), from Proto-Indo-European *áyos, h₂éyos. Compare Dutch oer (“ferrous hardpan; bog iron ore”). Compare Latin aes (“bronze, copper”), Avestan 𐬀𐬌𐬌𐬀𐬵 (aiiah), Sanskrit अयस् (áyas, “copper, iron”).
An emerging area in chemical science is the study of solid-phase redox reactions using ultrafast time-resolved spectroscopy. We have used molecules of the photoactive dye 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein (DCF) anchored to the surface of iron(III) oxide nanoparticles to create iron(II) surface atoms via photo-initiated interfacial electron transfer. This approach enables time-resolved study of the fate and mobility of electrons within the solid phase. However, complete analysis of the ultrafast processes following dye photoexcitation of the sensitized iron(III) oxide nanoparticles has not been reported. We addressed this topic by performing femtosecond transient absorption (TA) measurements of aqueous suspensions of uncoated and DCF-sensitized iron oxide and oxyhydroxide nanoparticles, and an aqueous iron(III)–dye complex.
Following light absorption, excited state relaxation times of the dye of 115–310 fs were found for all samples. Comparison between TA dynamics on uncoated and dye-sensitized hematite nanoparticles revealed the dye de-excitation pathway to consist of a competition between electron and energy transfer to the nanoparticles. We analyzed the TA data for hematite nanoparticles using a four-state model of the dye-sensitized system, finding electron and energy transfer to occur on the same ultrafast timescale. The interfacial electron transfer rates for iron oxides are very close to those previously reported for DCF-sensitized titanium dioxide (for which dye–oxide energy transfer is energetically forbidden) even though the acceptor states are different. Comparison of the alignment of the excited states of the dye and the unoccupied states of these oxides showed that the dye injects into acceptor states of different symmetry (Ti t2gvs. Fe eg).
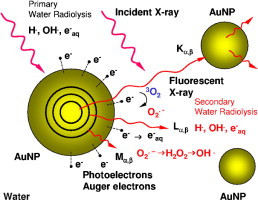
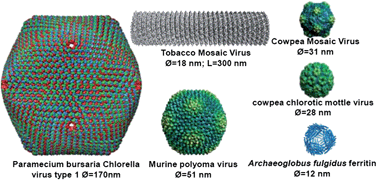
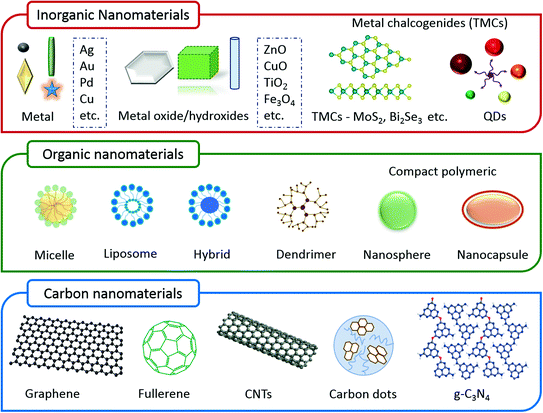
Iron oxide nanoparticles, with their superparamagnetic properties, are used in a rapidly expanding number of applications, such as for cell labeling, separation, and tracking; for therapeutic agents in cancer therapy; and for diagnostic agents
The popular TV series "CSI" is fiction, but every day, real-life investigators and forensic scientists collect and analyze evidence to determine what happened at crime scenes. In a study published in the ACS journal Analytical Chemistry, scientists say they have developed a more rapid and accurate method that could allow crime scene investigators to tell what kind of ammunition was shot from a gun based on the residue it left behind.
Firearms projectiles were being cast in the 14th century. Iron was used for cannon, while lead was the preferred material for small arms.
Heat treating can increase the hardness of commonly used lead alloys. The basic procedure is to rapidly cool, or quench, hot bullets.
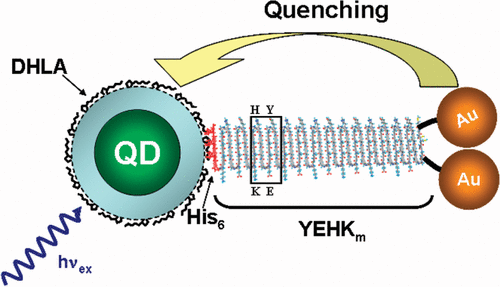
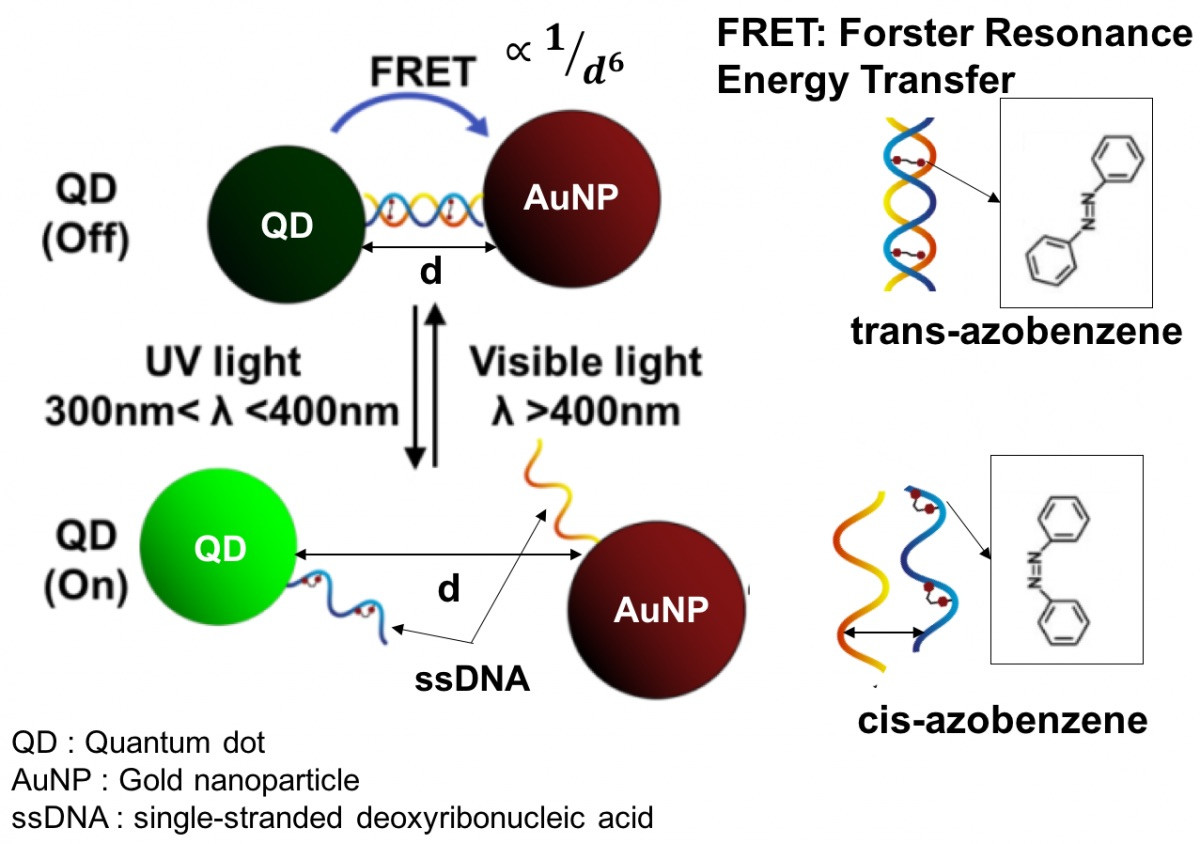
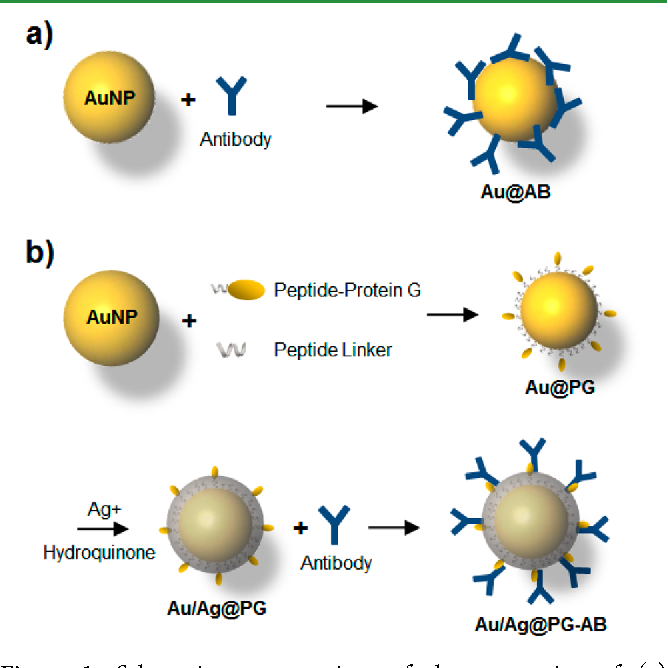
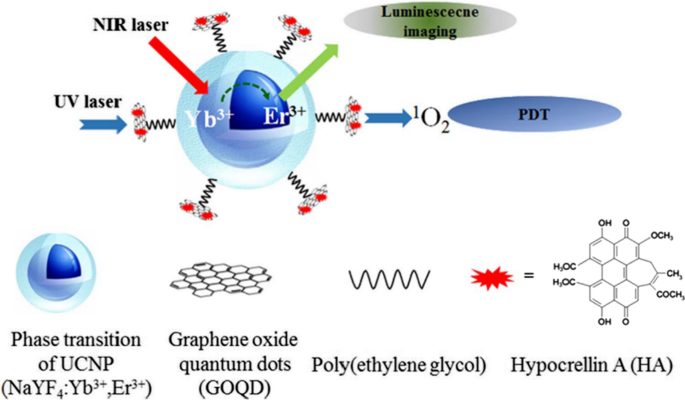
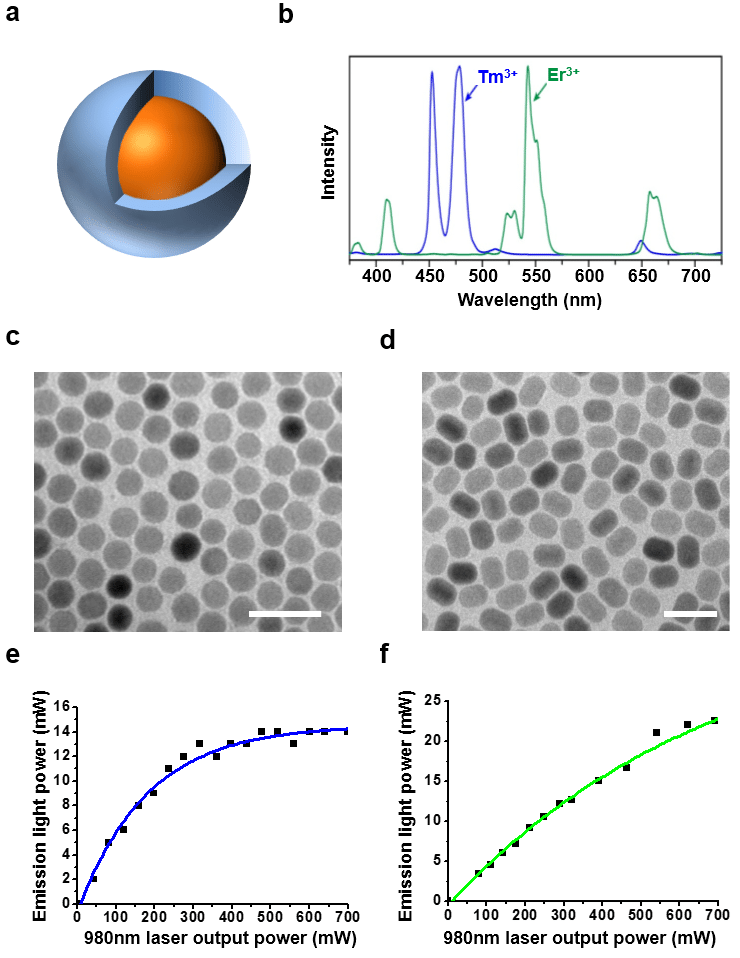
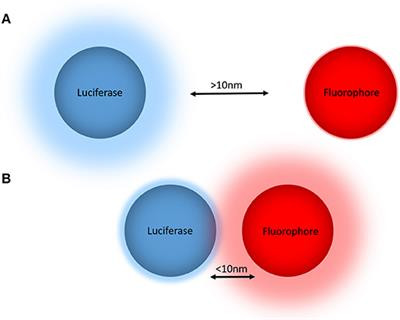
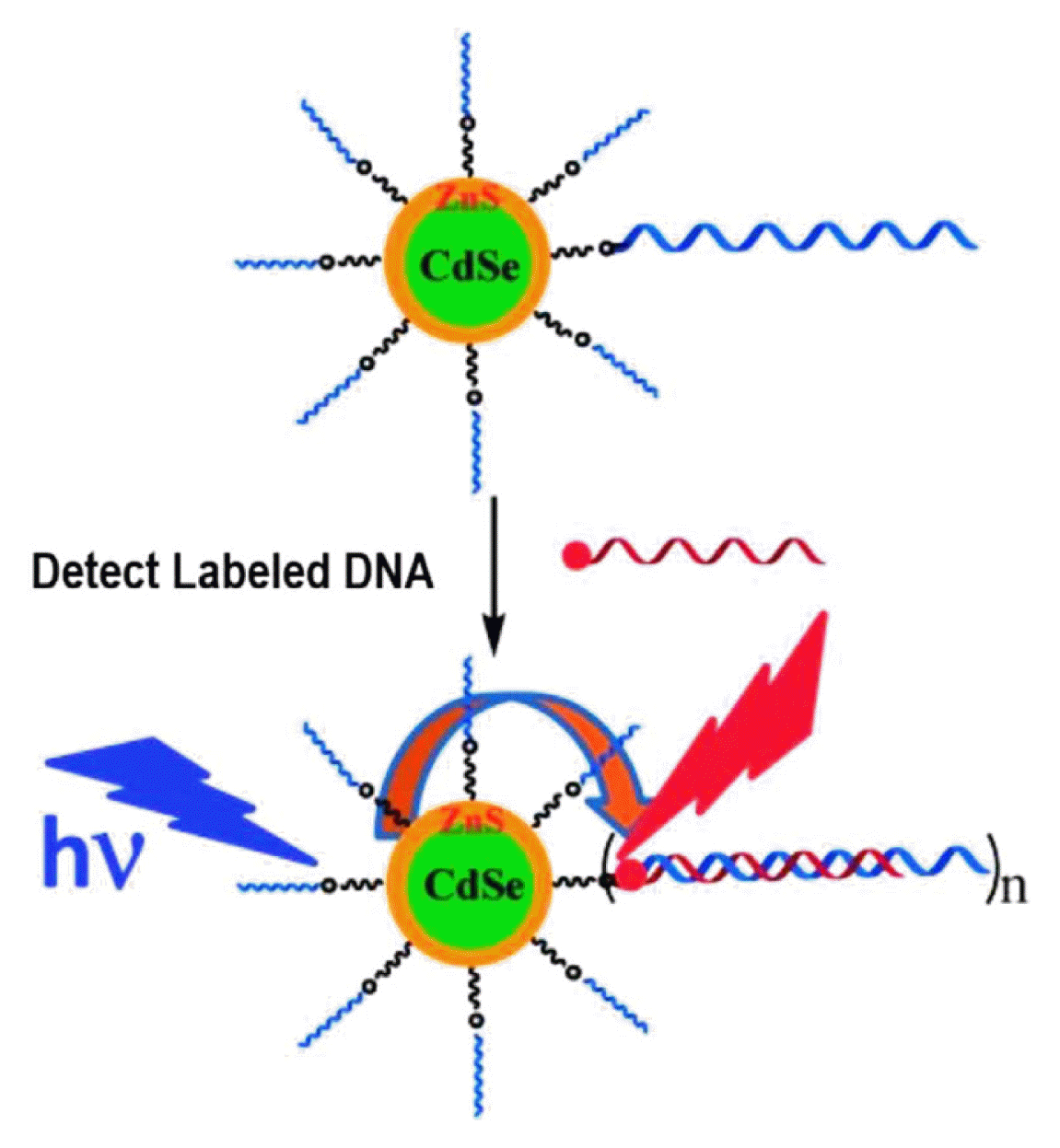
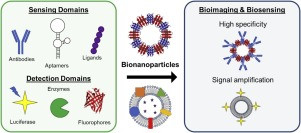
Luminescent quantum dots (QDs) were proven to be very effective fluorescence resonance energy transfer donors with an array of organic dye acceptors, and several fluorescence resonance energy transfer based biosensing assemblies utilizing QDs have been demonstrated in the past few years. Conversely, gold nanoparticles (Au-NPs) are known for their capacity to induce strong fluorescence quenching of conventional dye donors.
Using a rigid variable-length polypeptide as a bifunctional biological linker, we monitor the photoluminescence quenching of CdSe−ZnS QDs by Au-NP acceptors arrayed around the QD surface, where the center-to-center separation distance was varied over a broad range of values (∼50−200 Å). We measure the Au-NP-induced quenching rates for such QD conjugates using steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence measurements and examine the results within the context of theoretical treatments based on the Förster dipole−dipole resonance energy transfer, dipole−metal particle energy transfer, and nanosurface energy transfer. Our results indicate that nonradiative quenching of the QD emission by proximal Au-NPs is due to long-distance dipole−metal interactions that extend significantly beyond the classical Förster range, in agreement with previous studies using organic dye−Au-NP donor−acceptor pairs.
Quantum dot (QD) – Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) – Gold nanoparticle (AuNP) composite : FRET studies | QSTORM-AO
QSTORM-AO is a bold effort to build a new instrument capable of spying on the most fundamental biological processes occurring inside living cells in nanometer detail.
http://qstorm.org/node/661A gold rush or gold fever is a discovery of gold—sometimes accompanied by other precious metals and rare-earth minerals—that brings an onrush of miners seeking their fortune. Major gold rushes took place in the 19th century in Australia, New Zealand, Brazil, South Africa, the United States, and Canada while smaller gold rushes took place elsewhere.
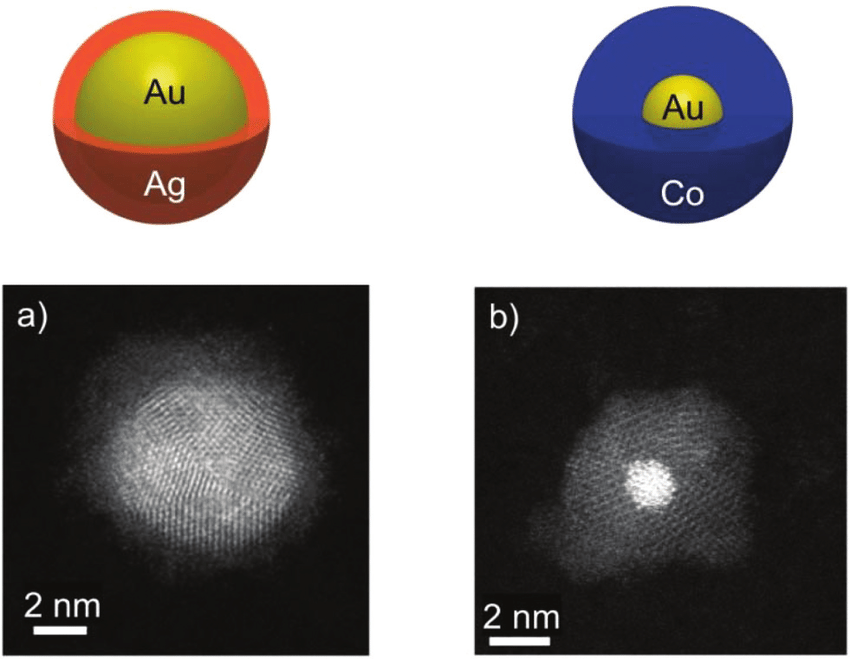
Conventionally, Au has been considered as a typical diamagnetic material*1 and is not considered to have strong magnetism, meaning that it cannot act as a magnet by itself.
Since there are 2 unpaired electrons, Au+ is paramagnetic.
Gold's chemical symbol is Au, which stands for aurum in Latin. Its yellowish luster. makes it an attractive metal to use in jewelry and its resistance to corrosion makes it good. for long-lasting electronics. - The element gold Au is a collection of gold atoms all joined together.
panned; past participle: panned
swing (a video or film camera) in a horizontal or vertical plane, typically to give a panoramic effect or follow a subject.
"he was panning the camera over everything in sight"
(of a camera) be swung in a horizontal or vertical plane.
"the camera panned to the dead dictator"
swing (round)
sweep
track
move
turn
circle
In cinematography and photography panning means swivelling a still or video camera horizontally from a fixed position. This motion is similar to the motion of a person when they turn their head on their neck from left to right. In the resulting image, the view seems to "pass by" the spectator as new material appears on one side of the screen and exits from the other, although perspective lines reveal that the entire image is seen from a fixed point of view.
The term panning is derived from panorama, suggesting an expansive view that exceeds the gaze, forcing the viewer to turn their head in order to take everything in.
late 18th century: from pan- ‘all’ + Greek horama ‘view’ (from horan ‘see’).
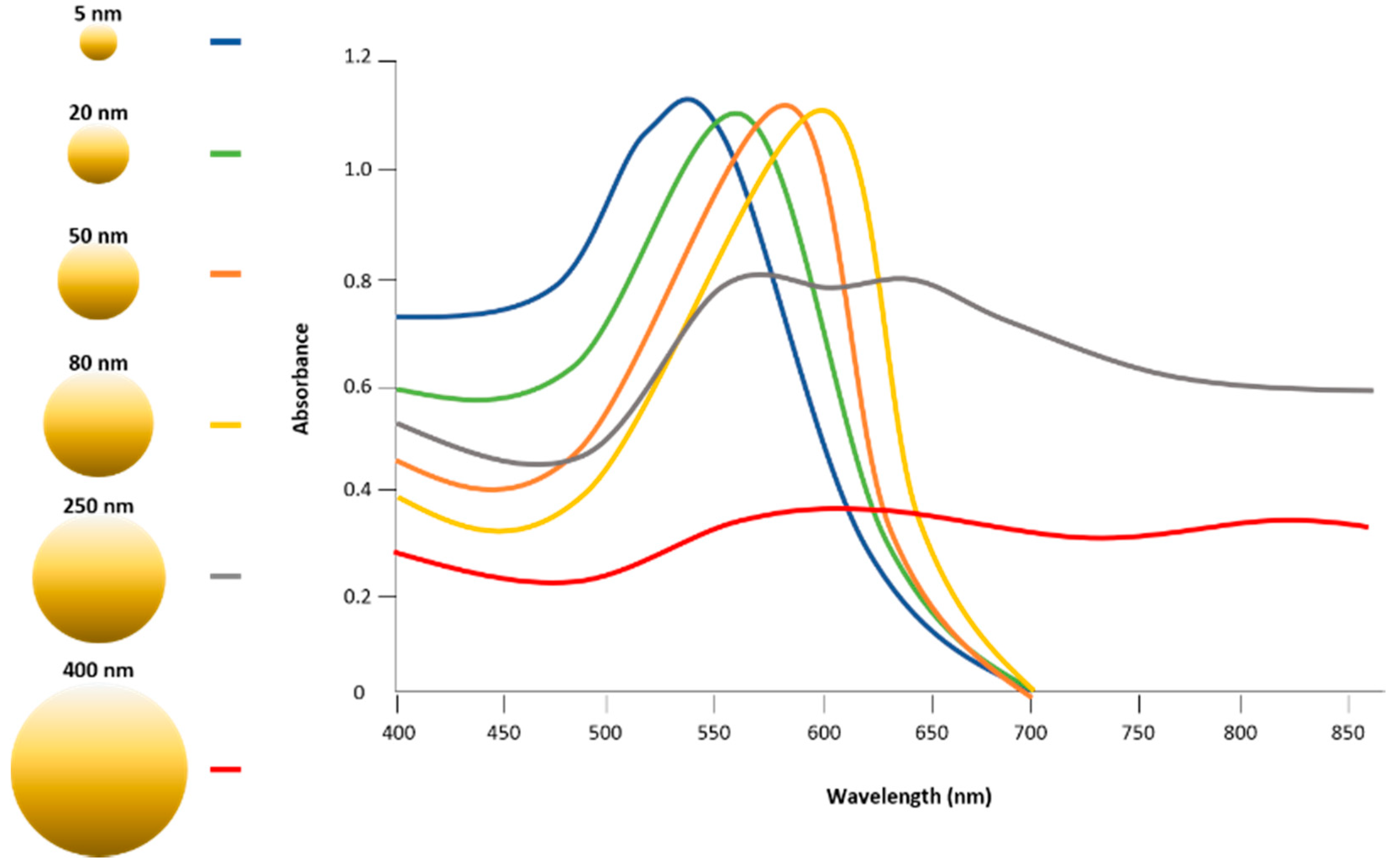
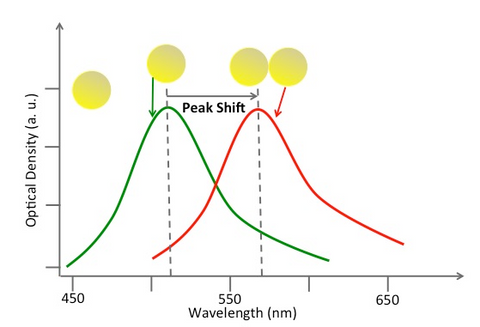
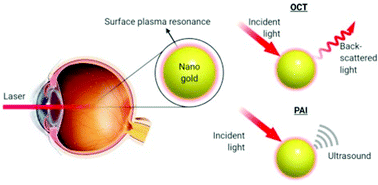
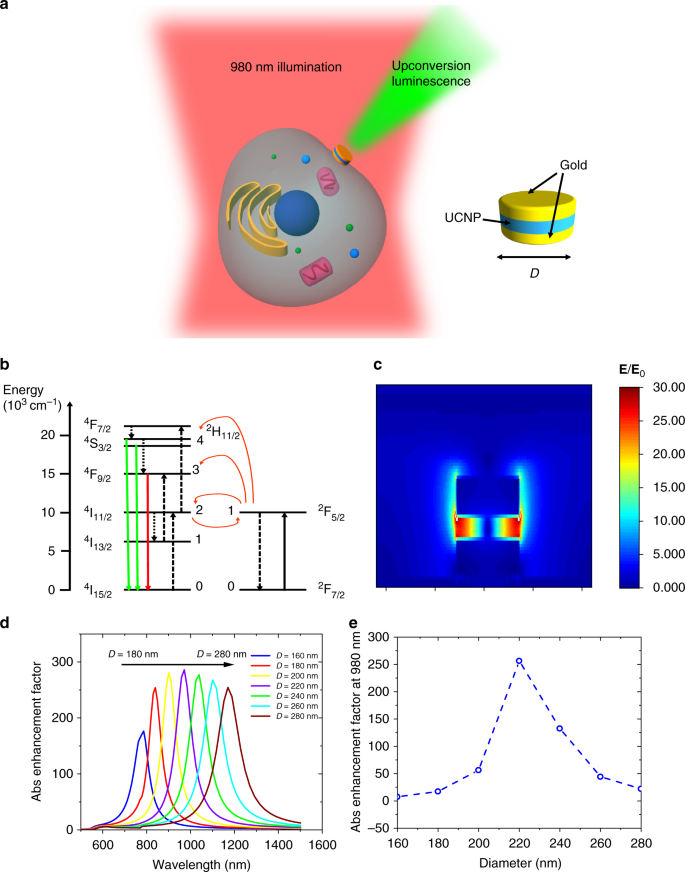
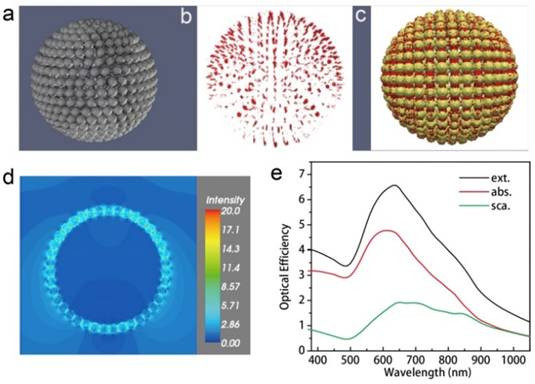
The use of gold nanoparticles as diagnostic tools is burgeoning, especially in the cancer community with a focus on theranostic applications to both cancer diagnosis and treatment. Gold nanoparticles have also demonstrated great potential for use in diagnostic and therapeutic approaches in ophthalmology.
Although many ophthalmic imaging modalities are available, there is still a considerable unmet need, in particular for ophthalmic molecular imaging for the early detection of eye disease before morphological changes are more grossly visible. An understanding of how gold nanoparticles are leveraged in other fields could inform new ways they could be utilized in ophthalmology. In this paper, we review current ophthalmic imaging techniques and then identify optical coherence tomography (OCT) and photoacoustic imaging (PAI) as the most promising technologies amenable to the use of gold nanoparticles for molecular imaging. Within this context, the development of gold nanoparticles as OCT and PAI contrast agents are reviewed, with the most recent developments described in detail.
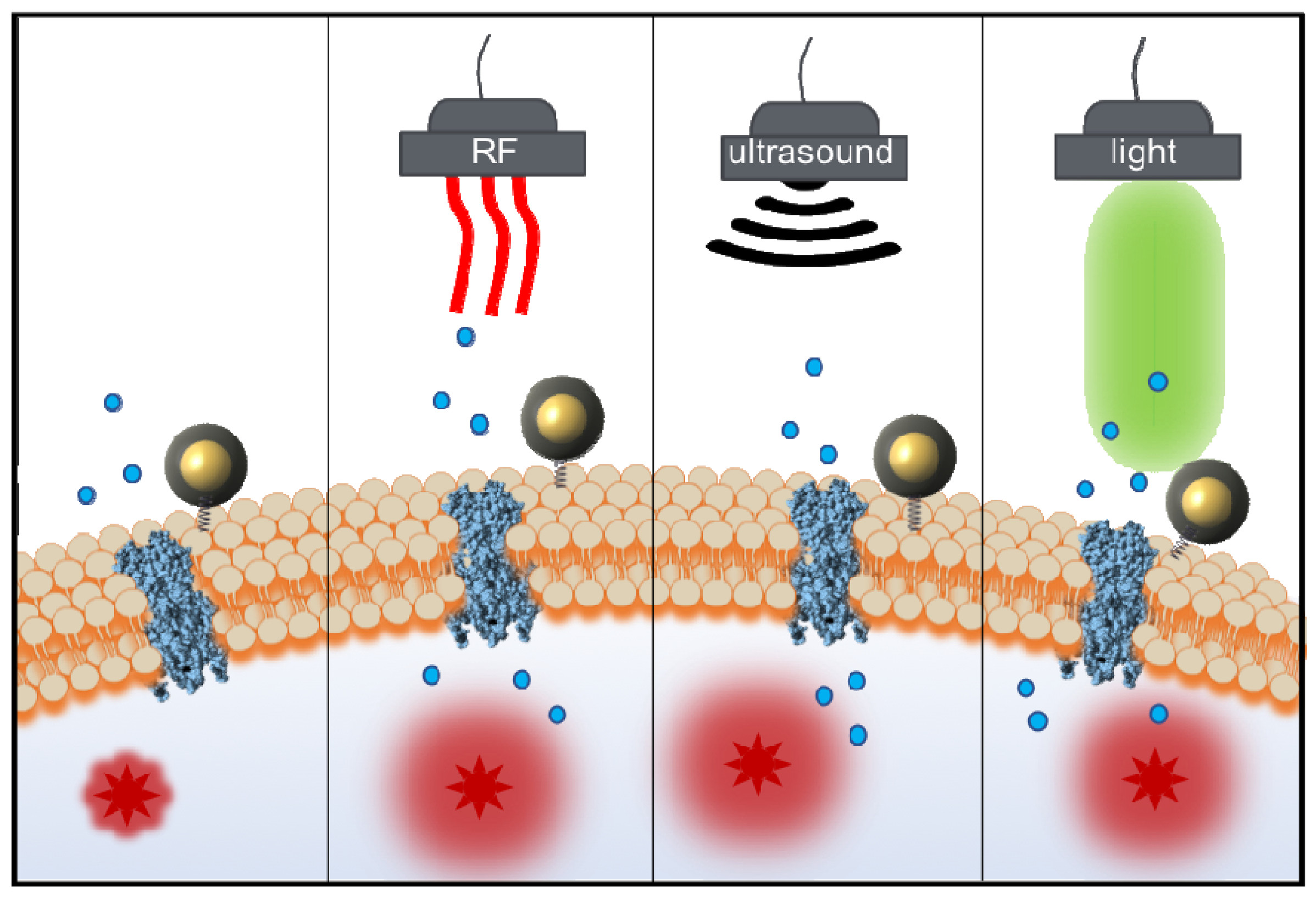
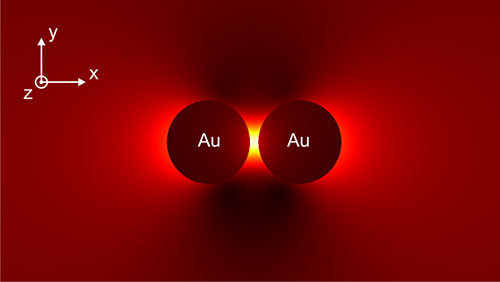
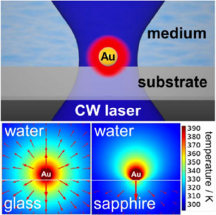
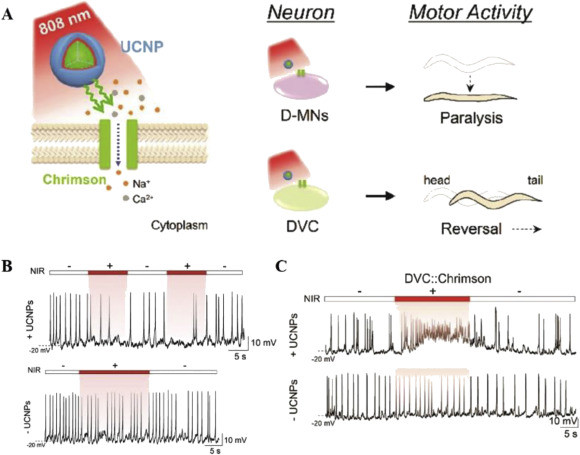
Nanoparticle (NP) bioconjugates have an important role in the development of photothermal (PT) therapy, a promising noninvasive approach wherein the NP acts as a light harvesting antenna to convert light into thermal energy to control cellular function. NP-mediated PT control of cellular membrane potential has gained significant interest in recent years as membrane potential regulates proliferation, migration, action potentials (in neurons), and contraction (in muscle cells). Recently gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) and Au nanorods have been demonstrated to induce action potentials via light-induced thermal activation of membrane tethered NPs.
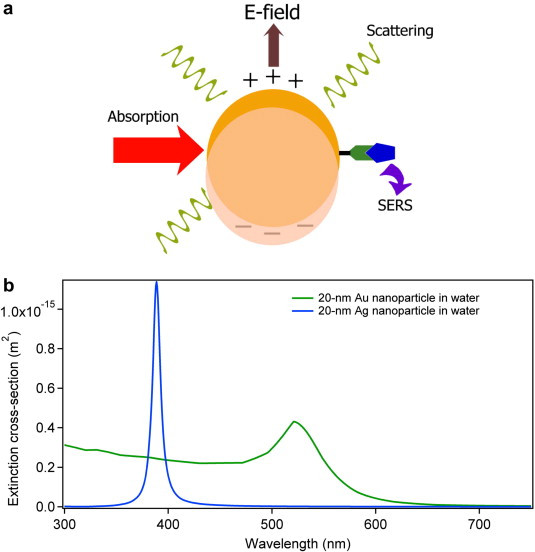
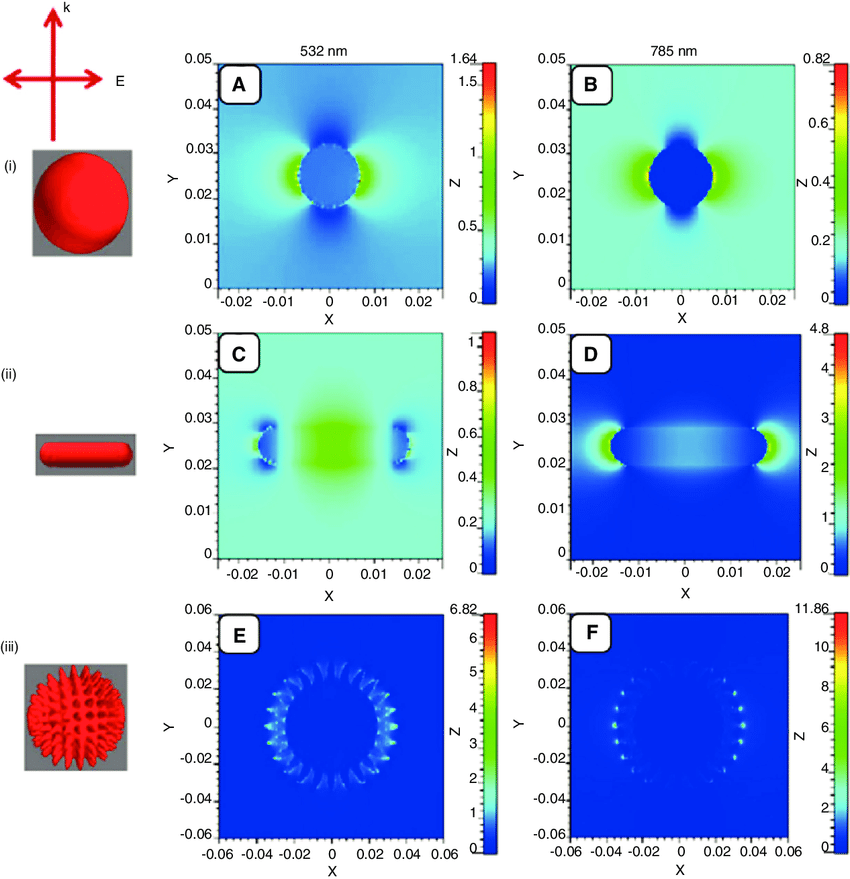
Spherical AuNPs have an efficient plasmonic output and are easily modified to interface with the cell surface. We demonstrate here that 20 nm diameter spherical AuNPs (tethered to the plasma membrane by a cholesterol moiety) transduce incident 532 nm light into proximal membrane heating that induces depolarization of membrane potential. Using these NP bioconjugates, we show the ability to controllably induce action potentials in dorsal root ganglion neurons and to control the membrane potential of rat pheochromocytoma cells. The ability to use light-actuated NP conjugates to control cellular behavior is an emerging research field with implications for neuronal and muscle cell modulation as well as in cancer therapeutics.
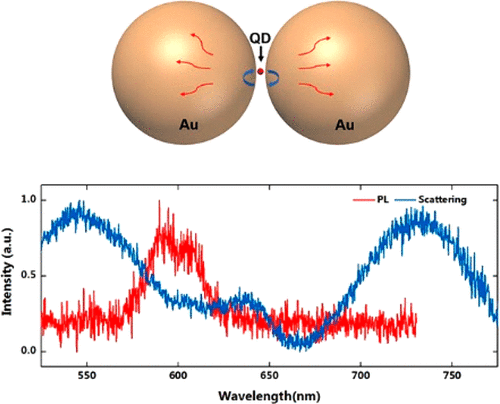
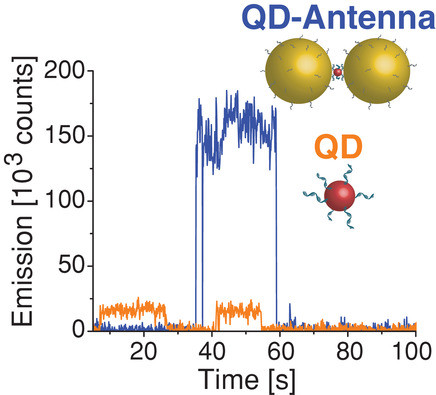
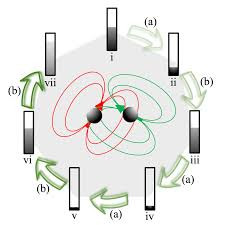
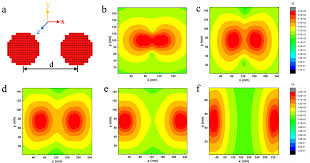
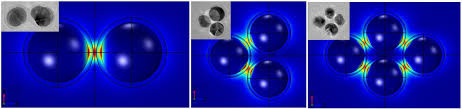
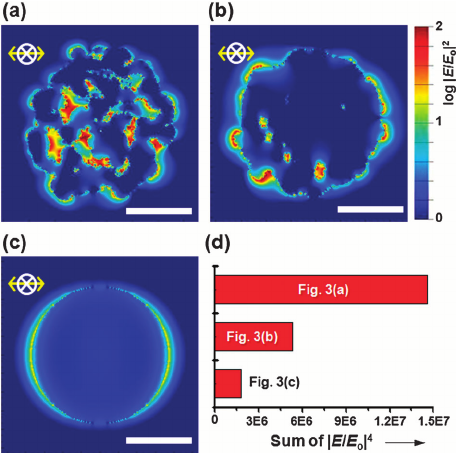
Strong plasmon–exciton coupling could occur in hybrid metal–dye/semiconductor nanostructures, where the fast energy exchange between plasmons and excitons leads to two new eigenmodes of the system, known as Rabi splitting. In experiments, strongly coupled nanosystems are difficult to obtain because they require some strict conditions, such as low plasmonic damping, small plasmon mode volume, and good spectral overlap. This work demonstrates strongly coupled metal–semiconductor nanostructures can be constructed using colloidal assembly.
Specifically, sandwiched Au–quantum dot–Au nanostructures were created through the assembly of Au nanoparticles and colloidal quantum dots (QDs). The sizes of the QDs and the assembly conditions were varied to control the mode volume of the plasmonic cavity formed between the two Au nanoparticles. With a decreased gap size, Rabi splitting was observed in both dark-field scattering and fluorescence spectra of single Au–QD–Au nanostructures. Theoretical simulations revealed that the strong coupling occurred between the excitons and the octupolar plasmon modes.
Kymeta raised $85.2 million in this latest round, with Bill Gates leading the investment with $78.5 million.
The company's core product is its "electronically steered" flat satellite antenna, built to replace the dish technology that track moving satellites but also capable of connecting with cellular networks.
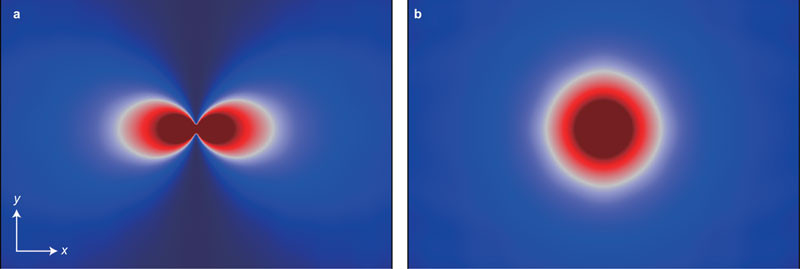
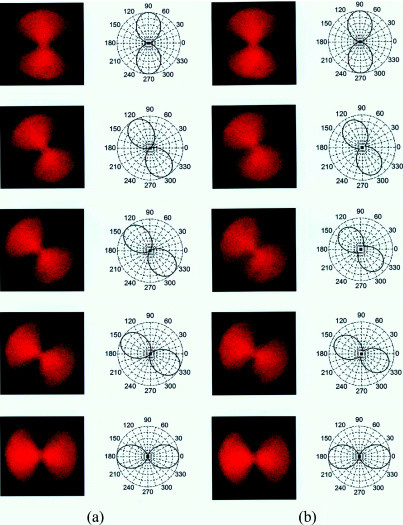
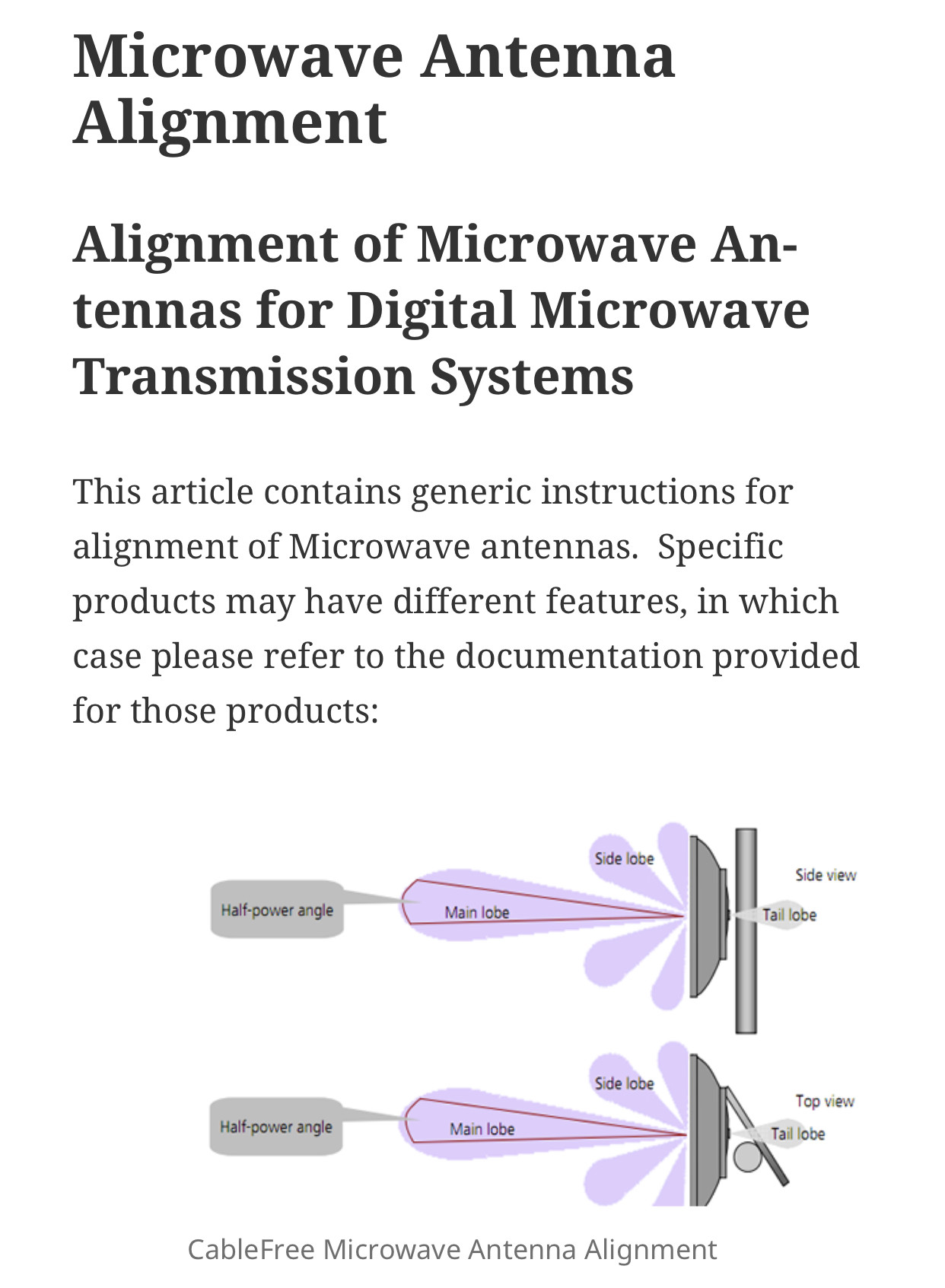
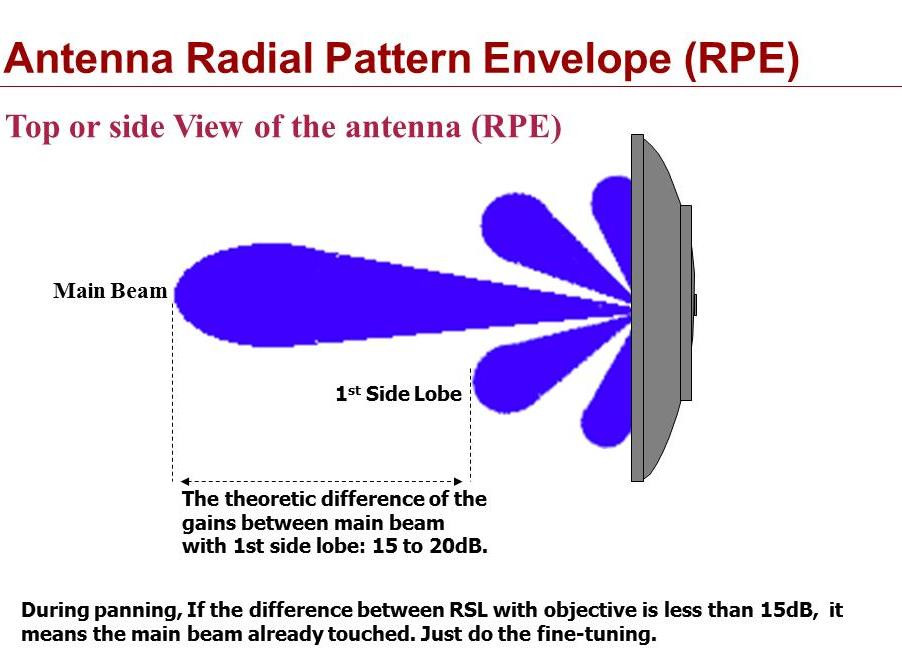
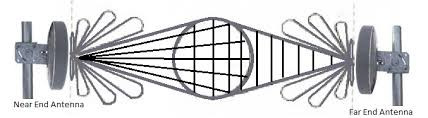
Antenna Theory - Radiation Pattern
Antenna Theory - Radiation Pattern, Radiation is the term used to represent the emission or reception of wave front at the antenna, specifying its strength. In any illustration, the sketch drawn t
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/antenna_theory/antenna_theory_radiation_pattern.htmAnyway you get the picture.
About 1 in 44 children has been identified with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) according to estimates from CDC’s Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring (ADDM) Network. [Read article]
ASD is reported to occur in all racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic groups. [Read article]
ASD is more than 4 times more common among boys than among girls. [Read article]
About 1 in 6 (17%) children aged 3–17 years were diagnosed with a developmental disability, as reported by parents, during a study period of 2009-2017. These included autism, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, blindness, and cerebral palsy, among others.
Lipid peroxidation markers are elevated in autism, indicating that oxidative stress is increased in this disease.
Quantum dots (QDs) are luminescent nanoparticles with unique optical properties that have been exploited for single-cell and whole-animal imaging. When coated with proteins or biocompatible polymers, QDs are not deleterious to cells and organisms. However, when QDs are retained in cells or accumulated in the body for a long period of time, their coatings may be degraded, yielding “naked” QDs. Here, we show that “naked” QDs induce damage to the plasma membrane, mitochondrion, and nucleus, leading to cell death. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are important players in mediating QD-induced cellular damage. QD-induced cytotoxicity can be reduced or even eliminated without covalent binding of protective agents to the QD surface. Results from these studies suggest the critical role of several subcellular compartments in QD-induced cytotoxicity and point toward multiple molecular targets in nonclassical apoptosis.
"The findings raise the exciting possibility that this new vaccine technology could provide protection against many coronavirus strains"
gerund or present participle: exciting
1.
cause (someone) to feel very enthusiastic and eager.
"flying still excites me"
thrill
exhilarate
animate
enliven
rouse
stir
move
stimulate
galvanize
electrify
fire the imagination of
fire the enthusiasm of
delight
enrapture
intoxicate
send
tickle
tickle someone pink
buck up
pep up
ginger up
give someone a buzz
give someone a kick
get someone going
light a fire under
give someone a charge
arouse (someone) sexually.
"his Mediterranean vibrancy excited and stimulated her"
arouse
arouse sexually
stimulate
titillate
inflame
please
attract
entice
turn someone on
give someone a thrill
get someone going
float someone's boat
do it for someone
light someone's fire
tickle someone's fancy
give rise to (a feeling or reaction).
"the ability to excite interest in others"
provoke
stir up
elicit
rouse
arouse
stimulate
kindle
trigger (off)
touch off
spark off
awaken
incite
instigate
foment
bring out
cause
bring about
enkindle
produce a state of increased energy or activity in (a physical or biological system).
"the energy of an electron is sufficient to excite the atom"
Middle English (in the sense ‘incite someone to do something’): from Old French exciter or Latin excitare, frequentative of exciere ‘call out or forth’. excite (sense 1) dates from the mid 19th century.