So basically anyone can steal an election, cause a nanoparticle pandemic, start a war or even put everyone under mind control using vaccines and the justice sytem will just ignore the truth, cover up the facts and turn a blind eye.
G I U S T I F I C A Z I O N I S T I C H E
Borrowed from Late Latin iustificationem, justificationem < iustificatio, from iustifico, from Latin iustus.
Noun
giustificazione f (plural giustificazioni)
justification, explanation
proof
Together as one
just us.
US ultrasound
justifiable
/ˈdʒʌstɪˌfʌɪəb(ə)l/
adjective
able to be shown to be right or reasonable; defensible.
deafening
/ˈdɛf(ə)nɪŋ/
(of a noise) so loud as to make it impossible to hear anything else.
"the music reached a deafening crescendo"
A CRESCENDO
verb: crescendo; 3rd person present: crescendoes; past tense: crescendoed; past participle: crescendoed; gerund or present participle: crescendoing
increase in loudness or intensity.
"the reluctant cheers began to crescendo"
late 18th century: Italian, present participle of crescere ‘to increase’, from Latin crescere ‘grow’.
From Middle English encresing, equivalent to increase + -ing.
Noun
increasing (plural increasings)
(knitting) An increase.
A N E N C R E S I N G
resing (third-person singular simple present resings, present participle resinging, simple past resang, past participle resung)
To sing again.
reasonable
/ˈriːz(ə)nəb(ə)l/
adjective
1.
having sound judgement; fair and sensible.
justified; past participle: justified
1.
show or prove to be right or reasonable.
Noun. 1. sound judgement - the capacity to assess situations or circumstances shrewdly and to draw sound conclusions. sound judgment, perspicacity, judgement, judgment. trait - a distinguishing feature of your personal nature.
From Middle English juste, from Old French juste, from Latin iūstus (“just, lawful, rightful, true, due, proper, moderate”), from Proto-Italic *jowestos, related to Latin iūs (“law, right”); ultimately from Proto-Indo-European *h₂yew-. Compare Scots juist (“just”), Saterland Frisian juust (“just”), West Frisian just (“just”), Dutch juist (“just”), German Low German jüst (“jüst”), German just (“just”), Danish just (“just”), Swedish just (“just”). Doublet of giusto.
Alternative forms
jes, jes', jest, jist, jus'
Adjective
just (comparative juster or more just, superlative justest or most just)
Factually right, correct; factual.
It is a just assessment of the facts.
Rationally right, correct.
Morally right; upright, righteous, equitable; fair.
It looks like a just solution at first glance.
Proper, adequate.
Synonyms
right, correct
righteous, equitable
proper, adequate
Antonyms
unjust
Derived terms
justly
justness
sleep of the just
Related terms
From Middle English justice, from Old French justise, justice (Modern French justice), from Latin iūstitia (“righteousness, equity”), from iūstus (“just”), from iūs (“right”), from Proto-Italic *jowos, perhaps literally "sacred formula", a word peculiar to Latin (not general Italic) that originated in the religious cults, from Proto-Indo-European *h₂yew-. Doublet of Justitia.
Displaced native Middle English rightwished, rightwisnes (“justice”) (from Old English rihtwīsnes (“justice, righteousness”), compare Old English ġerihte (“justice”)).
righteousness (countable and uncountable, plural righteousnesses)
(uncountable) The quality or state of being righteous.
(uncountable, theology) Holiness; conformity of life to the divine law.
Synonyms: rectitude, uprightness, holiness, godliness, equity, justice, rightfulness, integrity, honesty, faithfulness
The act or conduct of one who is righteous.
(theology) The state of being right with God;
justification; the work of Christ, which is the ground justification.
uprighteousness (uncountable)
Quality of being uprighteous.
uprighteous (comparative more uprighteous, superlative most uprighteous)
Righteous.
Related terms
upright
upright (comparative more upright, superlative most upright)
Vertical; erect.
resurrect (third-person singular simple present resurrects, present participle resurrecting, simple past and past participle resurrected)
(transitive) To raise from the dead, to bring life back to.
Synonym: revive
(transitive) To restore to a working state.
(transitive) To bring back to view or attention; reinstate.
reinstate (third-person singular simple present reinstates, present participle reinstating, simple past and past participle reinstated)
(transitive) To restore to a former position or rank.
(transitive) To bring back into use or existence; resurrect.
reinstatement (countable and uncountable, plural reinstatements)
The act of restoring something to its previous state.
restoring
present participle of restore
toring (plural torings)
tower
tower (third-person singular simple present towers, present participle towering, simple past and past participle towered)
(intransitive) To be very tall.
The office block towered into the sky.
(intransitive) To be high or lofty; to soar.
(obsolete, transitive) To soar into.
soar (third-person singular simple present soars, present participle soaring, simple past and past participle soared)
(intransitive) To fly high with little effort, like a bird.
To mount upward on wings, or as on wings.
To remain aloft by means of a glider or other unpowered aircraft.
To rise, especially rapidly or unusually high.
The pump prices soared into new heights as the strike continued.
(figuratively) To rise in thought, spirits, or imagination; to be exalted in mood.
AN IMAGINATION
AS JUSTIFICATION
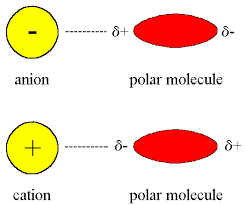
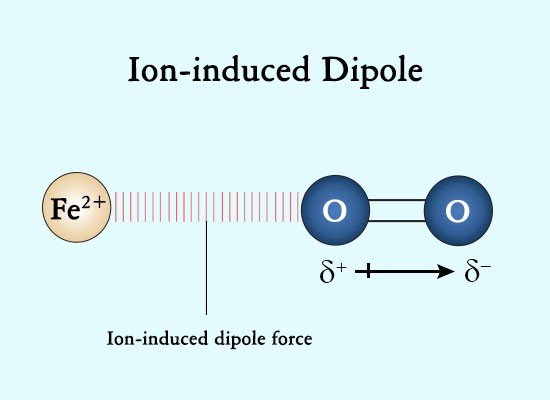
cation
/ˈkatʌɪən/
nounCHEMISTRY
noun: cation; plural noun: cations
a positively charged ion, i.e. one that would be attracted to the cathode in electrolysis
mid 19th century: from cata- ‘alongside’ or from cathode, + ion.
An ion is a charged atom or molecule. It is charged because the number of electrons do not equal the number of protons in the atom or molecule. ... When an atom is attracted to another atom because it has an unequal number of electrons and protons, the atom is called an ION.
Positively charged ions are called cations; negatively charged ions, anions.
Etymology
Borrowed from Vulgar Latin *fēdes, from Latin fidēs.
Pronunciation
IPA(key): /fɛ/
Noun
fe f (indefinite plural fe, definite singular feja, definite plural fetë)
religion
fidēs f (genitive fideī); fifth declension
faith, belief (belief without empirical evidence, direct experience, or observation)
reliance (act of relying (on) or trusting)
confidence, trust (confidence in or reliance on some person or quality)
credit (acceptance of the truth of something said or done)
loyalty, fidelity, faith (state of demonstrating undivided and constant support for someone or something)
good faith (good, honest intentions)
honesty (act, quality, or condition of being honest)
guarantee, promise (an assurance of something to be done)
help, assistance
"the output is left-justified"
adjust
/əˈdʒʌst/
verb: adjust; 3rd person present: adjusts; past tense: adjusted; past participle: adjusted; gerund or present participle: adjusting
1.
alter or move (something) slightly in order to achieve the desired fit, appearance, or result.
result (third-person singular simple present results, present participle resulting, simple past and past participle resulted) (intransitive)
To proceed, spring up or rise, as a consequence, from facts, arguments, premises, combination of circumstances, consultation, thought or endeavor.
(intransitive, followed by "in") To have as a consequence; to lead to; to bring about
This measure will result in good or in evil.
(law) To return to the proprietor (or heirs) after a reversion.
(obsolete) To leap back; to rebound.
Synonyms
(to proceed, spring, or rise, as a consequence): follow, arise
Related terms
resultant
resile
resilient
resilience
AS A CONSEQUENCE
AC
ON
SEQUENCE
a repetition of a phrase or melody at a higher or lower pitch.
"a restless search for interesting harmonic sequences"
BIOCHEMISTRY
the order in which amino-acid or nucleotide residues are arranged in a protein, DNA, etc.
"these are enzymes which will cleave only at specific base sequences in the DNA"
A key sequence, or key for short, is a sequence of one or more input events that form a unit. Input events include characters, function keys, mouse actions, or system events external to Emacs, such as iconify-frame (see Input Events).
The SAW RFID system is suited for high operating temperatures as it is purely based on piezoelectricity and therefore fully passive. ... A high-frequency electromagnetic (EM) interrogation signal is picked up by the antenna of the passive SAW device and conducted to a transducer.
QSI Telegram, learning about Quantum Stellar Financial System, Medbeds, Liberty/Freedom, Checks and Balances, disclosure, Ascension,💜♾️
-schizophrenia with persistent but non-progressive negative symptoms in the intervals between psychotic episodes connected such types of paraphilias, as pedophilia, exhibitionism, visionism.
by K Jordan · 2020 · Cited by 6 — Biological Underpinnings of Pedophilia and Child Sexual Offending—The Current ... MPAs and several neuropsychiatric disorders, such as autism and schizophrenia (31, 32).
The adrenochrome theory of schizophrenia waned, despite some evidence that it may be psychotomimetic, as adrenochrome was not detectable in people with schizophrenia.[citation needed]
In the early 2000s, interest was renewed by the discovery that adrenochrome may be produced normally as an intermediate in the formation of neuromelanin. This finding may be significant because adrenochrome is detoxified at least partially by glutathione-S-transferase. Some studies have found genetic defects in the gene for this enzyme.
Glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) quench reactive molecules with the addition of glutathione (GSH) and protect the cell from oxidative damage.
Oxidative stress and inflammation are intertwined processes that play roles in disease progression and response to therapy via interference with multiple signaling pathways. The redox status of a host cell is an important factor in viral entry due to the unique conditions required for the conformational changes that ensure the binding and entry of a virus into the host cell. Upon entry into the airways, viral replication occurs and the innate immune system responds by activating macrophage and dendritic cells which contribute to inflammation. This review examines available literature and proposes mechanisms by which oxidative stress and inflammation could contribute to COVID-19 pathogenesis. Further, certain antioxidants currently undergoing some form of trial in COVID-19 patients and the corresponding required research gaps are highlighted to show how targeting oxidative stress and inflammation could ameliorate COVID-19 severity.
Oxidative Stress in Schizophrenia
Increasing evidence indicates that oxidative damage exists in schizophrenia. Available literature about possible mechanisms of oxidative stress induction was reviewed. Furthermore, possibilities of measuring biomarkers of schizophrenia outside the central ...
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3131721/Oxidative stress in autism - ScienceDirect
Autism is a severe developmental disorder with poorly understood etiology. Oxidative stress in autism has been studied at the membrane level and also …
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0928468006000538Oxidative stress plays a critical role in nanotoxicity. Various types of nanoparticles are known to induce oxidative stress by generating intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS). ... Besides, ROS generation can result from interactions of nanoparticles and cells that lead to mitochondrial dysfunction.
Acquired conditions in which mitochondrial dysfunction has been involved are:
diabetes
Huntington's disease
cancer
Alzheimer's disease
Parkinson's disease
bipolar disorder,[1][2][3] schizophrenia, aging and senescence, anxiety disorders[4]
cardiovascular disease
sarcopenia
chronic fatigue syndrome[2]
"Oxidative stress and inflammation are intertwined processes"
25 Jun 2021 — FDA adds warning to COVID vaccine fact sheets about rare heart inflammation
In January 2018, the WHO produces a document on how to catalog the adverse reactions that are indicated by the acronym AEFI. The WHO states: “Causality assessment is the systematic review of data about an AEFI case; it aims to determine the likelihood of a causal association between the event and the vaccine(s) received” [50]. It also specifies: “At the individual level it is usually not possible to establish a definite causal relationship between a particular AEFI and a particular vaccine on the basis of a single AEFI case report” [50]. Since all adverse reactions are case reports (because they occur in a single vaccinated individual), excluding them results in the consequent elimination of all post-vaccine AEs. Furthermore, the report cases form the series of reports that will never exist with this evaluation system that excludes the individual case reports.
A practical example shows that the reports of AEs do not end up on the reports of the regulatory agencies. These are two cases of transient neutropenia from MMRV vaccines (Measles, Mumps, Rubeola and Varicella) that have been published [51] after reporting to the Italian Medicines Agency [52], but it do not appear in the Agency Report [53].
Taking as an example a vaccine widely used in Europe [54], we immediately notice that the adverse reactions are cataloged reporting the frequency of the single symptom, but there are no data on the combination of reactions in the same subject (GSK, 2018). Infanrix Hexa is indicated for primary and booster vaccination of infants and toddlers against diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, hepatitis B, poliomyelitis and disease caused by Haemophilus influenzae type b. The following drug-related reported adverse reactions in clinical studies (data from more than 16,000 subjects) and during post-marketing surveillance (GSK, 2018).
Very Common Adverse Events (≥ 1/10 doses)
Appetite lost.
Crying abnormal and pain.
Irritability.
Fever ≥ 38°C.
The presence of all these symptoms in the same subject suggests a post-vaccination reactive brain inflammation produced by proinflammatory cytokines, secreted after vaccine injection
Chelation /ˈkiːˌleɪˈʃən/ is a type of bonding of ions and molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central atom.[1][2] These ligands are called chelants, chelators, chelating agents, or sequestering agents. They are usually organic compounds, but this is not a necessity, as in the case of zinc and its use as a maintenance therapy to prevent the absorption of copper in people with Wilson's disease.[3]
Chelation is useful in applications such as providing nutritional supplements, in chelation therapy to remove toxic metals from the body, as contrast agents in MRI scanning, in manufacturing using homogeneous catalysts, in chemical water treatment to assist in the removal of metals, and in fertilizers.
Neuromelanin is found in higher concentrations in humans than in other primates.[2] Neuromelanin concentration increases with age, suggesting a role in neuroprotection (neuromelanin can chelate metals and xenobiotics[6]) or senescence.