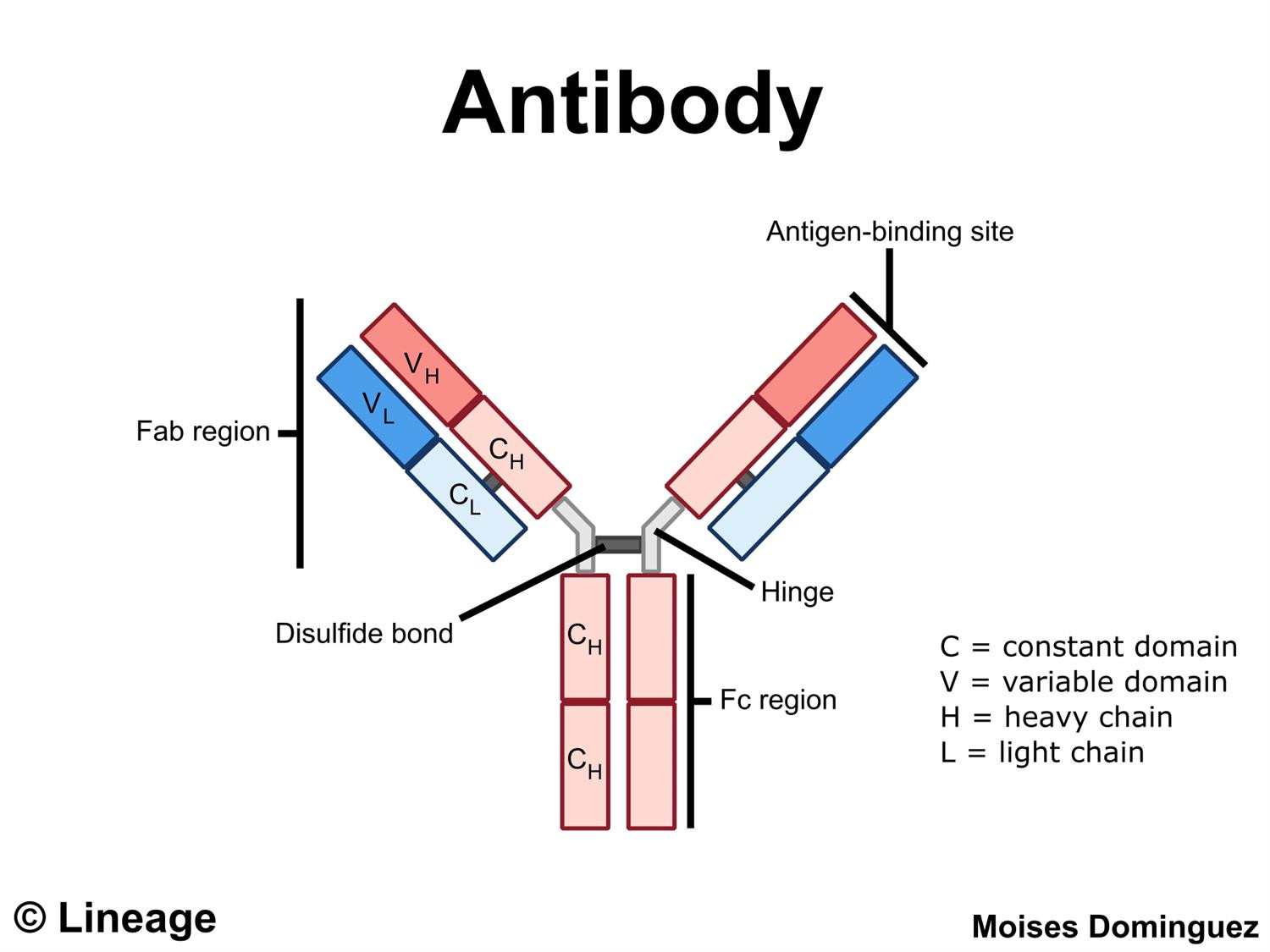
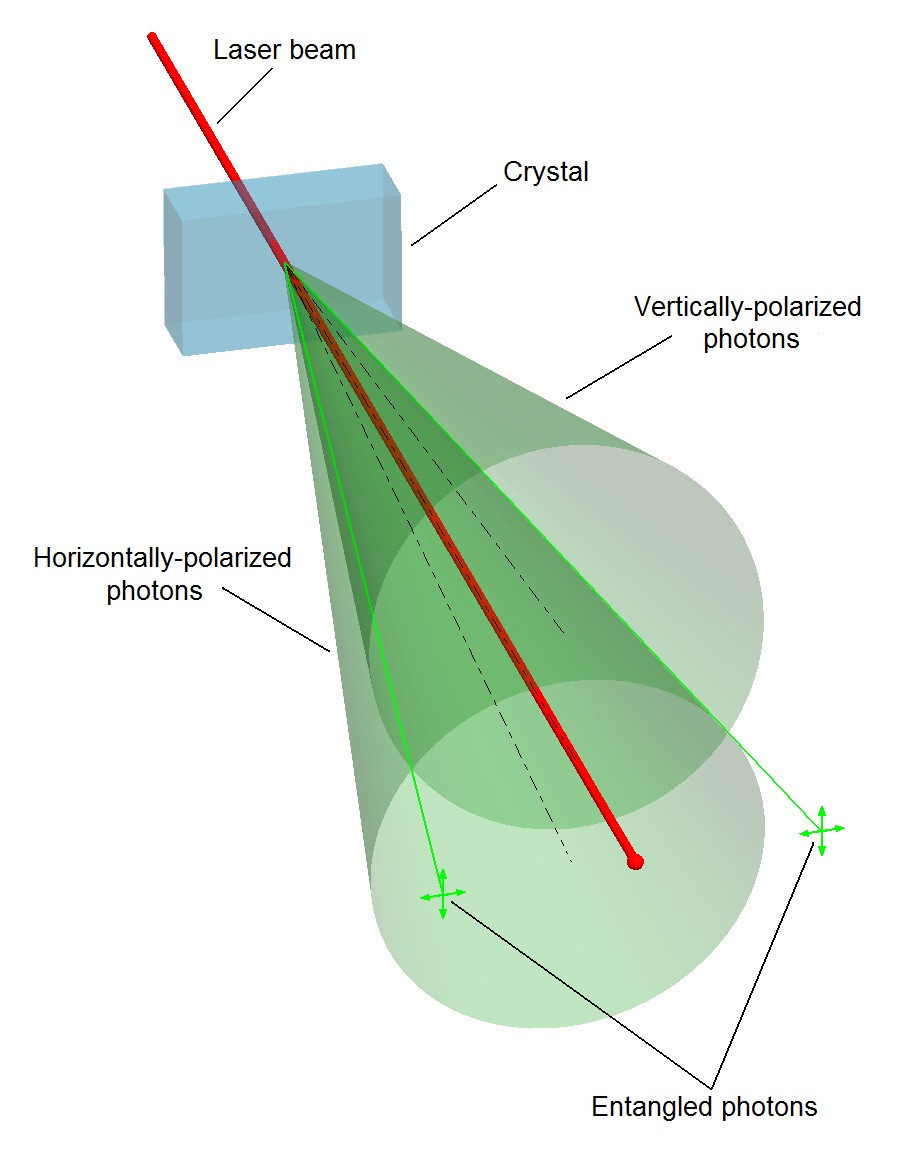
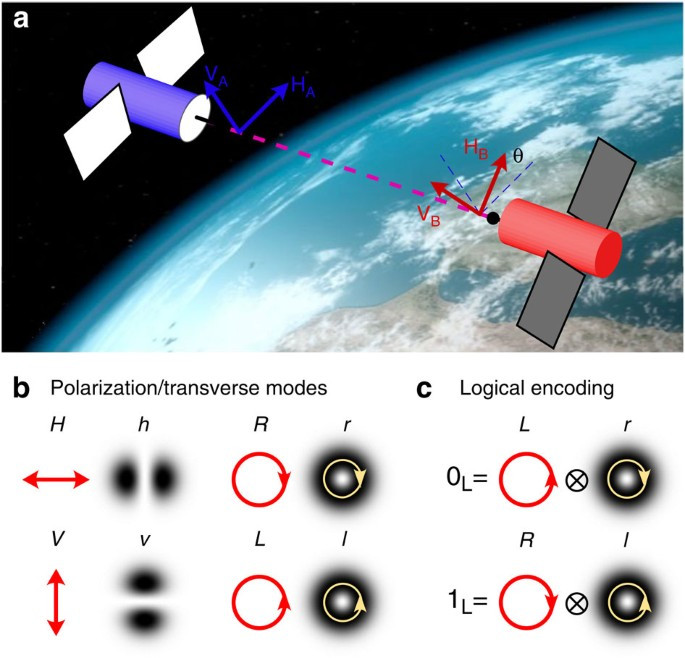
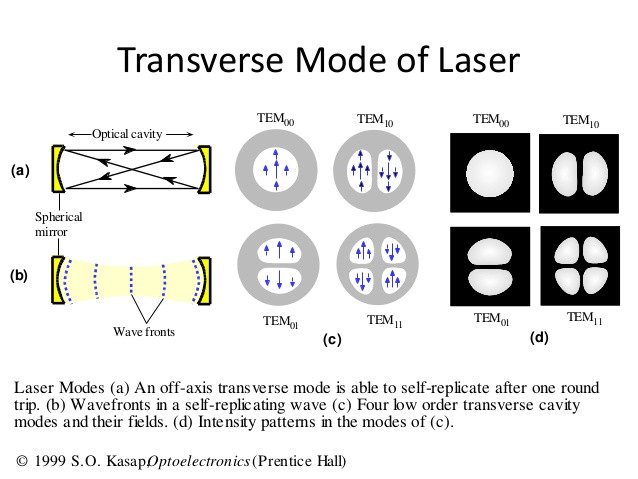
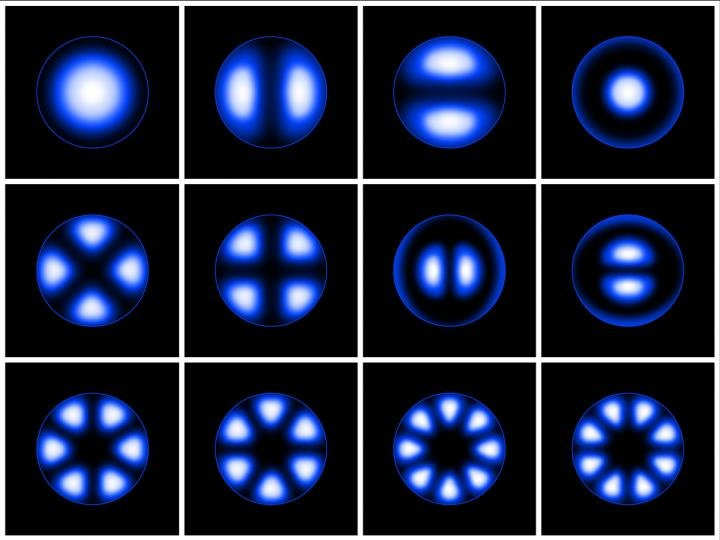
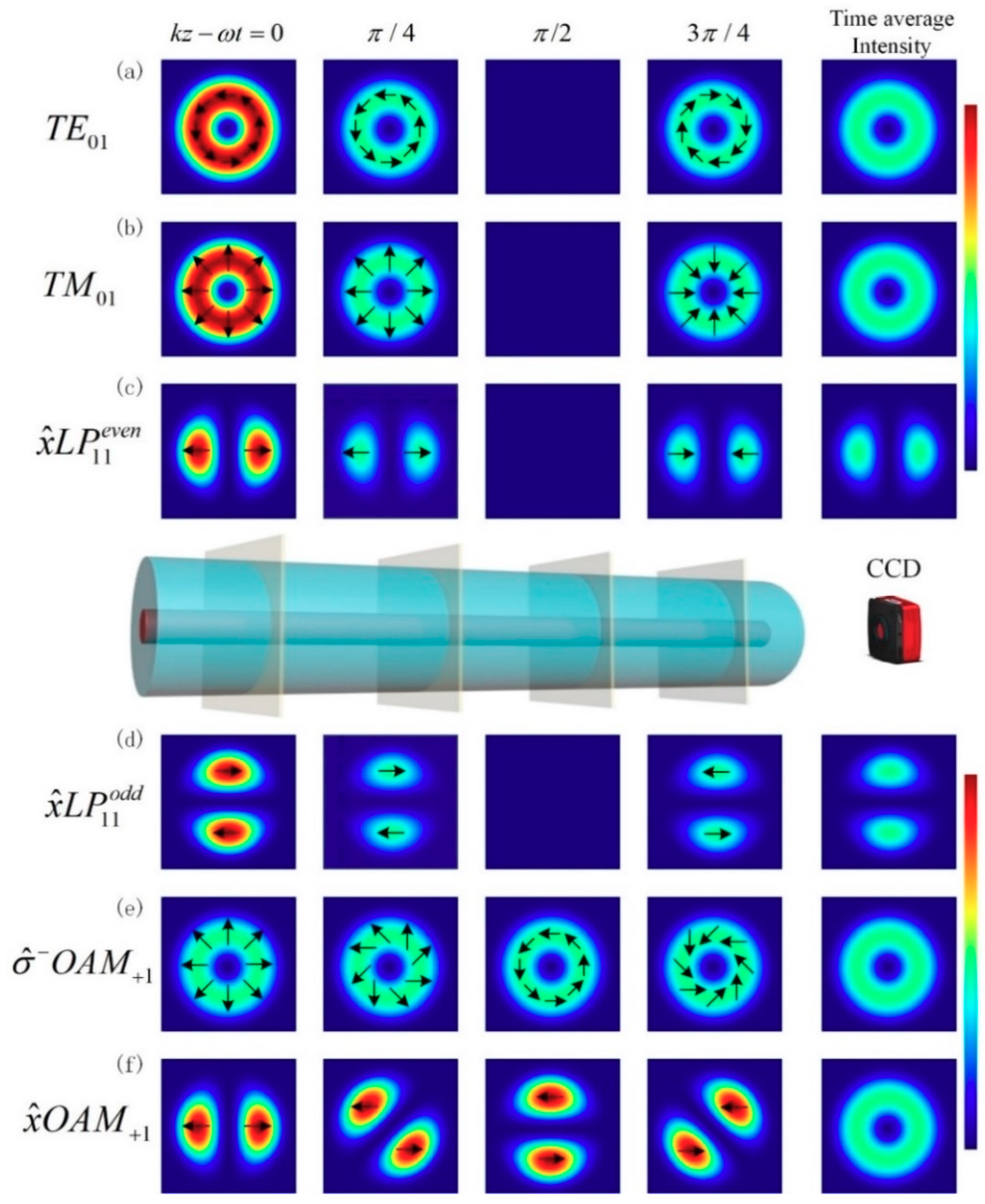
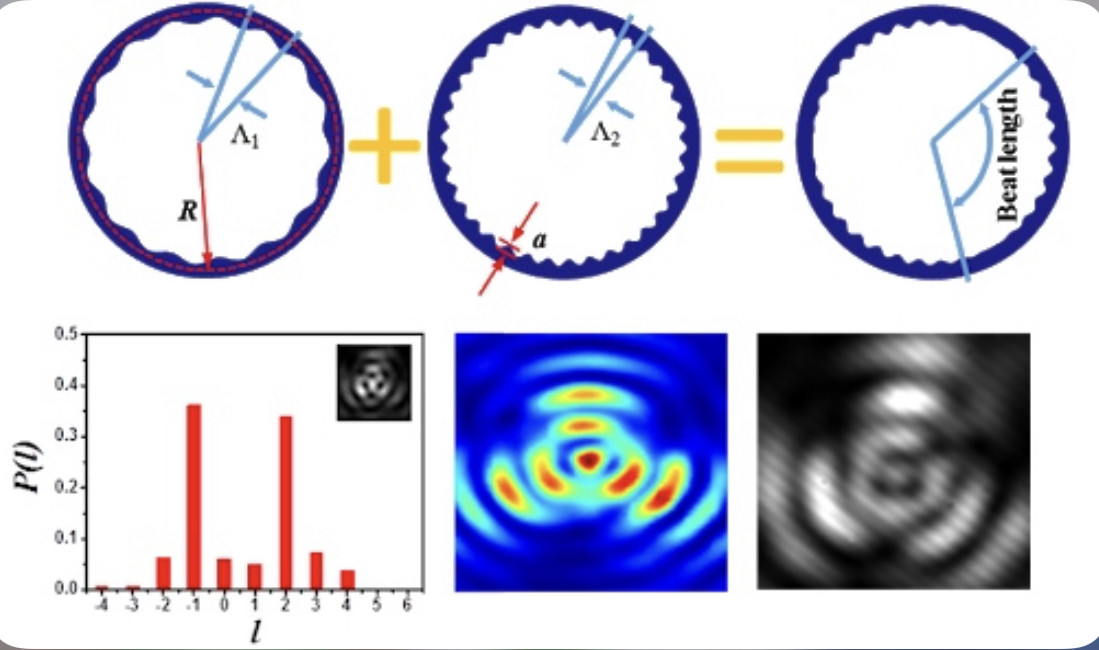
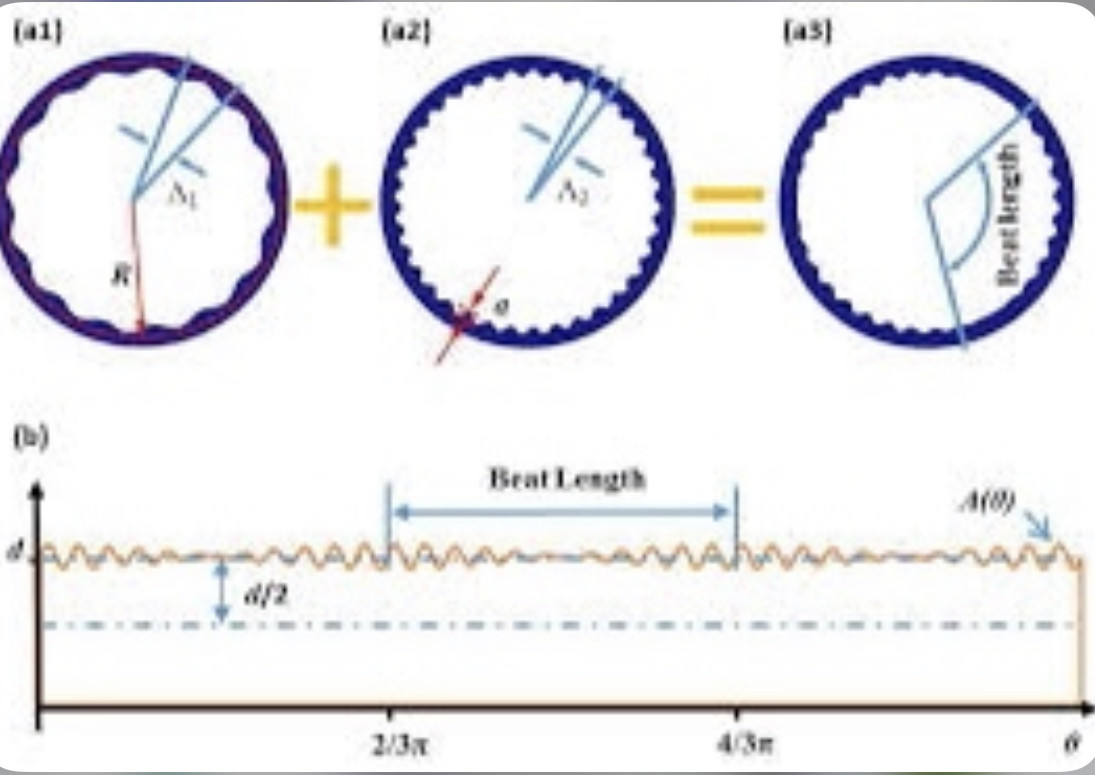
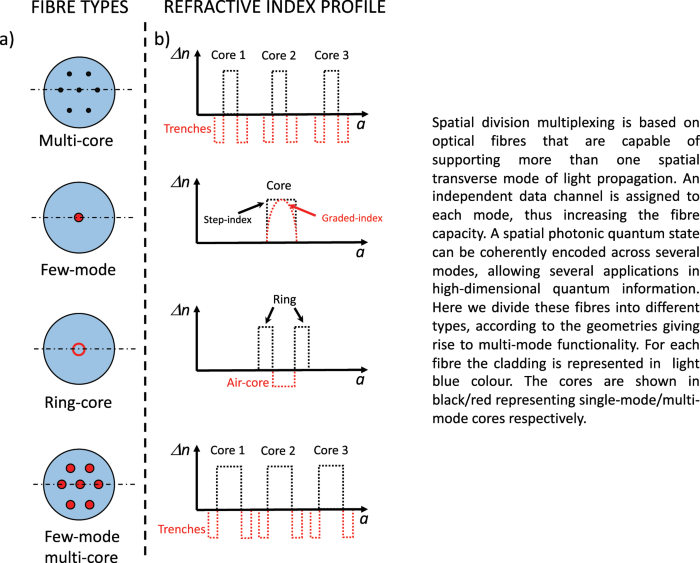
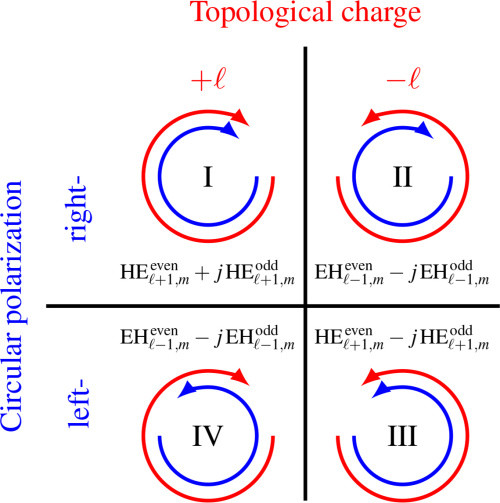
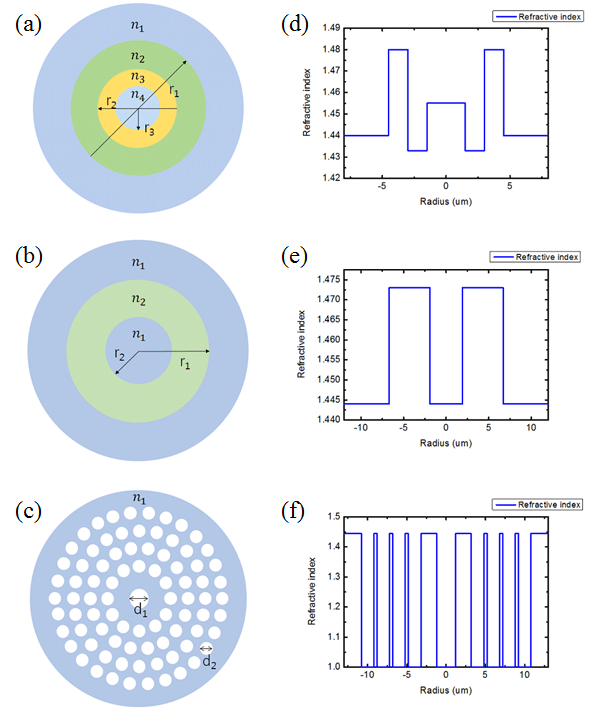
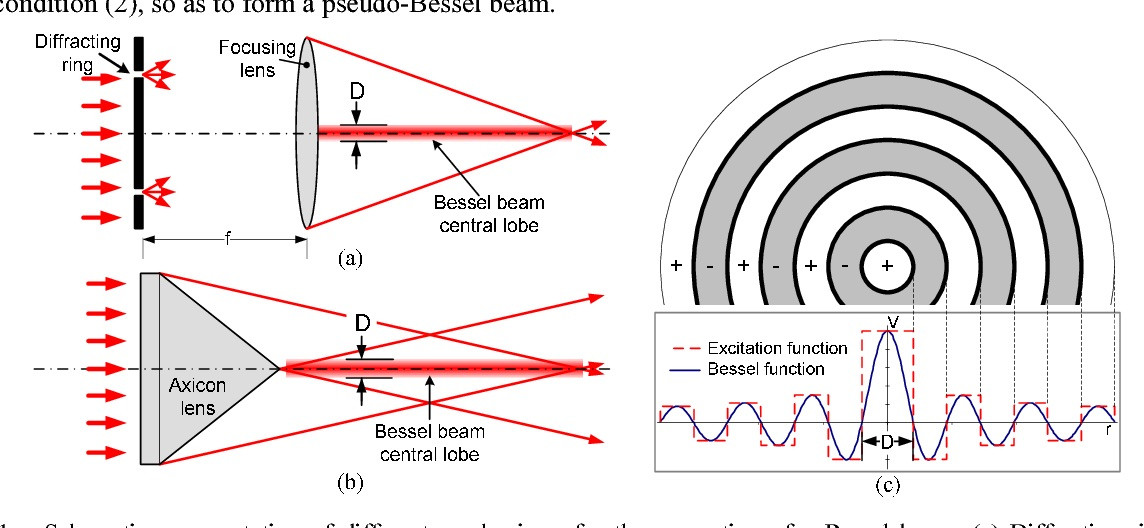
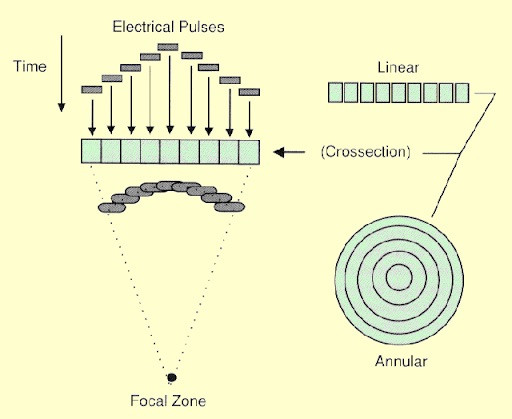
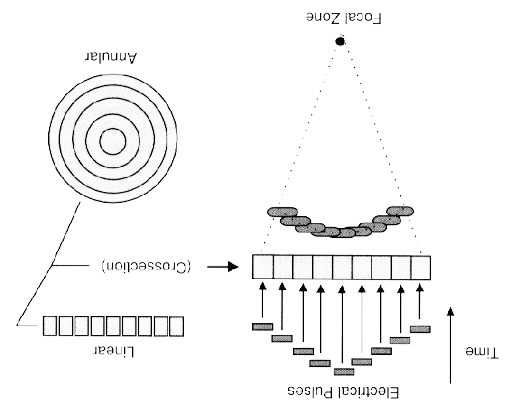
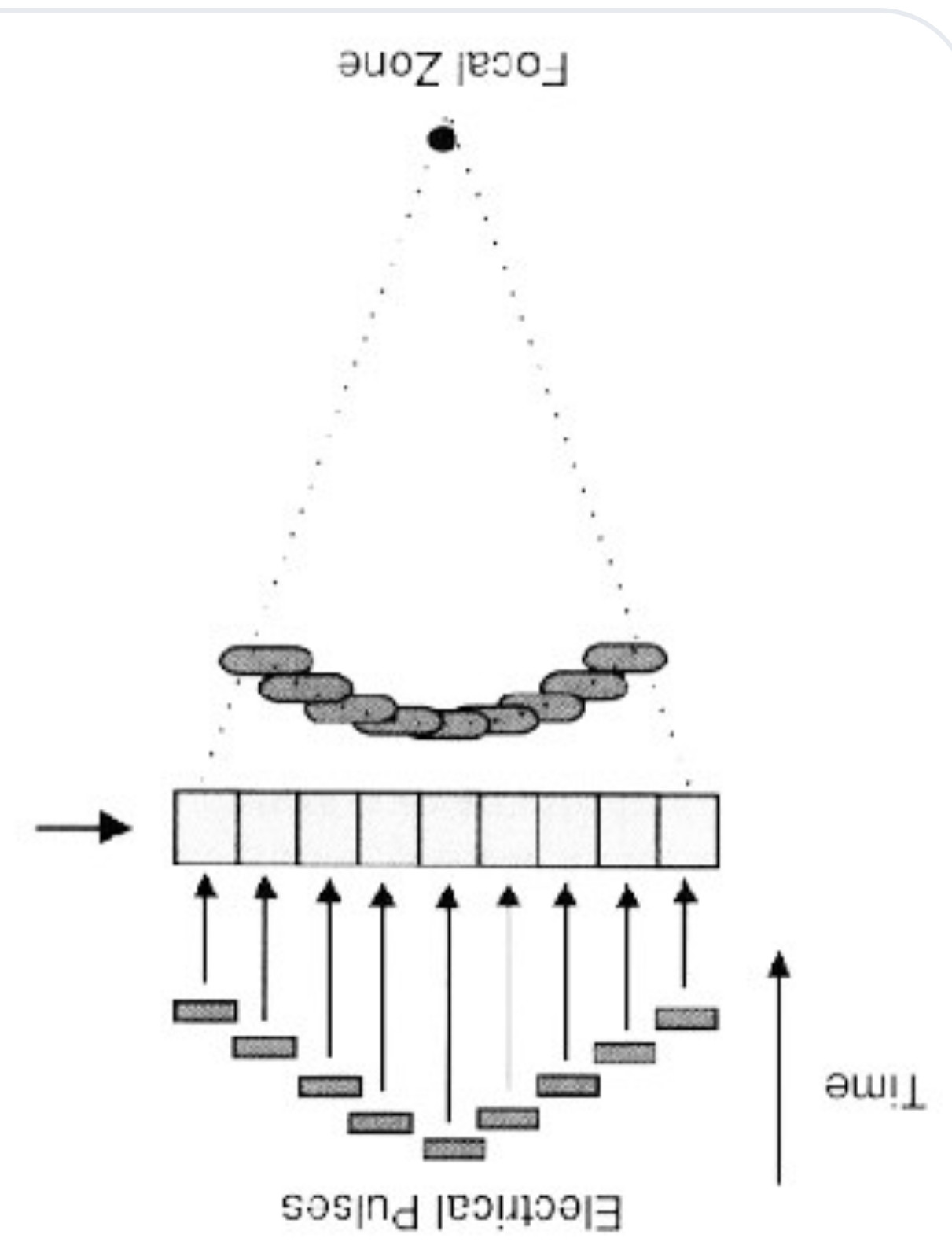
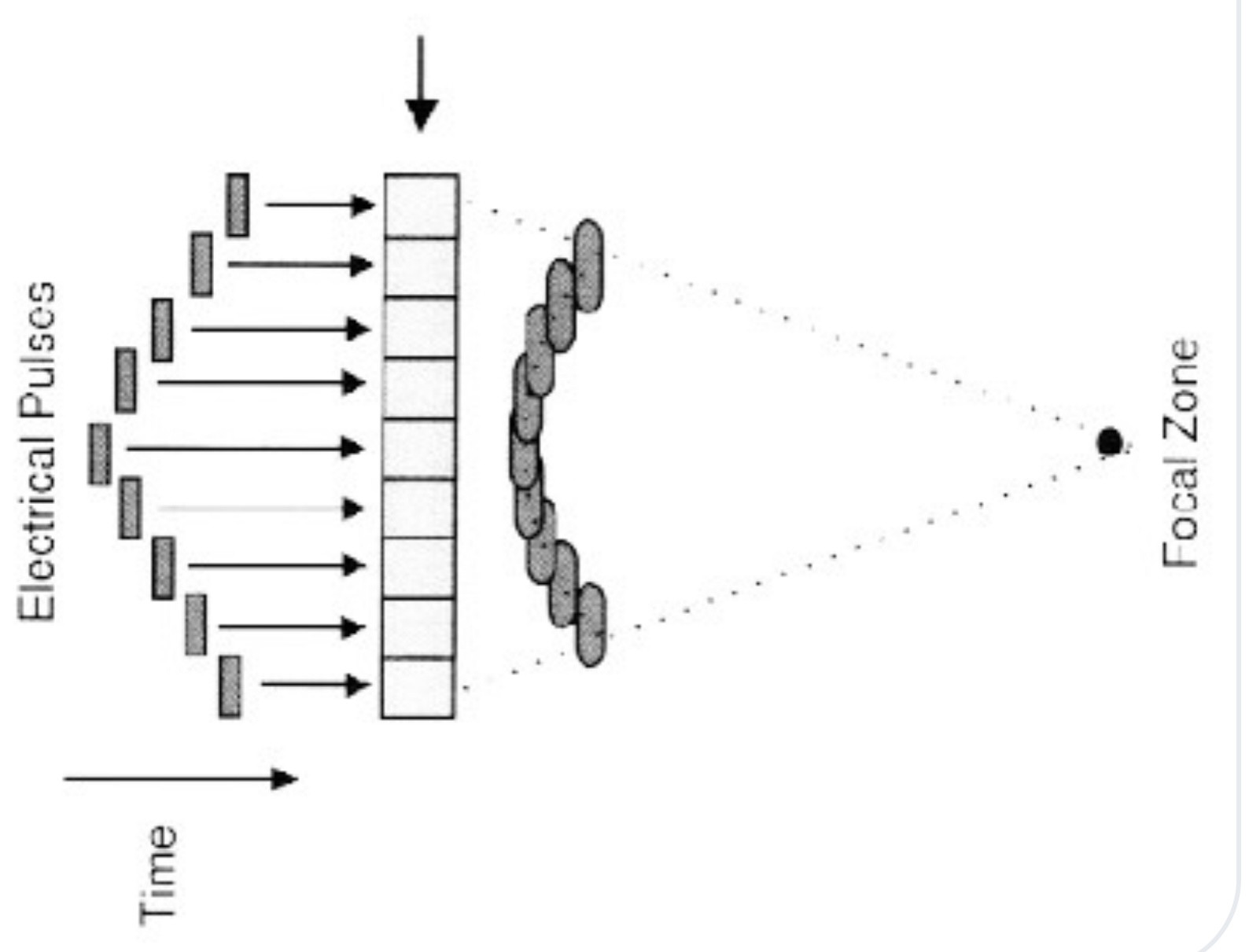
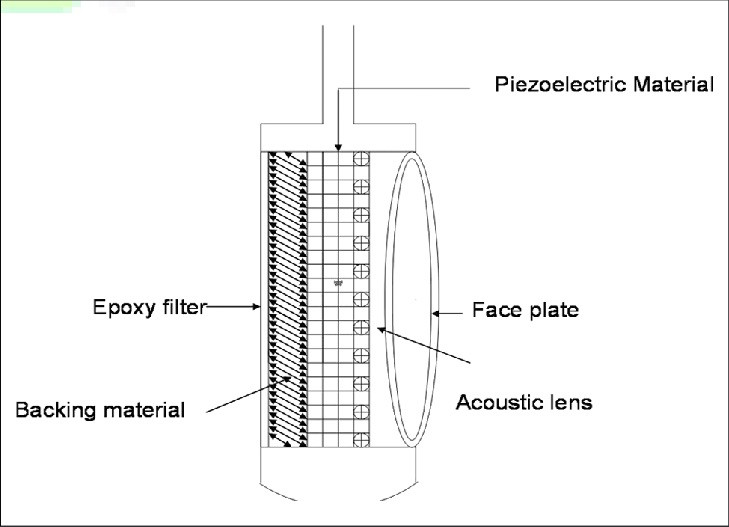
light chain
noun BIOCHEMISTRY
the protein subunit that, as one of a pair, forms part of the main antigen-binding region of an immunoglobulin molecule.
Never Forget Why This War Was Started It Is All About Saving The Children
Hi Tesla oh I mean Mac sending you all our love.
Sonic bomb?
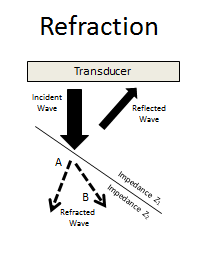
It's caused by shock waves created by any object that travels through the air faster than the speed of sound. Sonic booms create huge amounts of sound energy. When an object moves through the air, it makes pressure waves in front of and behind it.
How much evidence do we need to put these bastards away for good?
To say it was all an inside job is an understatement.
ding
verb: ding; 3rd person present: dings; past tense: dinged; past participle: dinged; gerund or present participle: dinging
make a ringing sound.
"cash registers were dinging softly"
exclamation
exclamation: ding
used to imitate a metallic ringing sound resembling a bell.
Origin
early 17th century: imitative.
A wee ding
Middle English: probably of Scandinavian origin; compare with Danish dænge ‘beat, bang’.
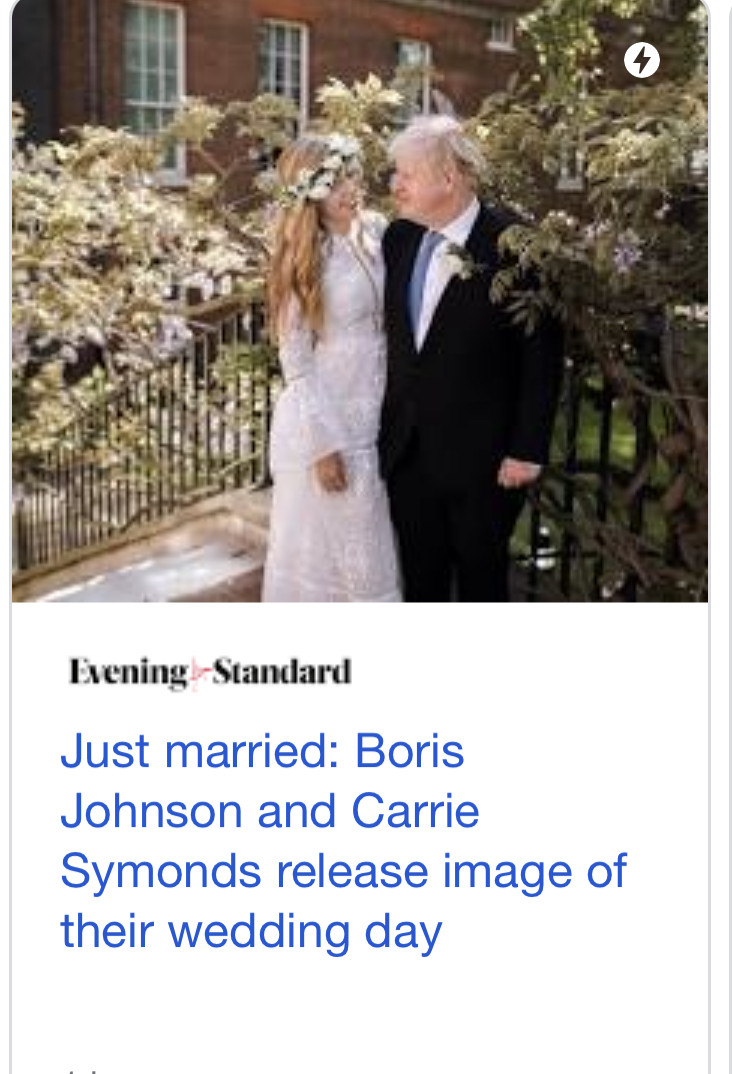
M A R R I E D
A MARRIAGE
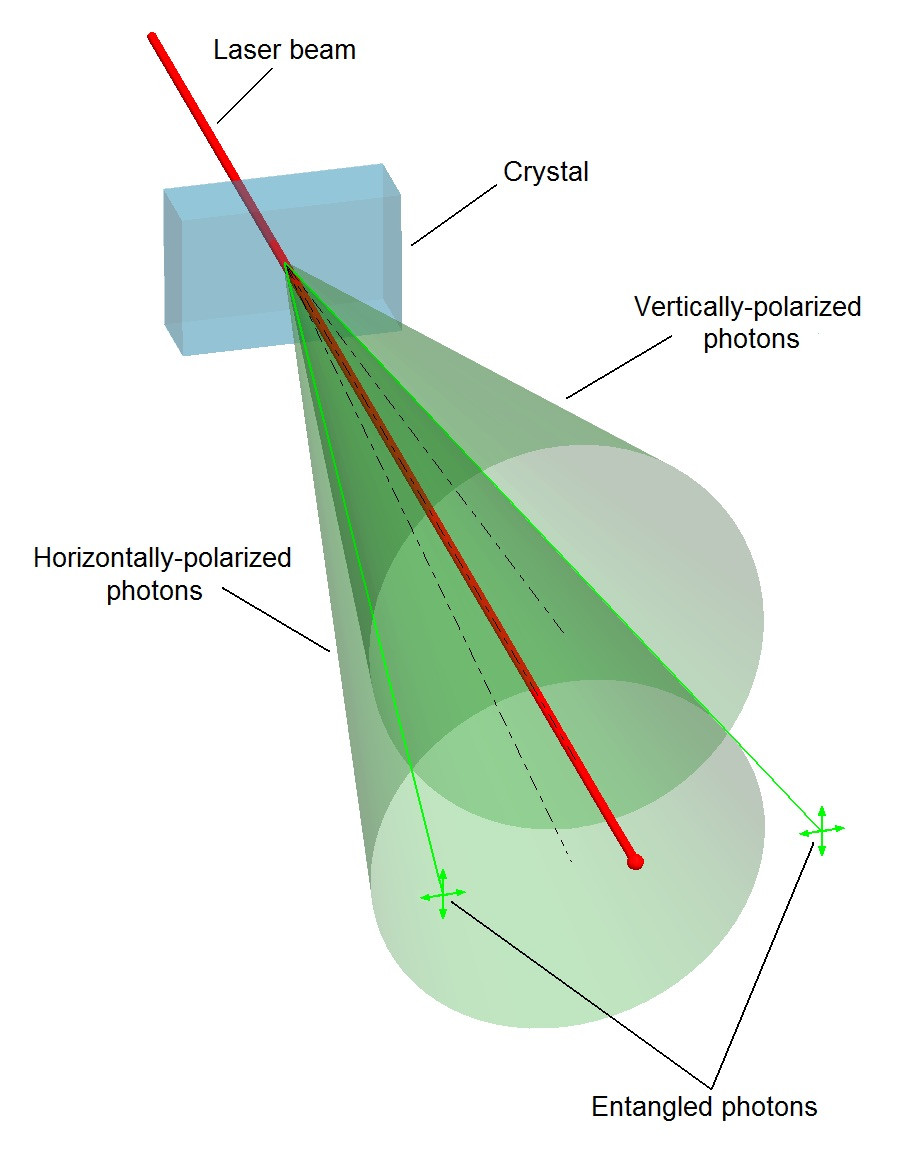
AN ENTANGLEMENT
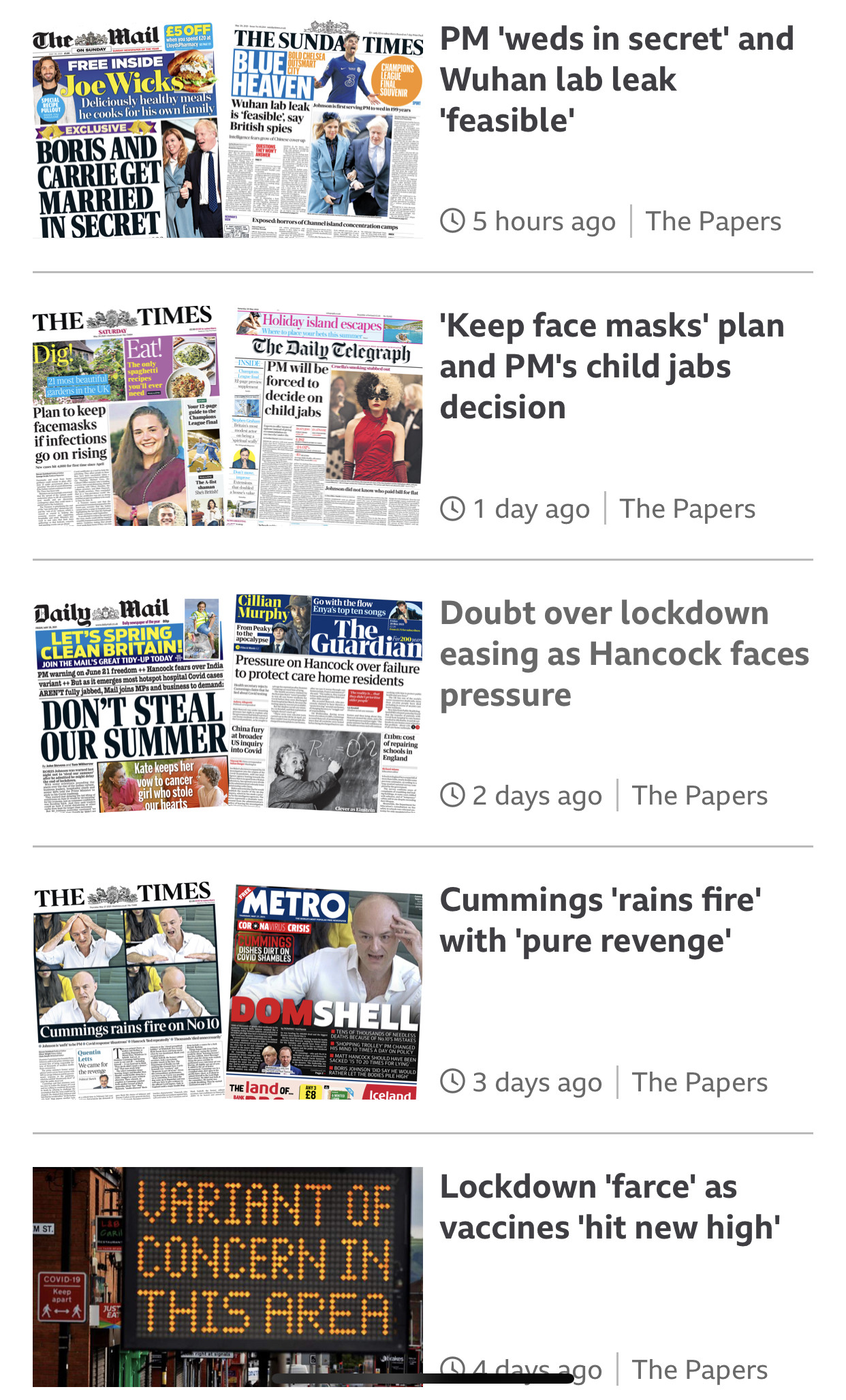
WE D DING IN S E C RE T
verb: return; 3rd person present: returns; past tense: returned; past participle: returned; gerund or present participle: returning
1.
come or go back to a place or person.
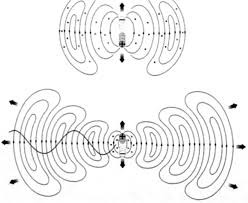
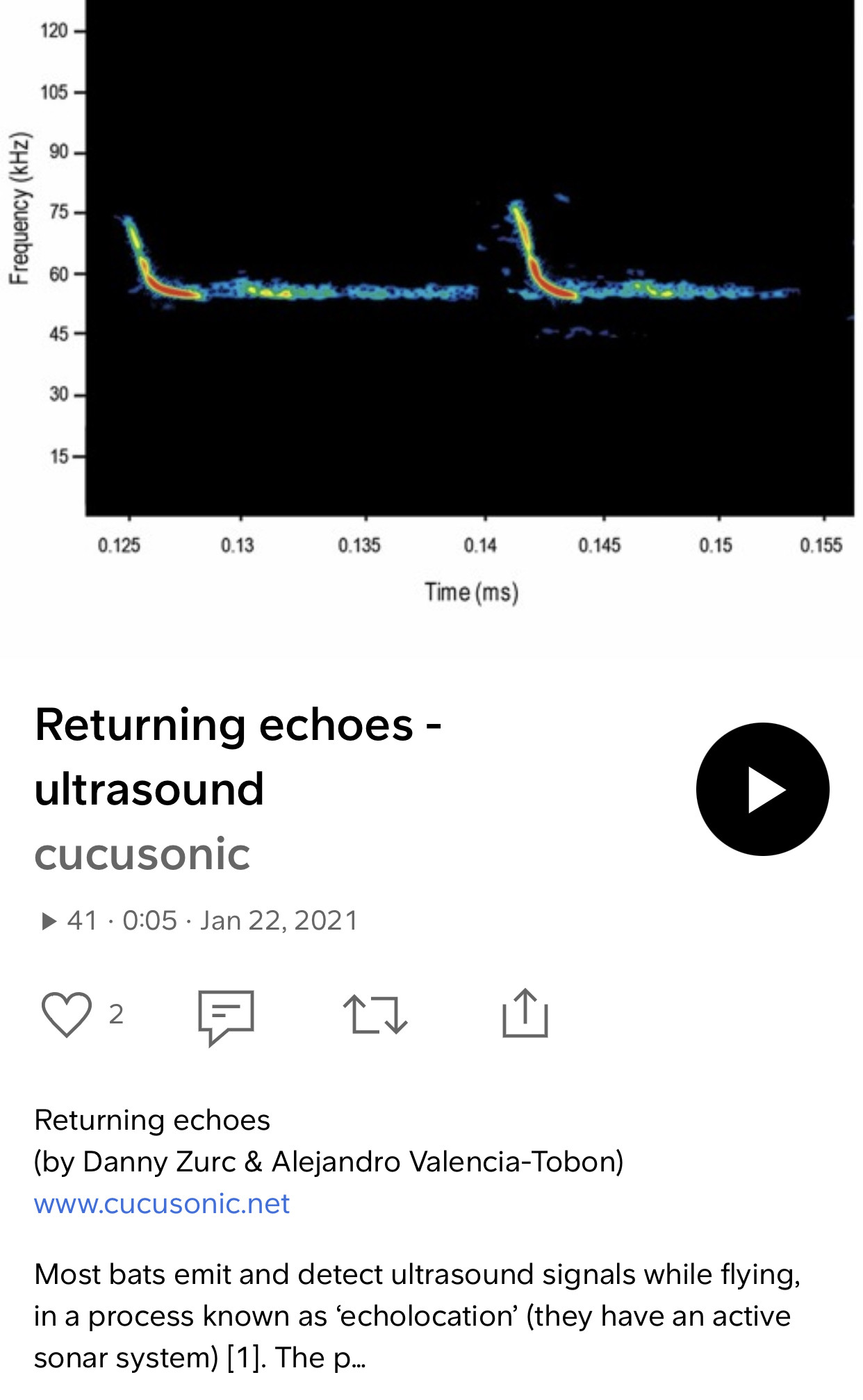
Echolocation, also called bio sonar, is a biological sonar used by several animal species. Echolocating animals emit calls out to the environment and listen to the echoes of those calls that return from various objects near them. They use these echoes to locate and identify the objects.
fracture (third-person singular simple present fractures, present participle fracturing, simple past and past participle fractured)
(transitive, intransitive) To break, or cause something to break.
(transitive, slang) To amuse (a person) greatly; to split someone's sides.
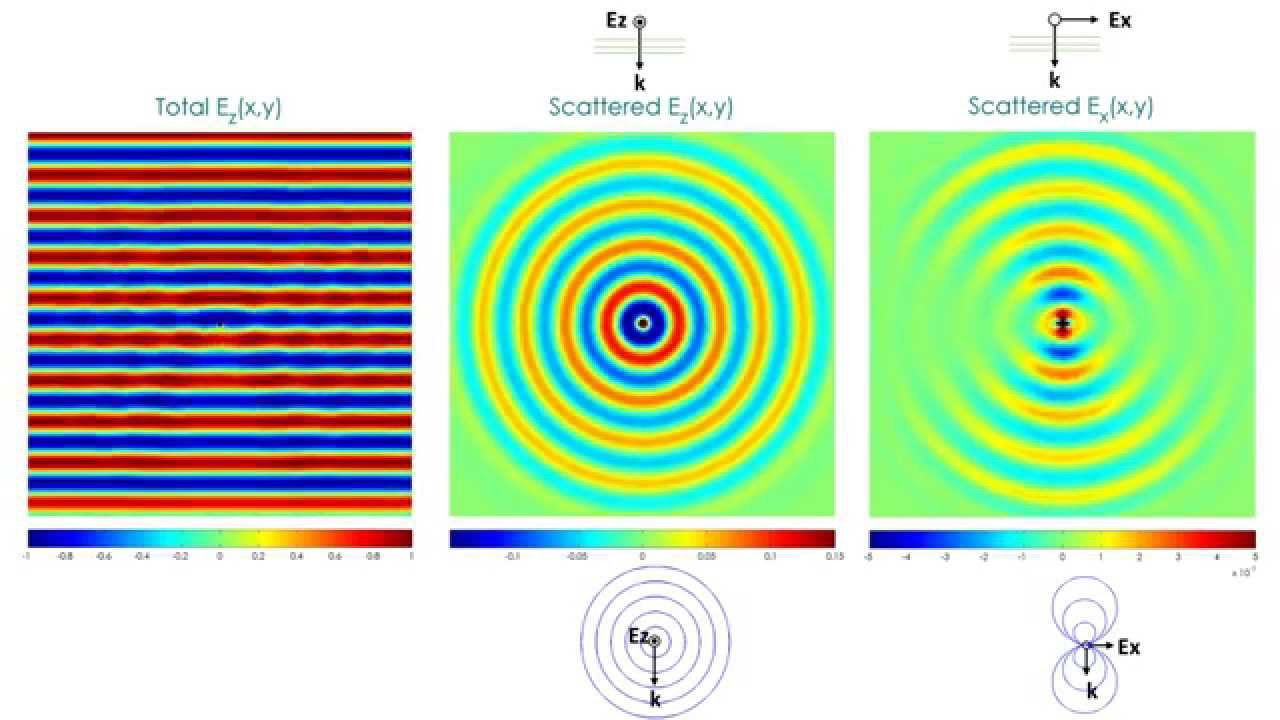
scattering (plural scatterings)
A small quantity of something occurring at irregular intervals and dispersed at random points,
There will be a scattering of showers, with heavy rain in places.
(physics) The process whereby a beam of waves or particles is dispersed by collisions or similar interactions.
Hypernyms
light-scattering
A L I G H T S C A T T E R I N G
PURE REVENGE
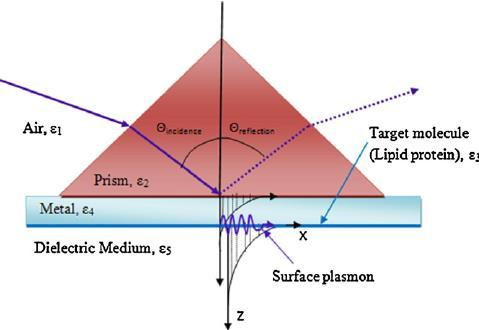
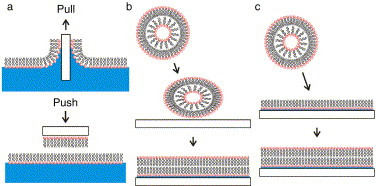
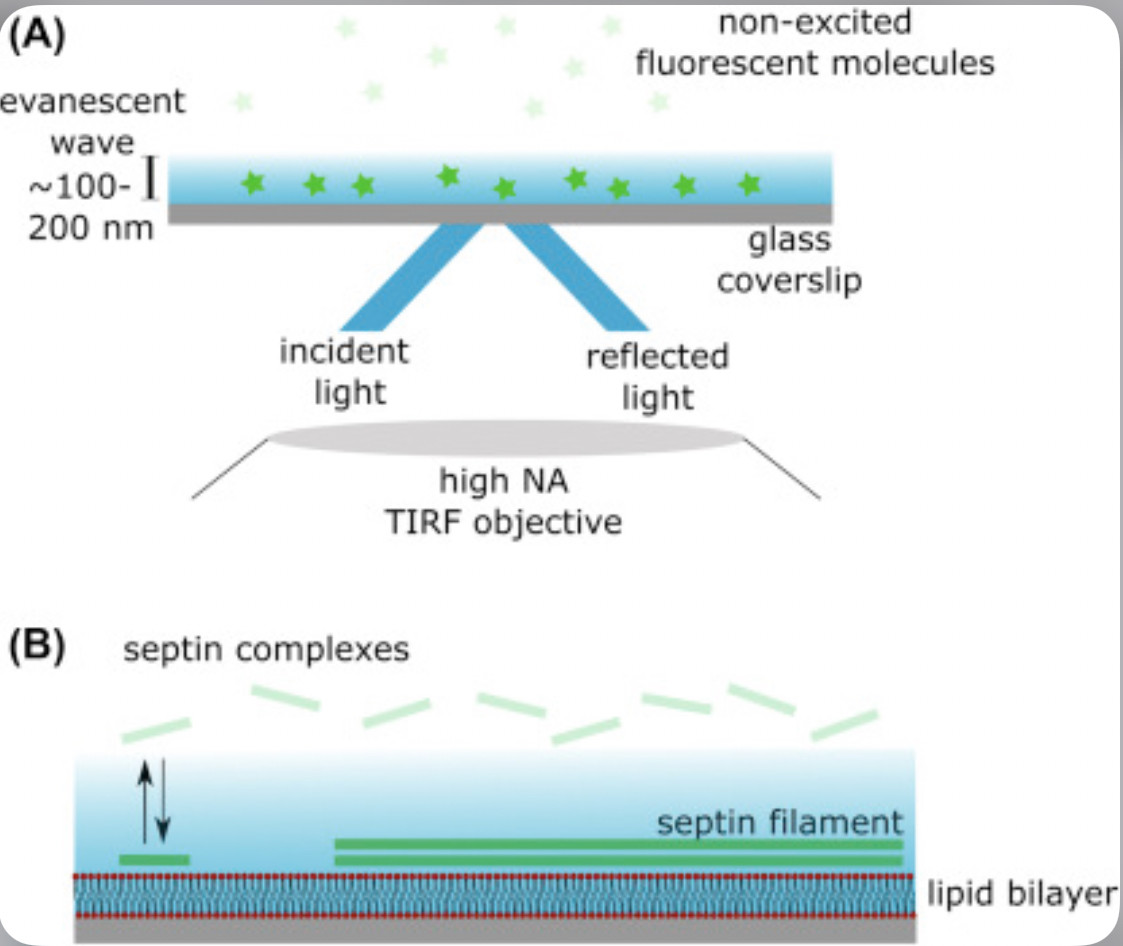
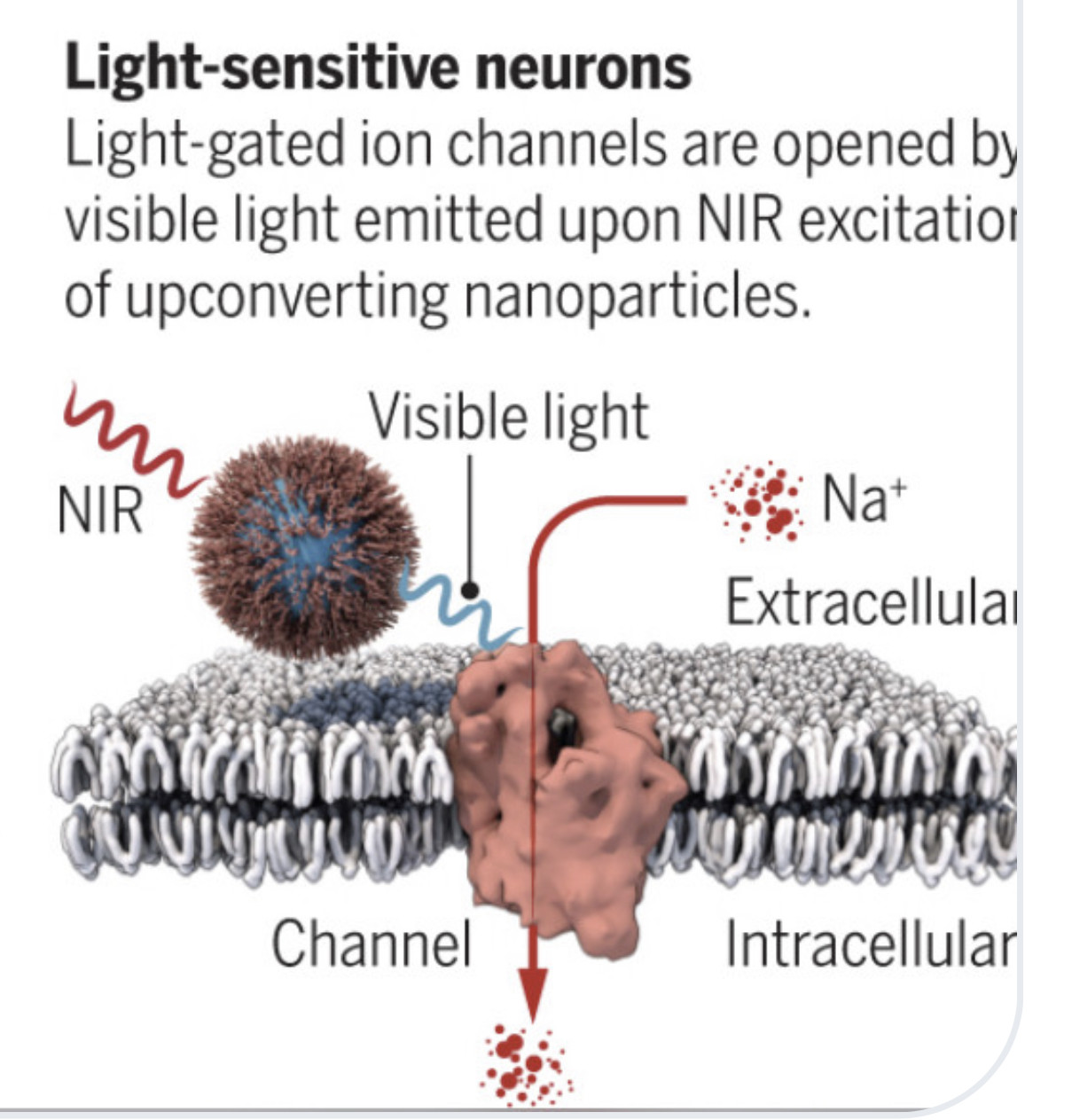
"lipid bilayers to mimic the eukaryotic plasma membrane."
What are the sites of photosynthesis in eukaryotic cells?
Organelles, called plastids, are the main sites of photosynthesis in eukaryotic cells. Chloroplasts, as well as any other pigment containing cytoplasmic organelles that enables the harvesting and conversion of light and carbon dioxide into food and energy, are plastids.
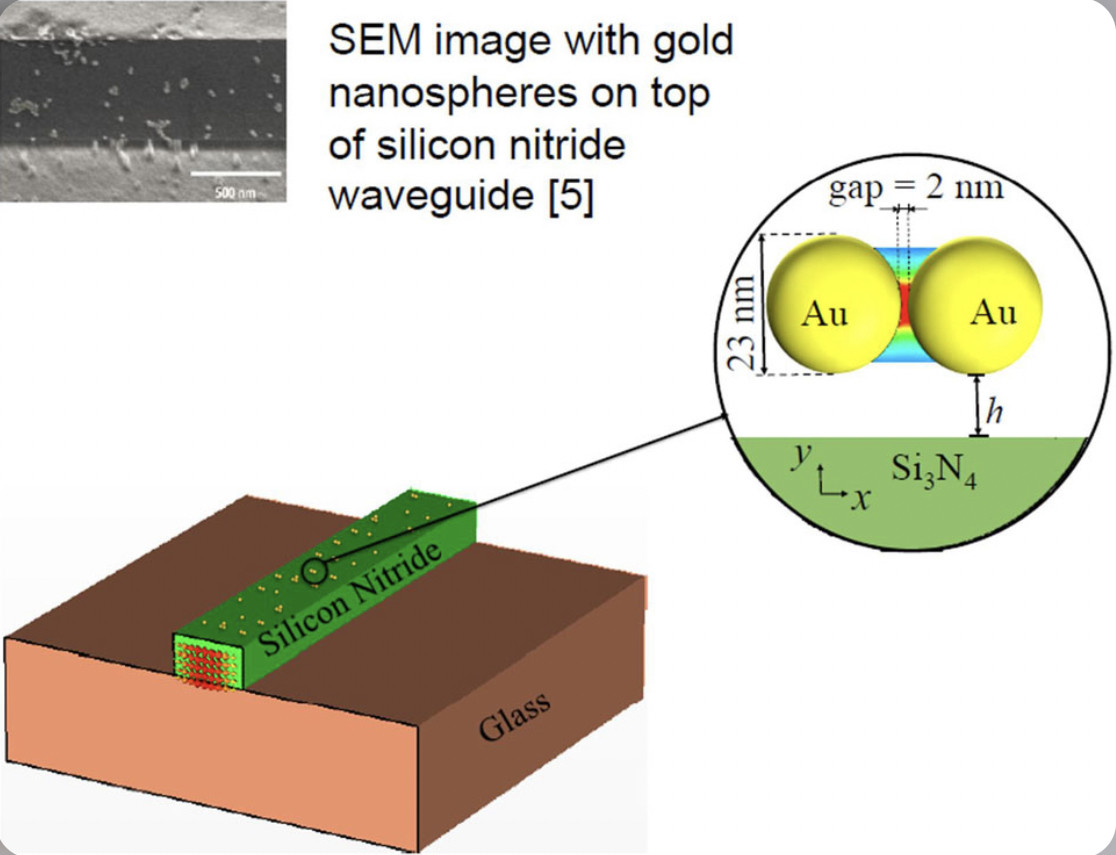
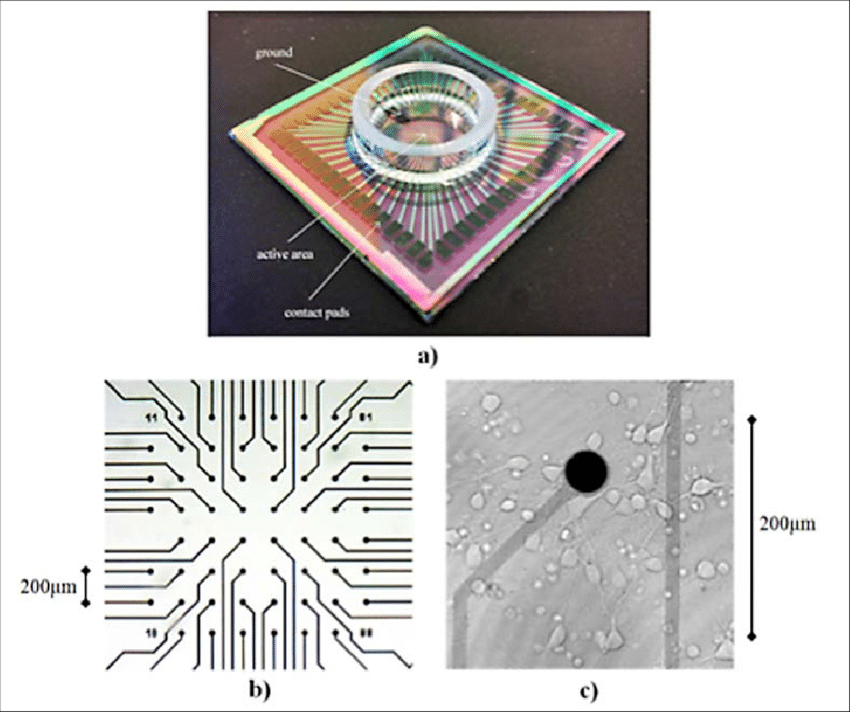
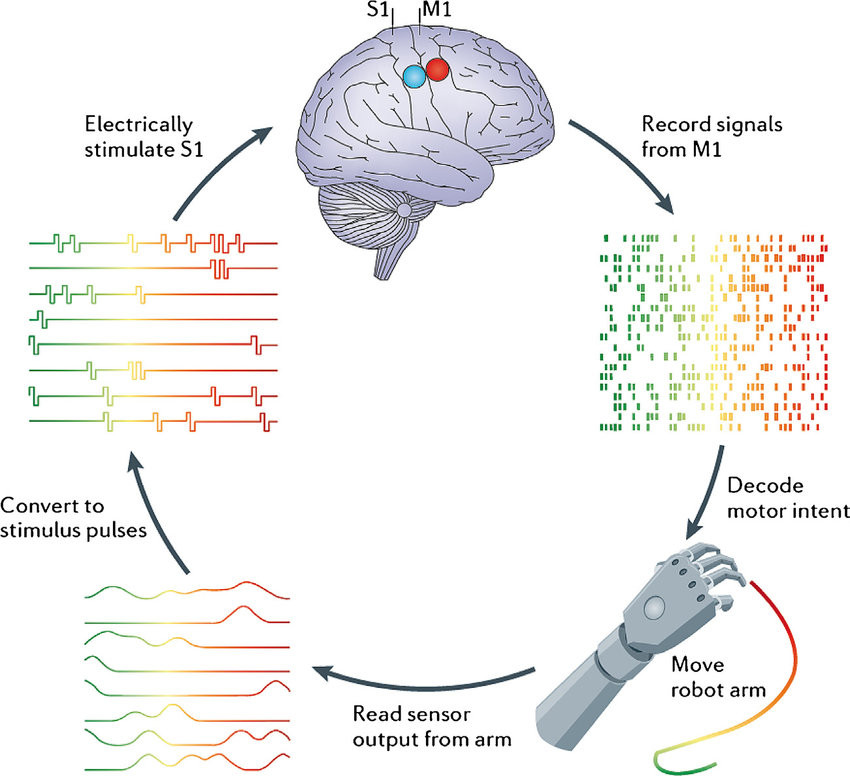
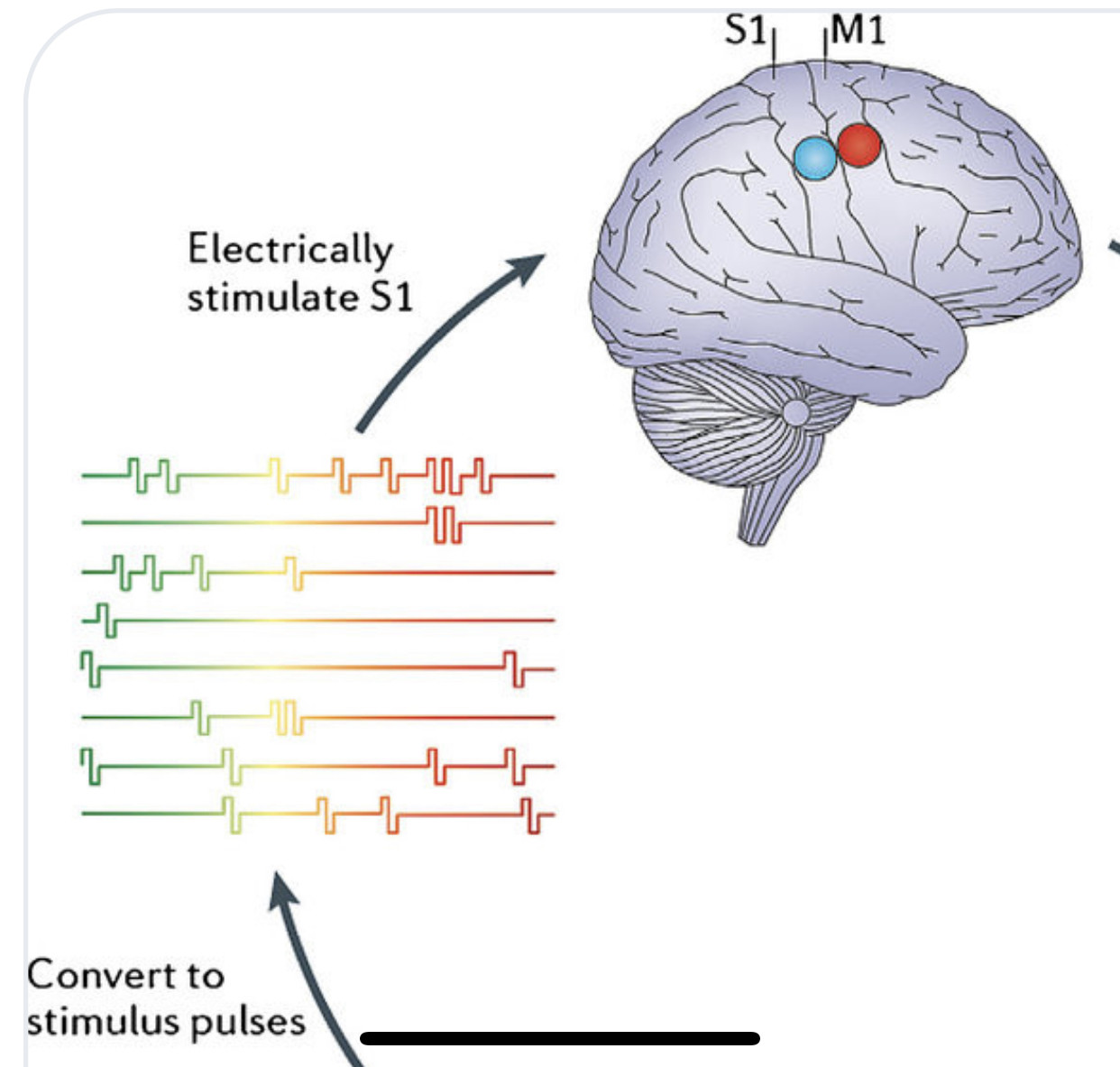
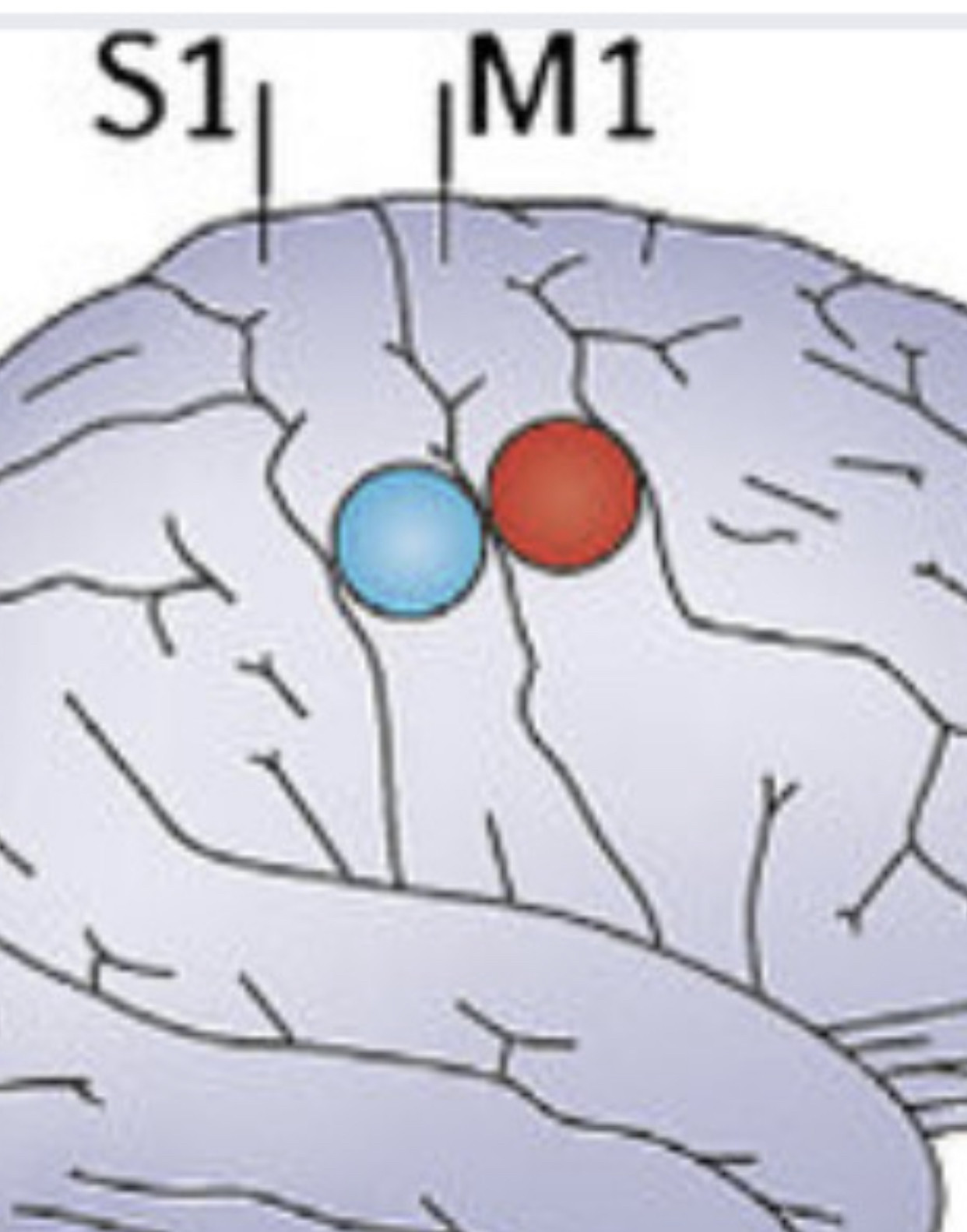
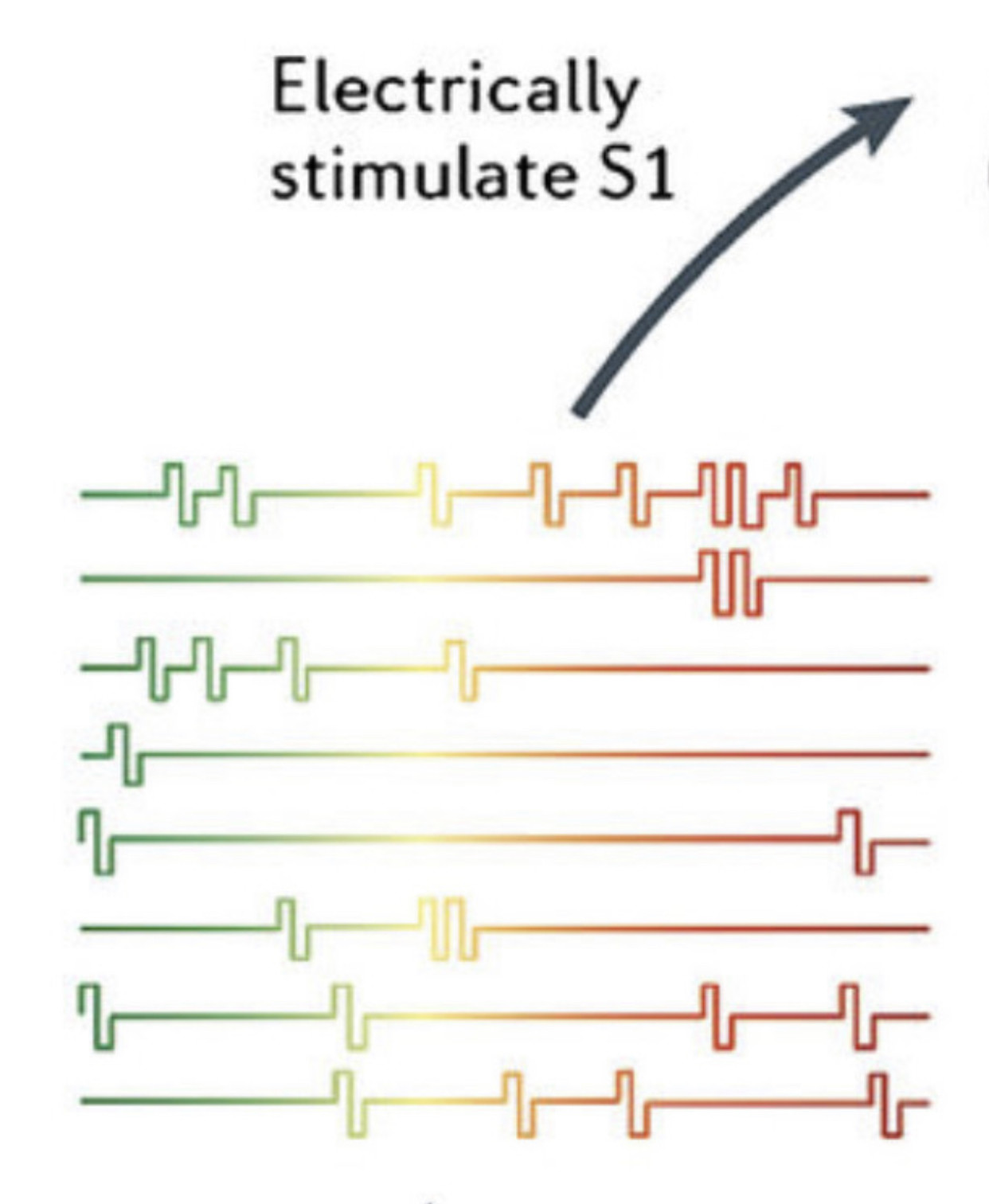
An electrode is a solid electric conductor that carries electric current into non-metallic solids, or liquids, or gases, or plasmas, or vacuums. ... In an electrochemical cell, reduction and oxidation reactions take place at the electrodes. The electrode at which reduction takes places is called the cathode.
An electrode array is a configuration of electrodes used for measuring either an electric current or voltage. Some electrode arrays can operate in a bidirectional fashion, in that they can also be used to provide a stimulating pattern of electric current or voltage.
A novel near-infrared-absorbing nanoformulation is fabricated by efficiently encapsulating plasmonic Cu2–xS nanocrystals (NCs) within the core of low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-mimetic solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs). Cu2–xS NCs are ideal candidates as photothermal or imaging agents for in vivo cancer treatment, thanks to their plasmonic properties, low toxicity, biodegradability, and low cost. Their incorporation in the LDL-mimetic nanocarriers enhances the nanoformulation potential in biomedical applications, resulting in nanosystems able to provide the concomitant delivery of anticancer molecules and cancer diagnosis and/or therapy.
Besides the comprehensive characterization of the prepared nanostructures, the paper aims to tackle the accurate determination of the NC concentration in the final nanoformulation. Since both photothermal therapy and imaging efficiency strongly depend on the concentration of the nanoagents, the availability of a real-time and nondestructive approach for the determination of NC concentration in the SLNs is essential for clinical studies addressing the possible administration of the nanoformulation for in vivo applications. Here, the Mie theory and Drude model-based fitting procedure of the experimental results from the morphological and spectroscopic characterization is proposed for the explanation of the plasmonic properties of the nanoformulation and for the determination of the concentration in terms of Cu2–xS NCs and SLNs.
16 Dec 2016 — PDF | Solid lipid nanoparticles are particles produced by high pressure homogenization or other suitable technique having photon correlation
DLS, also called photon correlation spectroscopy (PCS), is a light-scattering technique used to study the average particle size of NPs based on the laser diffraction method (Berne and Pecora, 2000). This technique uses the scattering of light from colloidal particles suspended in a liquid medium.