Near-infrared (NIR) dye-sensitized upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) can broaden the absorption range and boost upconversion efficiency of UCNPs. Here, we achieved significantly enhanced upconversion luminescence in dye-sensitized core/active shell UCNPs via the doping of ytterbium ions (Yb3+) in the UCNP shell, which bridged the energy transfer from the dye to the UCNP core. As a result, we synergized the two most practical upconversion booster effectors (dye-sensitizing and core/shell enhancement) to amplify upconversion efficiency. We demonstrated two biomedical applications using these UCNPs. By using dye-sensitized core/active shell UCNP embedded poly(methyl methacrylate) polymer implantable systems, we successfully shifted the optogenetic neuron excitation window to a biocompatible and deep tissue penetrable 800 nm wavelength. Furthermore, UCNPs were water-solubilized with Pluronic F127 with high upconversion efficiency and can be imaged in a mouse model.
so.. what technology operates an 800 nm frequency?
The organic terahertz (THz) generation crystal BNA has recently gained traction as a valuable source to produce broadband THz pulses. Even when pumped with 800-nm light, thin BNA crystals can produce relatively high electric fields with frequency components out to 5 THz. However, the THz output when pumped with 800-nm light is limited by the damage threshold of the organic crystal. Here we report that the damage threshold of BNA can be significantly improved by physically bonding BNA to a high-thermal conductivity sapphire window.
When pumped with 800-nm light from an amplified Ti:sapphire laser system, our bonded BNA (BNA-sapphire) generates 2.5 times higher electric field strengths compared to bare BNA crystals. We characterize the average damage threshold for bare BNA and BNA-sapphire, measure peak-to-peak electric field strengths and THz waveforms, and determine the nonlinear transmission in BNA. Pumping BNA-sapphire with 800-nm light results in peak-to-peak electric fields exceeding 1 MV/cm, with strong broadband frequency components from 0.5-5 THz. Our BNA-sapphire THz source is a promising alternative to tilted pulse front LiNbO3 THz sources, which will enable many research groups without optical parametric amplifiers to perform high-field, broadband THz spectroscopy.
BROADBAND TERAHERTZ CONCENTRATORS
To enable the performance of THz spectroscopy on subwavelength samples one needs to concentrate the electromagnetic field in a small volume compared to the wavelength. Such confinement has been a subject of interest in the THz community.
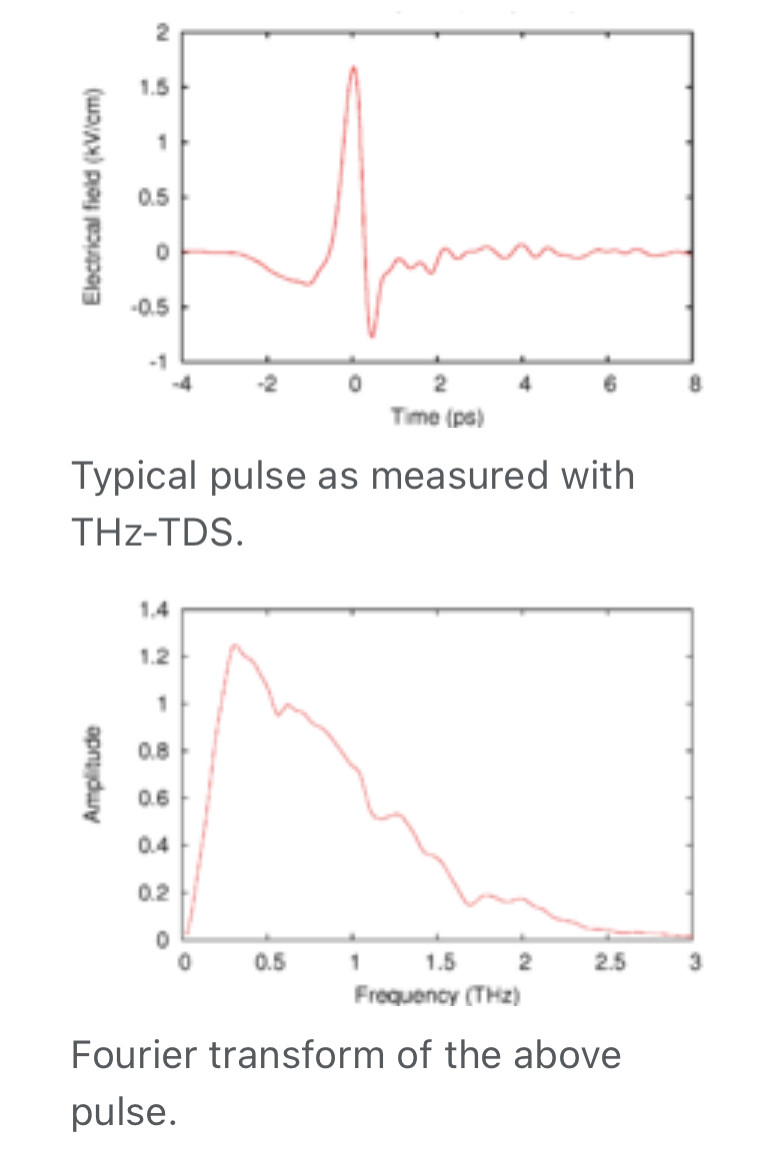
In physics, terahertz time-domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS) is a spectroscopic technique in which the properties of matter are probed with short pulses of terahertz radiation. The generation and detection scheme is sensitive to the sample's effect on both the amplitude and the phase of the terahertz radiation. By measuring in the time-domain, the technique can provide more information than conventional Fourier-transform spectroscopy, which is only sensitive to the amplitude.
Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy) is the spectroscopy that deals with the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum, that is light with a longer wavelength and lower frequency than visible light. It covers a range of techniques, mostly based on absorption spectroscopy.
Gold nanoparticles absorb and scatter light with extraordinary efficiency. Their strong interaction with light occurs because the conduction electrons on the metal surface undergo a collective oscillation when they are excited by light at specific wavelengths.
Near-infrared (NIR) luminescent quantum dots (QDs) have been studied very intensively. These QDs have excellent optical properties. Their emitting wavelength can be adjusted by their size and composition, and falls in the telecommunication window, making these QDs promising materials for telecommunication.
ok. I'm following.. what i like that I've read is that the bna crystals can be damaged even tho they have the "sapphire shell". it's been measured, but i bet they don't list either damage threshold. Matalo (kill it!) is it plausible to damage the armored bna without damaging the host body? sonic or light frequencies in excess?
overload the tech with too much input. another thought to consider though - what happens to the shattered crystals after neutralization? exit the body as waste eventually, or would the waste clog essential organ or vascular function?
since it is tech, how does it respond to magnetism? would one be able to centralize the bna waste with electromagnetism? since i just mentioned electricity, would electro shock therapy damage bna?
I like your thinking. 👍🏻
Plasmon-enhanced upconversion photoluminescence: Mechanism and application - ScienceDirect
The enhanced local electromagnetic field (EM) excited on the noble metallic nanostructure exhibits potential application in various areas, particularl…
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405428318300030Quenching refers to any process which decreases the fluorescence intensity of a given substance. A variety of processes can result in quenching, such as excited state reactions, energy transfer, complex-formation and collisional quenching
Sonication is widely used in the laboratory to disperse nanotubes into the polymer matrix. This process utilizes ultrasound energy to agitate nanoparticles in the polymer matrix. It is usually carried out by an ultrasonic bath or a horn/probe which is also known as the sonicator.
Squarewave frequency modulation is the pulse equivalent of sinewave frequency modulation (FM) and is closely related to PFM. It consists essentially of a series of squarewave edge transitions occurring at sinewave FM zero crossing points...
Magnetic dipole interactions. ... However, nanoparticles of ferromagnetic and ferrimagnetic materials with dimensions around 10 nm can have magnetic moments larger than 10,000 Bohr magnetons, and therefore, dipole interactions between nanoparticles can have a significant influence on the magnetic properties.
The assembly of tiny magnetic particles in external magnetic fields is important for many applications ranging from data storage to medical technologies. The development of ever smaller magnetic structures is restricted by a size limit, where the particles are just barely magnetic. For such particles we report the discovery of a kind of solution assembly hitherto unobserved, to our knowledge. The fact that the assembly occurs in solution is very relevant for applications, where magnetic nanoparticles are either solution- processed or are used in liquid biological environments. Induced by an external magnetic field, nanocubes spontaneously assemble into 1D chains, 2D monolayer sheets, and large 3D cuboids with almost perfect internal ordering.
The self-assembly of the nanocubes can be elucidated considering the dipole–dipole interaction of small superparamagnetic particles. Complex 3D geometrical arrangements of the nanodipoles are obtained under the assumption that the orientation of magnetization is freely adjustable within the super- lattice and tends to minimize the binding energy. On that basis the magnetic moment of the cuboids can be explained.
Superparamagnetism is a form of magnetism which appears in small ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic nanoparticles. In sufficiently small nanoparticles, magnetization can randomly flip direction under the influence of temperature. The typical time between two flips is called the Néel relaxation time. In the absence of an external magnetic field, when the time used to measure the magnetization of the nanoparticles is much longer than the Néel relaxation time, their magnetization appears to be in average zero; they are said to be in the superparamagnetic state. In this state, an external magnetic field is able to magnetize the nanoparticles, similarly to a paramagnet. However, their magnetic susceptibility is much larger than that of paramagnets.
Néel relaxation theory is a theory developed by Louis Néel in 1949[1] to explain time-dependent magnetic phenomena known as magnetic viscosity. It is also called Néel-Arrhenius theory, after the Arrhenius equation, and Néel-Brown theory after a more rigorous derivation by William Fuller Brown, Jr.[2] Néel used his theory to develop a model of thermoremanent magnetization in single-domain ferromagnetic minerals that explained how these minerals could reliably record the geomagnetic field. He also modeled frequency-dependent susceptibility and alternating field demagnetization.
Alternating Field Demagnetization
Demagnetization consists of applying a decaying alternating magnetic field to a sample. ... In this way, equal numbers of domains will be magnetized in the positive and negative directions oriented along the axis of demagnetization, resulting in a net zero remanent field on the sample.
God bless you all.