Child of God, truth-seeker finder and sharer, patriot, inspired and fired up!
@TheMac I just saw this on a telegram channel and thought of you😊.
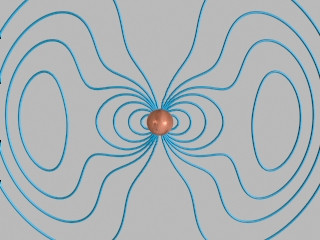
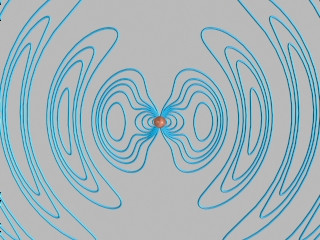
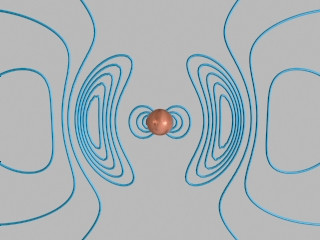
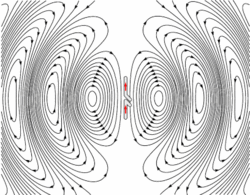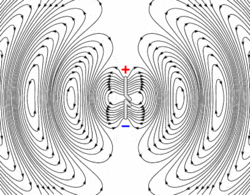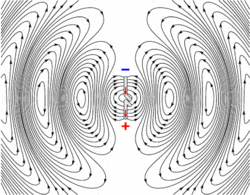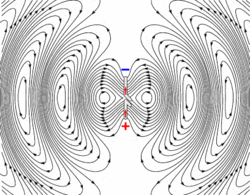
Magnetite crystals in the brain... GO!
God bless you. 🙏🏻❤️
A cell becomes polarized by moving and storing different types of electrically-charged molecules on different sides of its membrane. ... The inside of the cell also contains molecules called organic acids. These acids have negative charges on them, so they add to the negative charge inside the cell.
Magnetofection is a simple and highly efficient transfection method that uses magnetic fields to concentrate particles containing nucleic acid into the target cells.
Magnet-assisted transfection is a transfection method which uses magnetic interactions to deliver DNA into target cells. Nucleic acids are associated with magnetic nanoparticles, and magnetic fields drive the nucleic acid-particle complexes into target cells, where the nucleic acids are released.
Nucleic acid and amino acid are two types of biomolecules in the cell. Nucleic acid is a polymer that stores genetic information. ... Amino acid is a monomer that serves as a building block of a protein. The main difference between amino acid and protein is the structure and role of each biomolecule inside the cell.
A poly(amino acid) is a polymer composed of amino acids as monomeric units. Structural and functional proteins, polypeptides, peptides and polymers derived from amino acids, that is, poly(β-alanine) and ɛ-poly(lysine), are classified as poly(amino acid)s.
Amino acids in solution at neutral pH exist predominantly as dipolar ions (also called zwitterions). In the dipolar form, the amino group is protonated (-NH3+) and the carboxyl group is deprotonated (-COO-). ... As the pH is raised, the carboxylic acid is the first group to give up a proton, inasmuch as its pKa is near 2.
What are dipolar ions?
: an ion charged both positively and negatively (as that of an amino acid in solution) : an amphoteric ion the dipolar ion +H3NCH2COO− of glycine.