Happiness lowers your risk for cardiovascular disease, lowers your blood pressure, enables better sleep, improves your diet, allows you to maintain a normal body weight through regular exercise and reduces stress.
Have a lovely day. 🙏🏻❤️
Being in the sun can make people feel better and have more energy. Sunlight increases the levels of serotonin in the brain, which is associated with improved mood.
🌞
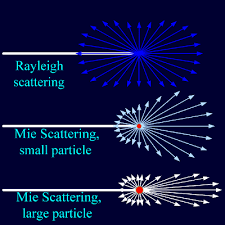
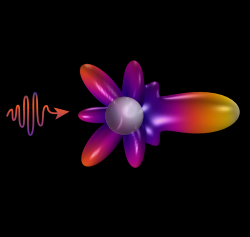
Metamaterial cloaking, based on transformation optics, describes the process of shielding something from view by controlling electromagnetic radiation. Objects in the defined location are still present, but incident waves are guided around them without being affected by the object itself.
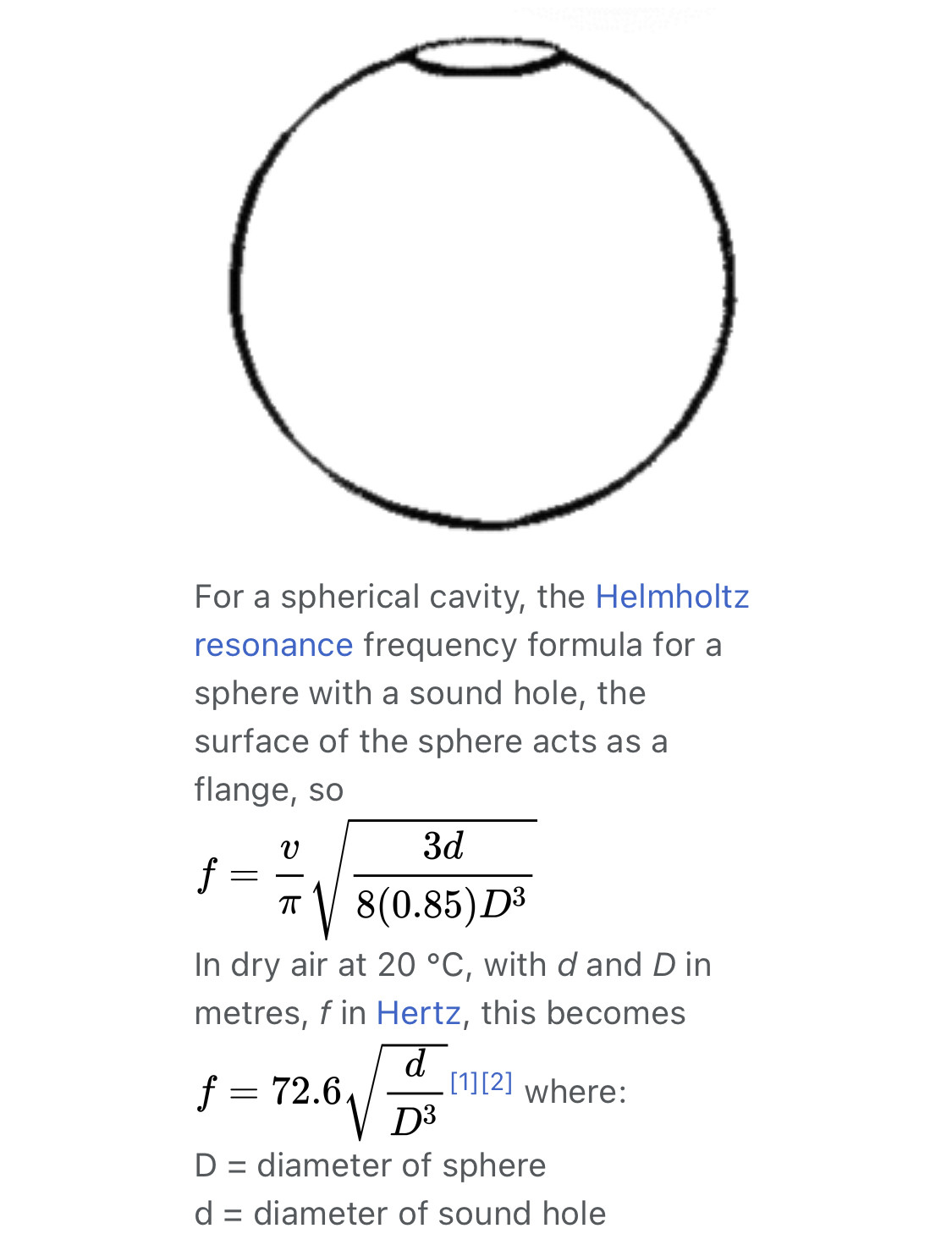
A resonance chamber uses resonance to enhance the transfer of energy from a sound source (e.g. a vibrating string) to the air. The chamber has interior surfaces which reflect an acoustic wave. When a wave enters the chamber, it bounces back and forth within the chamber with low loss (See standing wave). As more wave energy enters the chamber, it combines with and reinforces the standing wave, increasing its intensity.
Since the resonance chamber is an enclosed space that has an opening where the sound wave enters and exits after bouncing off of the internal walls producing resonance, commonly acoustic resonance as in many musical instruments (see Sound board (music)), the material of the chamber, particularly that of the actual internal walls, its shape and the position of the opening, as well as the finish (porosity) of the internal walls are contributing factors for the final resulting sound produced.
The Schumann resonances (SR) are a set of spectrum peaks in the extremely low frequency (ELF) portion of the Earth's electromagnetic field spectrum. Schumann resonances are global electromagnetic resonances, generated and excited by lightning discharges in the cavity formed by the Earth's surface and the ionosphere.
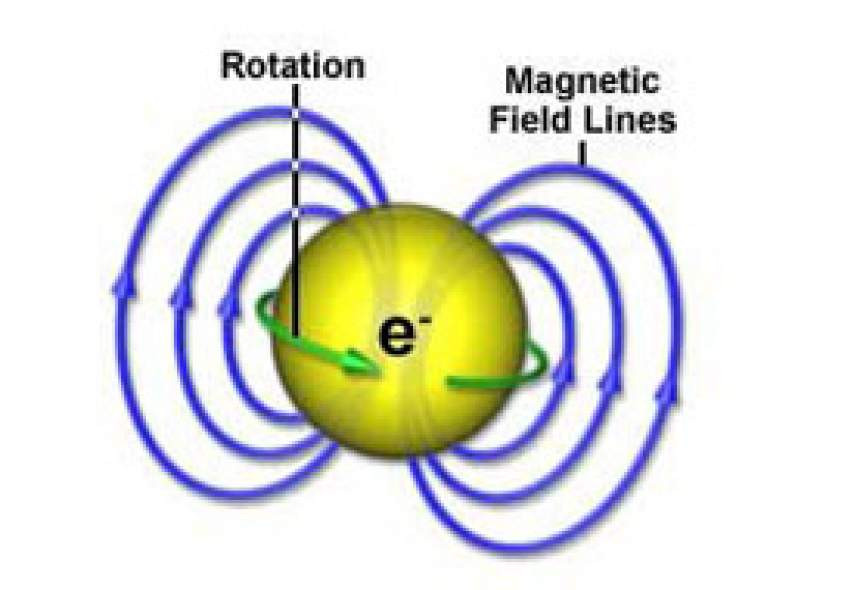
Electromagnetic resonance is a phenomenon produced by simultaneously applying steady magnetic field and electromagnetic radiation (usually radio waves) to a sample of electrons and then adjusting both the strength of the magnetic field and the frequency of the radiation to produce absorption of the radiation.
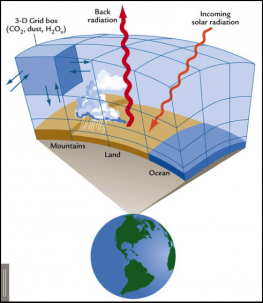
Climate models include more atmospheric, oceanic and land processes than weather models do—such as ocean circulation and melting glaciers. These models are typically generated from mathematical equations that use thousands of data points to simulate the transfer of energy and water that takes place in climate systems.
simulate
/ˈsɪmjʊleɪt/
verb
imitate the appearance or character of.
imitate
reproduce
replicate
duplicate
mimic
parallel
be a mock-up of
artificial
imitation
fake
false
faux
mock
synthetic
man-made
manufactured
ersatz
plastic
fakey
Opposite:
real
pretend to have or feel (an emotion).
"it was impossible to force a smile, to simulate pleasure"
Similar:
feign
pretend
fake
sham
affect
put on
counterfeit
go through the motions of
give the appearance of
feigned
mock
pretended
affected
assumed
insincere
not genuine
false
bogus
spurious
put-on
phoney
fakey
cod
Opposite:
genuine
real
produce a computer model of.
"future population changes were simulated by computer"
Does population cause climate change?
The largest single threat to the ecology and biodiversity of the planet in the decades to come will be global climate disruption due to the buildup of human-generated greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.?
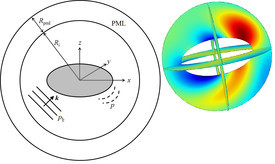
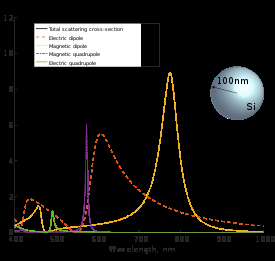
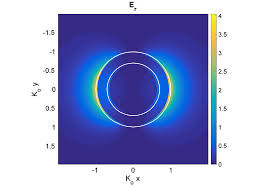
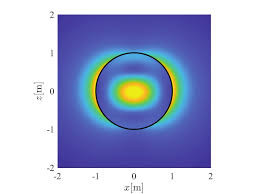
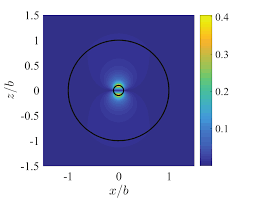
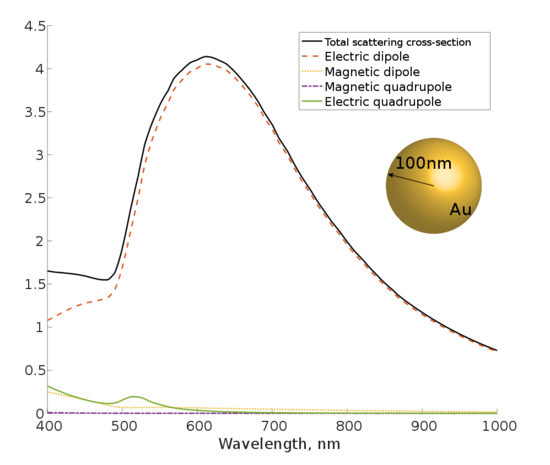
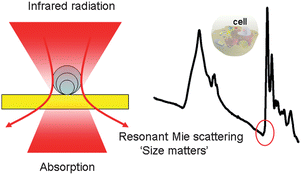
We present an on-chip tunable infrared (IR) metamaterial emitter for gas sensing applications. The proposed emitter exhibits high electrical-thermal-optical efficiency, which can be realized by the integration of microelectromechanical system (MEMS) microheaters and IR metamaterials. According to the blackbody radiation law, high-efficiency IR radiation can be generated by driving a Direct Current (DC) bias voltage on a microheater. The MEMS microheater has a Peano-shaped microstructure, which exhibits great heating uniformity and high energy conversion efficiency.
The implantation of a top metamaterial layer can narrow the bandwidth of the radiation spectrum from the microheater to perform wavelength-selective and narrow-band IR emission. A linear relationship between emission wavelengths and deformation ratios provides an effective approach to meet the requirement at different IR wavelengths by tailoring the suitable metamaterial pattern.
Nanostructured Metamaterial Enables Invisibility Cloak - IEEE Spectrum
6 Aug 2010 — Now we have a metamaterial consisting of fishnet-like film containing holes about 100 nanometers in diameter that could serve as an invisibility cloak. ... The Purdue researchers have addressed one of the key limitations of metamaterials in optical devices: the absorption of too much light by metals in the metamaterials.
Short description of the method Photoconvertable fluorescent proteins exhibit a change in fluorescence excitation and emission spectra after excitation at a specific wavelength, and are thus useful as optical highlighters.
The emission spectrum of a chemical element or chemical compound is the spectrum of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation emitted due to an atom or molecule making a transition from a high energy state to a lower energy state.
A carbon footprint is the total greenhouse gas emissions caused by an individual, event, organization, service, or product, expressed as carbon dioxide equivalent.
Greenhouses can have artificial light so that photosynthesis can continue beyond daylight hours, or at a higher than normal light intensity.. .
So, how does artificial photosynthesis work?
For starters, it uses solar cells instead of chlorophyll to absorb sunlight and turn it into electricity. Artificial "leaves" also use either an artificial or an organic catalyst to split the water from the air into hydrogen and oxygen.
Nanoparticle cells
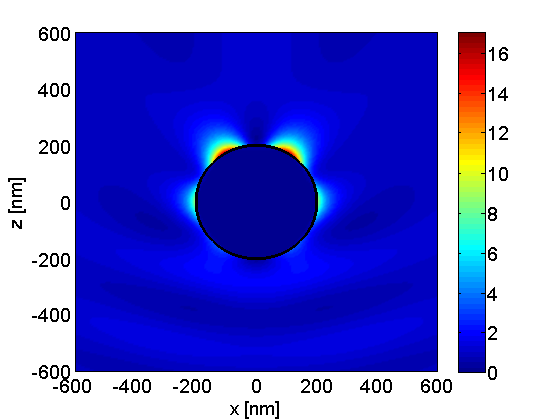
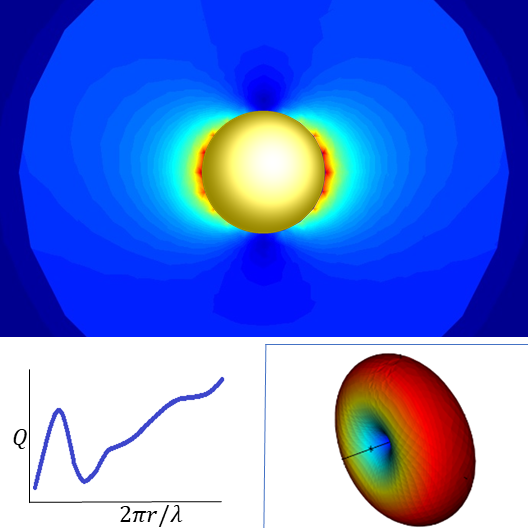
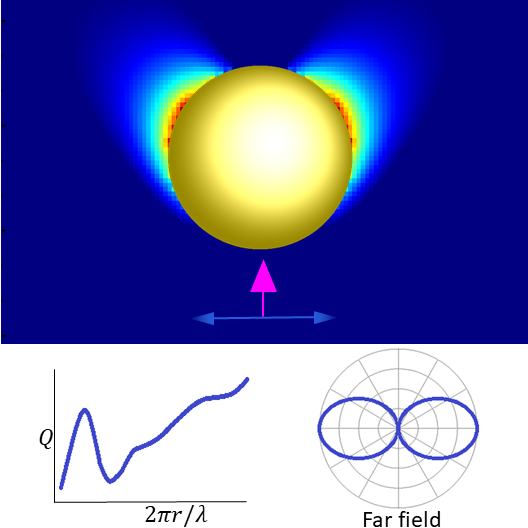
A common design is to deposit metal nano-particles on the top surface of the surface of the solar cell. When light hits these metal nano-particles at their surface plasmon resonance, the light is scattered in many different directions.
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) is the resonant oscillation of conduction electrons at the interface between negative and positive permittivity material stimulated by incident light. SPR is the basis of many standard tools for measuring adsorption of material onto planar metal (typically gold or silver) surfaces or onto the surface of metal nanoparticles. It is the fundamental principle behind many color-based biosensor applications, different lab-on-a-chip sensors and diatom photosynthesis.
Mitochondria are dynamic organelles with the ability to fuse and divide (fission), forming constantly changing tubular networks in most eukaryotic cells. These mitochondrial dynamics, first observed over a hundred years ago[1] are important for the health of the cell, and defects in dynamics lead to genetic disorders.
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality.
Although polygenic disorders are the most common, the term is mostly used when discussing disorders with a single genetic cause, either in a gene or chromosome.
The mutation responsible can occur spontaneously before embryonic development (a de novo mutation), or it can be inherited from two parents who are carriers of a faulty gene (autosomal recessive inheritance) or from a parent with the disorder (autosomal dominant inheritance).
Listen to pronunciation. (deh NOH-voh myoo-TAY-shun) A genetic alteration that is present for the first time in one family member as a result of a variant (or mutation) in a germ cell (egg or sperm) of one of the parents, or a variant that arises in the fertilized egg itself during early embryogenesis.