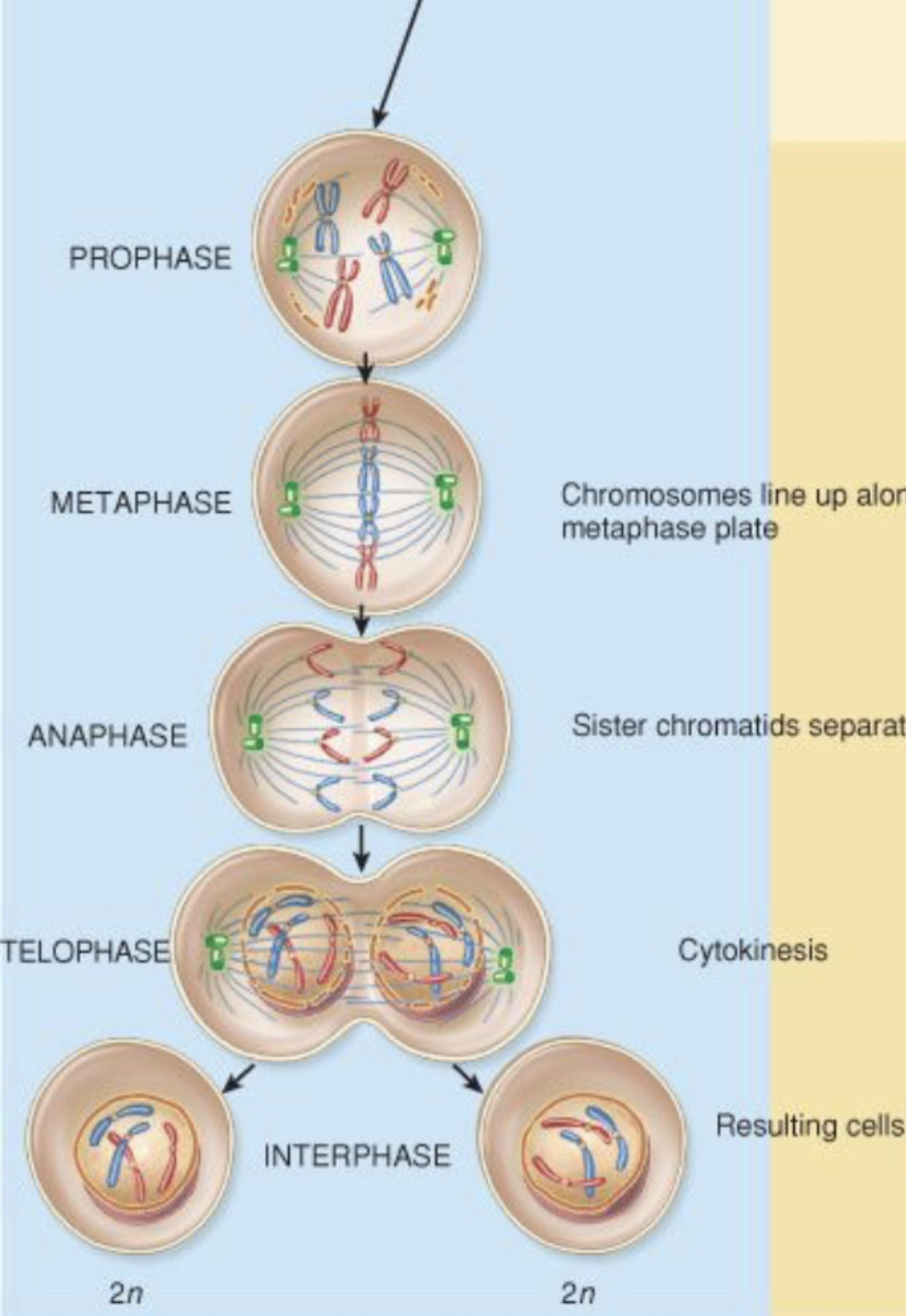
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle.
The Light of God lives in our hearts. Love, work, and knowledge are the wellsprings of the life He gives us; they should also govern it.
This work is focused on the preparation of a multifunctional compound consisting of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) embedded in a matrix of amorphous carbon previously loaded with Fe3C magnetic particles. The objective is to use the antibacterial properties of the AgNPs for environmental purposes, in such a way that the AgNPs can be recovered by physical means (magnetic separation).
The synthesis method was direct from ferrocene, silver nitrate and polyethylene glycol placed in a reaction tube and pyrolyzed by a plasma produced under vacuum conditions. For this, a conventional microwave oven was used. The compound obtained is a black powder, with similar consistency to graphite, but it responds strongly to the application of magnetic fields.
The material was thoroughly characterized by X-ray photoelectron, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopies; transmission and scanning electron microscopies; X-ray diffraction, as well magnetic characterizations using a vibrating sample magnetometer. The material showed a homogeneous dispersion of metal particles in the carbon matrix. We conclude that the combination of magnetic and antibacterial properties makes this material interesting for several applications through the use of magnetic separation protocols.
Magnetic separation is the process of separating components of mixtures by using magnets to attract magnetic materials. The process that is used for magnetic separation detaches non-magnetic material with those that are magnetic.
This technique is useful for not all, but few minerals such as Ferromagnetism/ferromagnetic (materials strongly affected by magnetic fields) and paramagnetic (materials that are less affected) but the effect is A large diversity of mechanical means are used to separate magnetic materials. During magnetic separation, magnets are situated inside two separator drums which bear liquids. Due to the magnets, magnetic particles are being drifted by the movement of the drums. This can create a magnetic concentrate (e.g. an ore concentrate)
A colloid is a mixture in which one substance of microscopically dispersed insoluble particles are suspended throughout another substance. However, some definitions specify that the particles must be dispersed in a liquid, and others extend the definition to include substances like aerosols and gels.