"to make vaccines and the temperature-controlled supply chains needed to deliver them"
This paper describes the design and operation of a system used for the accurate control and measurement of temperature in micro-fluidic channels. Ultrasonic transducers are used for both heating and measuring the temperature of fluids inside the channel. Heating is performed by exciting the transducer with a tone burst at a single frequency...
"to improve uptake”
With this technique, the uptake of MNPs in cells can be imaged and quantified directly from the first MNP cell contact, providing information on the dynamics of cellular uptake.
"We focus on better service delivery,”
Focused ultrasound is an early-stage, non-invasive therapeutic technology with the potential to transform the treatment of many medical disorders by using ultrasonic energy to target tissue deep in the body without incisions or radiation.
"transitioning from donor funding in order to sustain the gains"
FRET is the radiationless transmission of energy from a donor molecule to an acceptor molecule. The donor molecule is the dye or chromophore that initially absorbs the energy and the acceptor is the chromophore to which the energy is subsequently transferred.
The gain of electrons is called reduction. Because any loss of electrons by one substance must be accompanied by a gain in electrons by something else, oxidation and reduction always occur together. As such, electron-transfer reactions are also called oxidation-reduction reactions, or simply redox reactions.
The unpaired electron in free radicals makes the atom or molecule unstable. Electrons in atoms "hate" not existing in pairs. An atom with an unpaired electron (a free radical) wants to become stable again, so it quickly seeks out another electron to "steal" from another atom or molecule.
Oxidative stress is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in your body.
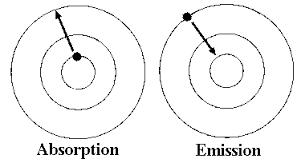
An atom changes from a ground state to an excited state by taking on energy from its surroundings in a process called absorption. The electron absorbs the energy and jumps to a higher energy level. In the reverse process, emission, the electron returns to the ground state by releasing the extra energy it absorbed.