A seed crystal is a small crystal that is used as a base to grow a large single crystal. Without a seed, crystals form slowly from random intermolecular interactions. When the seed is placed in a saturated or supersaturated solution it acts as a nucleation site. This decreases the time needed to grow a crystal and directs growth to a single region. Here’s how to grow a seed crystal and how to use one to get a large, perfect crystal.
MAGA🇺🇸🇺🇸🇺🇸Trump Won🇺🇸🇺🇸WWG1WGA 🙏🏻Save The Children🙏🏻 💛💛Trump is Still my President💛💛 PLEASE no DM’s
Crystal recipes ☺️
https://www.thoughtco.com/easy-crystal-growing-recipes-606259
Collection of Easy Crystal Growing Recipes
Growing crystals does not have to be complicated! This is a collection of crystal growing recipes you can safely make at home or in the classroom.
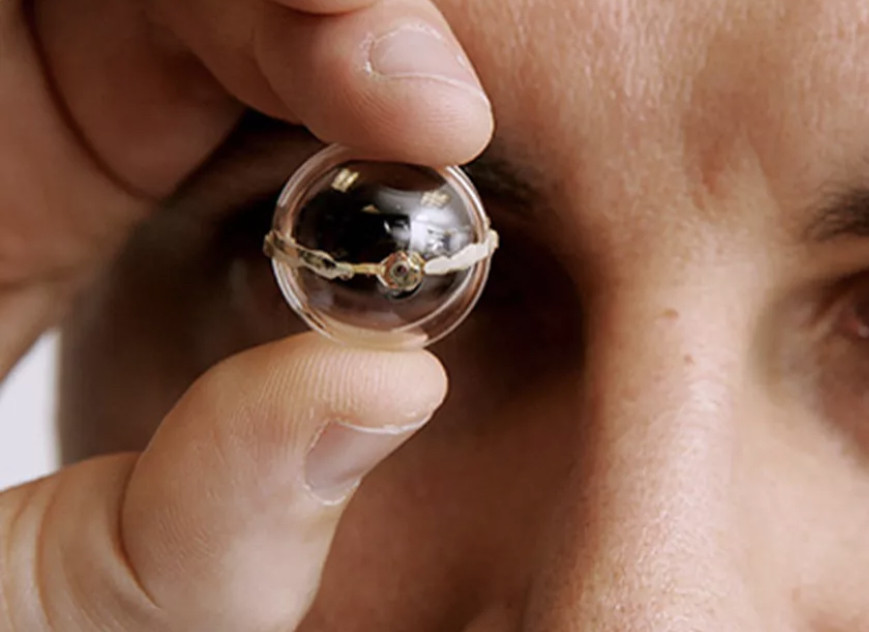
https://www.thoughtco.com/easy-crystal-growing-recipes-606259Neurostimulation has proved to be an effective method for the restoration of visual perception lost due to retinal diseases. However, the clinically available retinal neurostimulation method is based on invasive electrodes, making it a high-cost and high-risk procedure. Recently, ultrasound has been demonstrated to be an effective way to achieve noninvasive neurostimulation. In this work, a novel racing array transducer with a contact lens shape is proposed for ultrasonic retinal stimulation. The transducer is flexible and placed outside the eyeball, similar to the application of a contact lens. Ultrasound emitted from the transducer can reach the retina without passing through the lens, thus greatly minimizing the acoustic absorption in the lens.
The discretized Rayleigh–Sommerfeld method was employed for the acoustic field simulation, and patterned stimulation was achieved. A 5 MHz racing array transducer with different element numbers was simulated to optimize the array configuration. The results show that a 512-element racing array is the most appropriate configuration considering the necessary tradeoff between the element number and the stimulation resolution. The stimulation resolution at a focus of 24 mm is about 0.6 mm. The obtained results indicate that the proposed racing array design of the ultrasound transducer can improve the feasibility of an ultrasound retinal prosthesis.
The new coronavirus behind the pandemic causes a respiratory illness called COVID-19. Its most common symptoms are a fever, coughing, and breathing problems. Rarely, it also can cause an eye infection called conjunctivitis.
UV-C has promise as a means of environmental control for SARS-CoV-2. To understand the potential of UV-C as a tool in the pandemic, we must first understand the effect of UV-C on SARS-CoV-2 and the necessary operating time to reduce the bioburden of SARS-CoV-2 in the environment. Herein, we present the results of a laboratory study that assessed the efficacy of full-germicidal-spectrum UV-C from a pulsed-xenon source (PX-UV) on SARS-CoV-2 on hard surfaces and N95 respirators.
We found that PX-UV significantly reduces SARS-CoV-2 on hard surfaces and N95 respirators. With the potential to rapidly disinfectant environmental surfaces and N95 respirators, PX-UV devices are a promising technology for the reduction of environmental and PPE bioburden.
In these experiments, specific light sources were shown to activate the HIV gene and/or promote viral replication. UVC was the most potent activator. UVB, sunlight, and PUVA were also capable of activating HIV, albeit to lesser degrees (1–5).
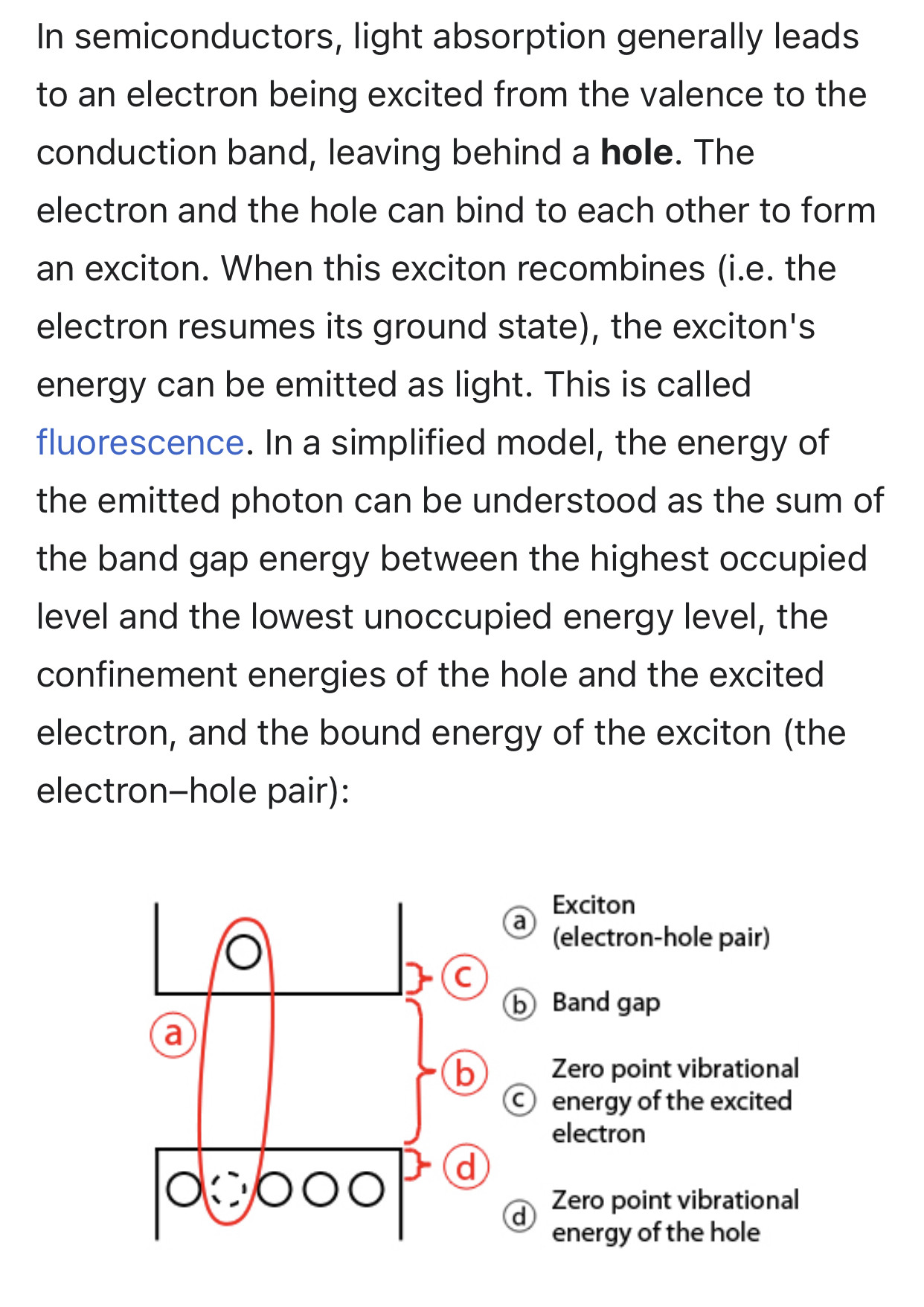
Also known as “zero-dimensional electronic structures,” quantum dots are unique in that their semiconductor energy levels can be tailored by simply altering size, shape and charge potential. These energy levels result in distinct color identifications for different-sized quantum dots.
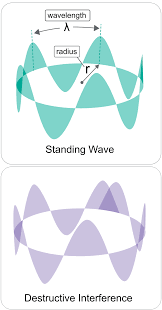
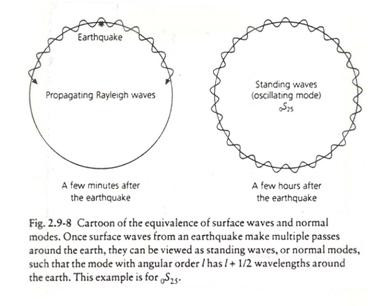
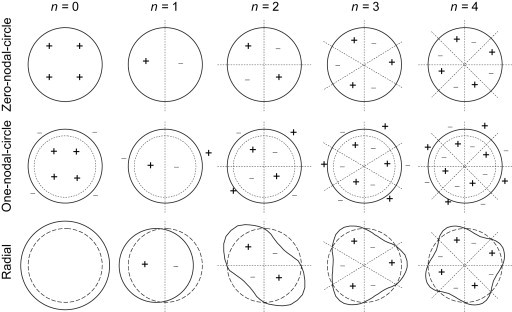
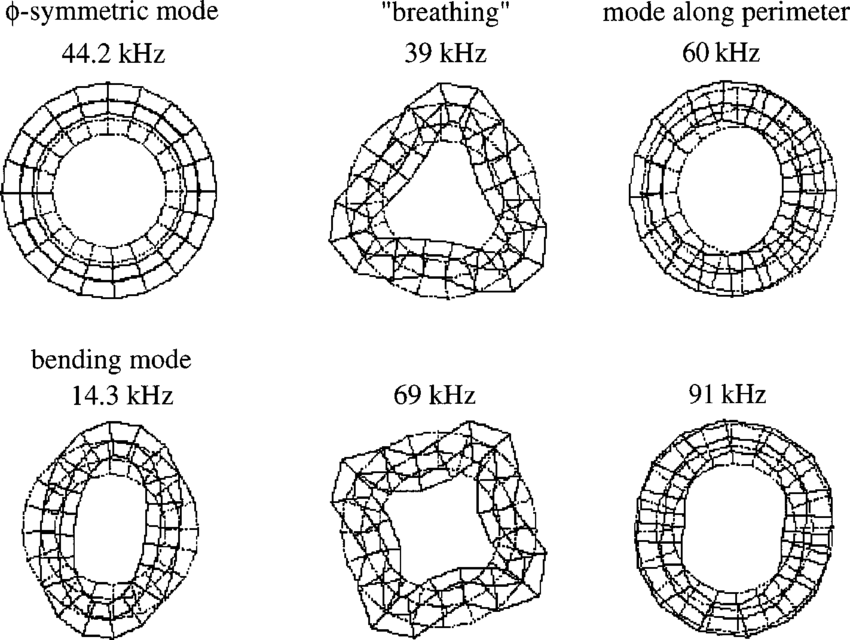
A microwave cavity or radio frequency (RF) cavity is a special type of resonator, consisting of a closed (or largely closed) metal structure that confines electromagnetic fields in the microwave region of the spectrum. The structure is either hollow or filled with dielectric material. The microwaves bounce back and forth between the walls of the cavity. At the cavity's resonant frequencies they reinforce to form standing waves in the cavity. Therefore, the cavity functions similarly to an organ pipe or sound box in a musical instrument, oscillating preferentially at a series of frequencies, its resonant frequencies. Thus it can act as a bandpass filter, allowing microwaves of a particular frequency to pass while blocking microwaves at nearby frequencies.
A microwave cavity acts similarly to a resonant circuit with extremely low loss at its frequency of operation, resulting in quality factors (Q factors) up to the order of 106, compared to 102 for circuits made with separate inductors and capacitors at the same frequency. They are used in place of resonant circuits at microwave frequencies, since at these frequencies discrete resonant circuits cannot be built because the values of inductance and capacitance needed are too low. They are used in oscillators and transmitters to create microwave signals, and as filters to separate a signal at a given frequency from other signals, in equipment such as radar equipment, microwave relay stations, satellite communications, and microwave ovens.
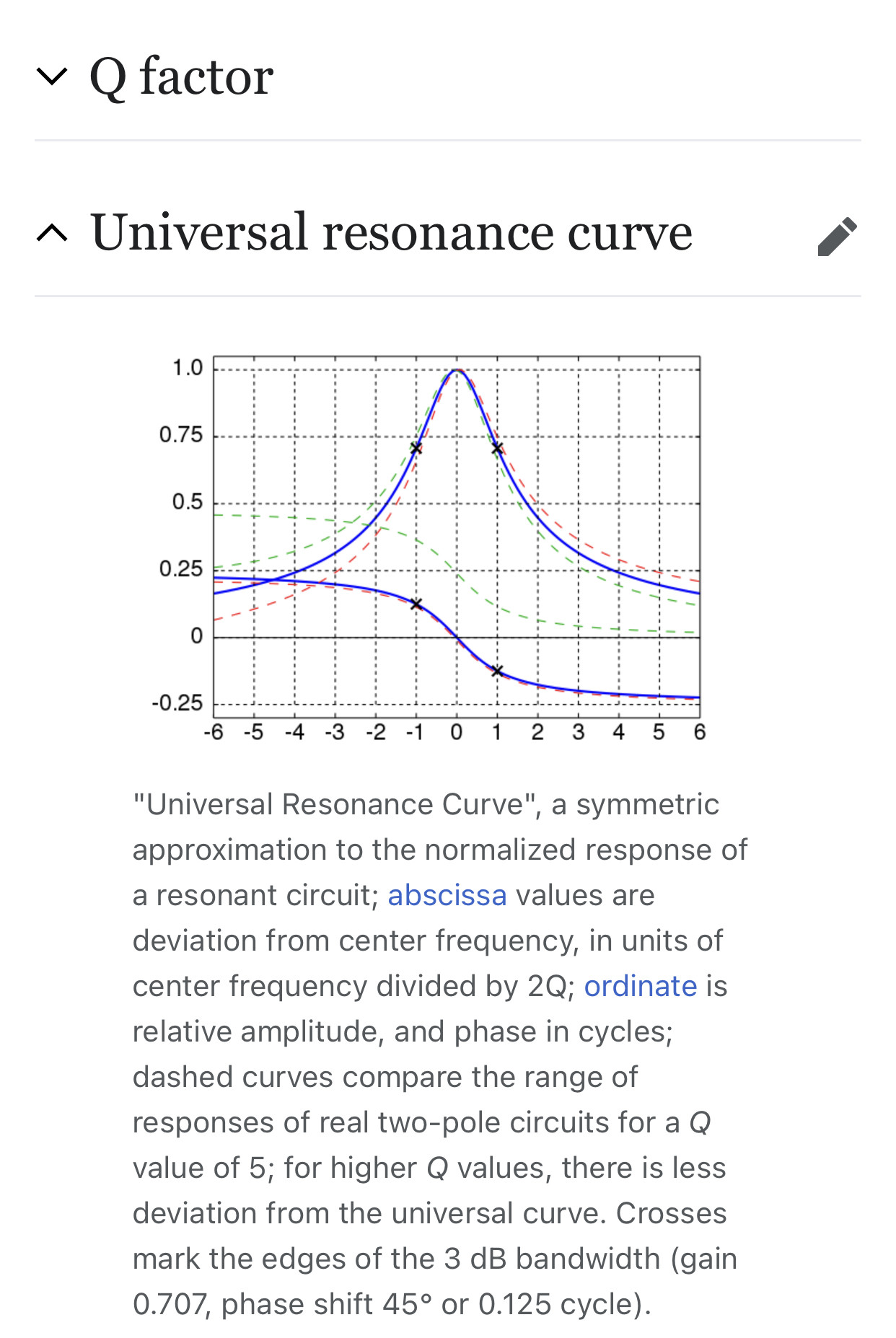
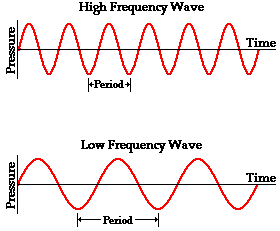
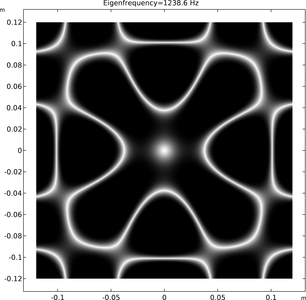
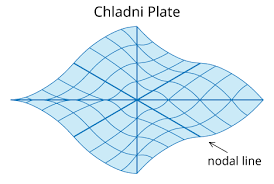
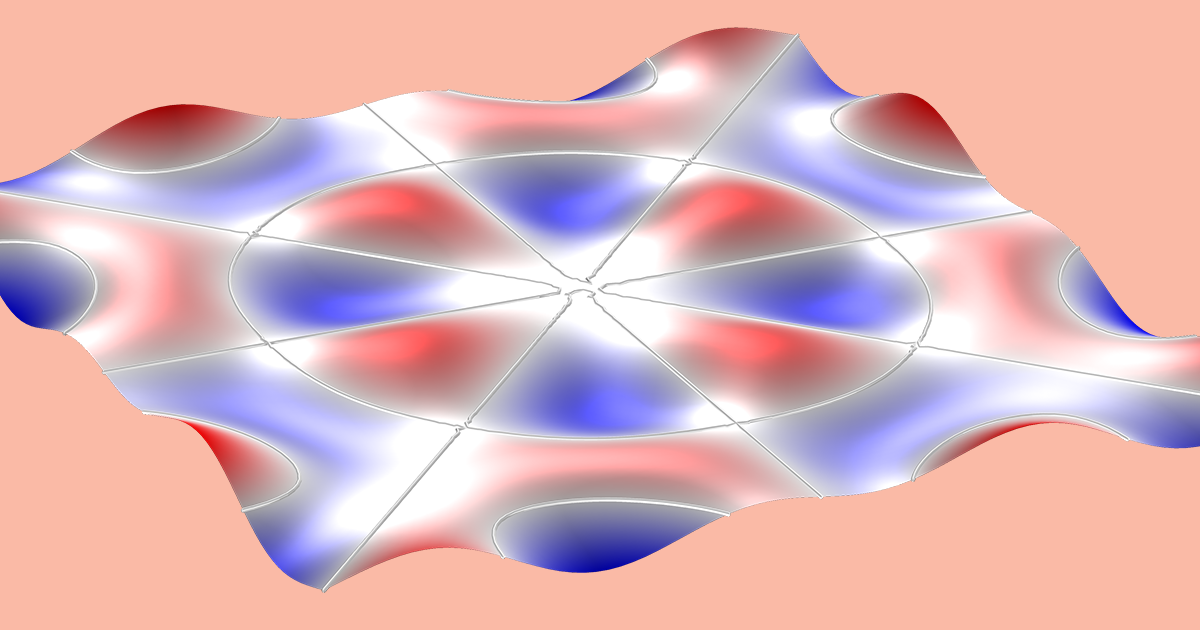
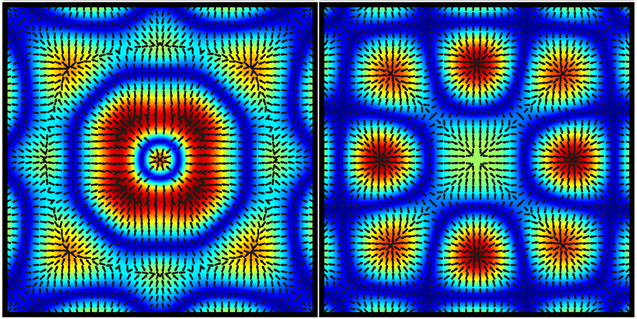
Resonance describes the phenomenon of increased amplitude that occurs when the frequency of a periodically applied force (or a Fourier component of it) is equal or close to a natural frequency of the system on which it acts. When an oscillating force is applied at a resonant frequency of a dynamic system, the system will oscillate at a higher amplitude than when the same force is applied at other, non-resonant frequencies.
Frequencies at which the response amplitude is a relative maximum are also known as resonant frequencies or resonance frequencies of the system.[3] Small periodic forces that are near a resonant frequency of the system have the ability to produce large amplitude oscillations in the system due to the storage of vibrational energy.
Resonance phenomena occur with all types of vibrations or waves: there is mechanical resonance, acoustic resonance, electromagnetic resonance, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), electron spin resonance (ESR) and resonance of quantum wave functions. Resonant systems can be used to generate vibrations of a specific frequency (e.g., musical instruments), or pick out specific frequencies from a complex vibration containing many frequencies (e.g., filters).
Other applications
In addition to common uses previously mentioned, FRET and BRET are also effective in the study of biochemical reaction kinetics. FRET is increasingly used for monitoring pH dependent assembly and disassembly and is valuable in the analysis of nucleic acids. This technique can be used to determine factors affecting various types of nanoparticle formation as well as the mechanisms and effects of nanomedicines.
Crystallography is the major method of determining structures of biological macromolecules yet crystallization techniques are still regarded as difficult to perform. This new edition of Crystallization of Nucleic Acids and Proteins: A Practical Approach continues in the vein of the first edition by providing a detailed and rational guide to producing crystals of proteins and nucleic acids of sufficient quantity and quality for diffraction studies. It has been thoroughly updated to include all the major new techniques such as the uses of molecular biology in structural biology (maximizing expression systems, sequence modifications to enable crystallization, and the introduction of anomalous scatterers); diagnostic analysis of prenucleation and nucleation by spectroscopic methods; and the two- dimensional electron crystallography of soluble proteins on planar lipid films.
As well as an introduction to crystallogenesis, the other topics covered are: Handling macromolecular solutions, experimental design, seeding, proceeding from solutions to crystals Crystallization in gels Crystallization of nucleic acid complexes and membrane proteins Soaking techniques Preliminary characterization of crystals in order to tell whether they are suitable for diffraction studies. As with all Practical Approach books the protocols have been written by experienced researchers and are tried an tested methods. The underlying theory is brought together with the laboratory protocols to provide researchers with the conceptual and methodological tools necessary to exploit these powerful techniques. Crystallization of Nucleic Acids and Proteins: A Practical Approach 2e will be an invaluable manual of practical crystallization methods to researchers in molecular biology, crystallography, protein engineering, and biological chemistry.
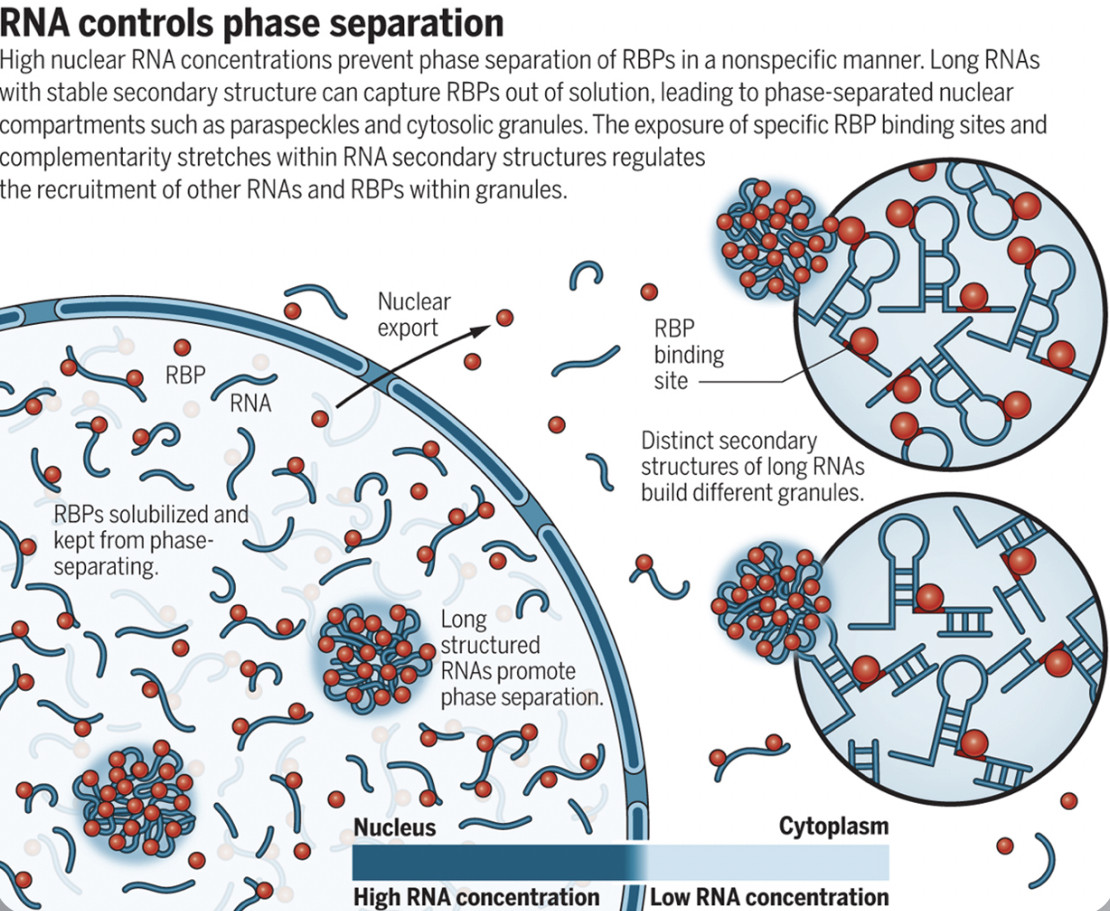
Proteins and RNAs inside the cell nucleus are organized into distinct phases, also known as liquid-liquid phase separated (LLPS) droplet organelles or nuclear bodies. These regions exist within the spaces between chromatin-rich regions but their function is tightly linked to gene activity.
The types of phase separation as a function of the dipolar interaction. By modifying the strength of the dipolar interaction, the types of phase separation undergo transitions from azimuthal (a) to inner-outer radial (b), and then to outer-inner radial (c) separation. Here the contact interactions are fixed at g = 5, g12 = 55, and the aspect ratio of the potential is λ = 100. The strengths of dipolar interaction are set as (a) εdd = 0, (b) εdd = −0.3 and (c) εdd = 0.2, respectively. The field of view in each panel is 6.4 × 6.4 in units of a0.
The direct dipole-dipole coupling is very useful for molecular structural studies, since it depends only on known physical constants and the inverse cube of internuclear distance. Estimation of this coupling provides a direct spectroscopic route to the distance between nuclei and hence the geometrical form of the molecule, or additionally also on intermolecular distances in the solid state leading to NMR crystallography notably in amorphous materials.
The residual dipolar coupling (RDC) occurs if the molecules in solution exhibit a partial alignment leading to an incomplete averaging of spatially anisotropic magnetic interactions i.e. dipolar couplings. RDC measurement provides information on the global folding of the protein-long distance structural information. It also provides information about "slow" dynamics in molecules.
Cut and paste RNA for nuclear magnetic resonance, paramagnetic resonance enhancement, and electron paramagnetic resonance structural studies - PubMed
RNA is a crucial regulator involved in most molecular processes of life. Understanding its function at the molecular level requires high-resolution structural information. However, the dynamic nature of RNA complicates structure determination because crystallization is often not possible or can resu..
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26577744/Current extraction methods often extract DNA and RNA separately, and few methods are capable of co-extracting DNA and RNA from sputum. We established a nucleic acid co-extraction method from sputum based on magnetic beads and optimized the method by evaluating influencing factors, such as the guanidinium thiocyanate (GTC) and dithiothreitol (DTT) concentrations, magnetic bead amount, incubation temperature, lysis buffer pH and RNA carrier type.
The feasibility of the simultaneous nucleic acid co-extraction method was evaluated by amplifying DNA and RNA viruses from a single clinical specimen with a multiplex RT-qPCR method. Both DNA and RNA were most efficiently extracted when the GTC and DTT concentrations were 2.0 M and 80 mM, respectively, 20 μl magnetic beads were added, the incubation temperature was 80 °C, the pH was 8 or 9, and RNA carrier A was used. Therefore, we established a simple method to extract nucleic acids from two important respiratory viruses compared with other commercial kits. This magnetic beads-based co-extraction method for sputum followed by a multiplex RT-qPCR can rapidly and precisely detect DNA and RNA viruses from a single clinical specimen and has many advantages, such as decreased time, low cost, and a lack of harmful chemicals.
The efficiency of delivery of DNA vaccines is often relatively low compared to protein vaccines. The use of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) to deliver genes via magnetofection shows promise in improving the efficiency of gene delivery both in vitro and in vivo.
Magnetofection is a transfection method that uses magnetic fields to concentrate particles containing vectors to target cells in the body. Magnetofection has been adapted to a variety of vectors, including nucleic acids, non-viral transfection systems, and viruses. This method offers advantages such as high transfection efficiency and biocompatibility which are balanced with limitations.
"particles containing vectors"
"Magnetofection has been adapted to a variety of vectors, including nucleic acids, non-viral transfection systems,
and viruses."
Through decades of research, biologists have determined that under the right conditions, viruses can assemble themselves from their constituent proteins.
Droplet microfluidics allows a higher degree of control over the crystallization conditions than conventional methodologies. To extend this approach, this work explores the synergistic effect of low-frequency pulsed ultrasound on lysozyme crystallization in microdroplets. Pulsed actuation allows control of the crystallization temperature, while the ultrasound effect significantly reduces the induction time and crystal size. Therefore, protein nucleation is enhanced by pulsed sonication without causing precipitation, resulting in uniform crystal size. Finally, the initial supersaturation ratio has a crucial contribution to the crystal size for silent experiments, while a threshold for induction time is observed in ultrasonic crystallization.
Phased Array is an ultrasonic testing technique that uses specialized multi-element “array” transducers and pulses those elements separately in a patterned sequence called “phasing”. This phasing sequence allows wave steering, focusing, and scanning. This is all performed electronically.
phasing
present participle of phase
Noun
phasing (plural phasings)
Movement through phases; arrangement of a sequence or cycle.
A codon is a sequence of three DNA or RNA nucleotides that corresponds with a specific amino acid or stop signal during protein synthesis. The genetic code includes 64 possible permutations, or combinations, of three-letter nucleotide sequences that can be made from the four nucleotides.
Protein synthesis is the process in which cells make proteins. It occurs in two stages: transcription and translation. Transcription is the transfer of genetic instructions in DNA to mRNA in the nucleus. It includes three steps: initiation, elongation, and termination.
Self-assembly of proteins holds great promise for the bottom-up design and production of synthetic biomaterials. In conventional approaches, designer proteins are pre-programmed with specific recognition sites that drive the association process towards a desired organized state. Although proven effective, this approach poses restrictions on the complexity and material properties of the end-state. An alternative, hierarchical approach that has found wide adoption for inorganic systems, relies on the production of crystalline nanoparticles that become the building blocks of a next-level assembly process driven by oriented attachment (OA).
As it stands, OA has not yet been observed for protein systems. Here we employ cryo-transmission electron microscopy (cryoEM) in the high nucleation rate limit of protein crystals and map the self-assembly route at molecular resolution. We observe the initial formation of facetted nanocrystals that merge lattices by means of OA alignment well before contact is made, satisfying non-trivial symmetry rules in the process. As these nanocrystalline assemblies grow larger we witness imperfect docking events leading to oriented aggregation into mesocrystalline assemblies. These observations highlight the underappreciated role of the interaction between crystalline nuclei, and the impact of OA on the crystallization process of proteins.
Nucleation is the first step in the formation of either a new thermodynamic phase or a new structure via self-assembly or self-organization. Nucleation is typically defined to be the process that determines how long an observer has to wait before the new phase or self-organized structure appears.
For example, if a volume of water is cooled (at atmospheric pressure) below 0 °C, it will tend to freeze into ice, but volumes of water cooled only a few degrees below 0 °C often stay completely free of ice for long periods. At these conditions, nucleation of ice is either slow or does not occur at all. However, at lower temperatures ice crystals appear after little or no delay. At these conditions ice nucleation is fast.[1][2] Nucleation is commonly how first-order phase transitions start, and then it is the start of the process of forming a new thermodynamic phase. In contrast, new phases at continuous phase transitions start to form immediately.
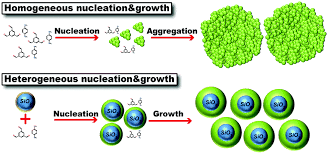
Nucleation is often found to be very sensitive to impurities in the system. These impurities may be too small to be seen by the naked eye, but still can control the rate of nucleation. Because of this, it is often important to distinguish between heterogeneous nucleation and homogeneous nucleation. Heterogeneous nucleation occurs at nucleation sites on surfaces in the system.[1] Homogeneous nucleation occurs away from a surface.
In many cases, liquids and solutions can be cooled down or concentrated up to conditions where the liquid or solution is significantly less thermodynamically stable than the crystal, but where no crystals will form for minutes, hours, weeks or longer. Nucleation of the crystal is then being prevented by a substantial barrier. This has consequences, for example cold high altitude clouds may contain large numbers of small liquid water droplets that are far below 0 °C.
In small volumes, such as in small droplets, only one nucleation event may be needed for crystallisation. In these small volumes, the time until the first crystal appears is usually defined to be the nucleation time.[3] Visualization of the initial stage of crystal nucleation of sodium chloride was achieved through atomic-resolution real-time video imaging.[10] Calcium carbonate crystal nucleation depends not only on degree of supersaturation but also the ratio of calcium to carbonate ions in aqueous solutions.[11] In larger volumes many nucleation events will occur. A simple model for crystallisation in that case, that combines nucleation and growth is the KJMA or Avrami model.
The time until the appearance of the first crystal is also called primary nucleation time, to distinguish it from secondary nucleation times. Primary here refers to the first nucleus to form, while secondary nuclei are crystal nuclei produced from a preexisting crystal. Primary nucleation describes the transition to a new phase that does not rely on the new phase already being present, either because it is the very first nucleus of that phase to form, or because the nucleus forms far from any pre-existing piece of the new phase. Particularly in the study of crystallisation, secondary nucleation can be important. This is the formation of nuclei of a new crystal directly caused by pre-existing crystals.
Here, the constructed lipid-based liquid crystalline nanoparticles, called nano-Transformers, can transform thestructure in the intracellular acidic environment and perform high-efficient siRNA delivery for cancer treatment. The developed nano-Transformers have satisfactory siRNA loading efficiency and
low cytotoxicity.?
odd
/ɒd/
adjective: odd; comparative adjective: odder; superlative adjective: oddest
1.
different to what is usual or expected; strange.
(of whole numbers such as 3 and 5) having one left over as a remainder when divided by two.
"atoms which possess an odd number of electrons"
Similar:
uneven
not divisible by two
Odin (/ˈoʊdɪn/; from Old Norse: Óðinn, IPA: [ˈoːðenː]) is a widely revered god in Germanic mythology. Norse mythology, the source of most surviving information about him, associates him with wisdom, healing, death, royalty, the gallows, knowledge, war, battle, victory, sorcery, poetry, frenzy, and the runic alphabet, and depicts him as the husband of the goddess Frigg. In wider Germanic mythology and paganism, the god was known in Old English as Wōden, in Old Saxon as Wōdan, in Old Dutch as Wuodan, and in Old High German as Wuotan, all ultimately stemming from the Proto-Germanic theonym *Wōđanaz, meaning 'lord of frenzy', or 'leader of the possessed'.
The figure of Odin is a frequent subject of interest in Germanic studies, and scholars have advanced numerous theories regarding his development. Some of these focus on Odin's particular relation to other figures; for example, Freyja's husband Óðr appears to be something of an etymological doublet of the god, while Odin's wife Frigg is in many ways similar to Freyja, and Odin has a particular relation to Loki.