Virosomes are reconstituted liposomes containing viral (typically influenza virus) proteins in the liposomal membrane and, optionally, with additional antigens incorporated in the liposomal membrane or attached to the membrane.
From: Vaccines (Sixth Edition), 2013
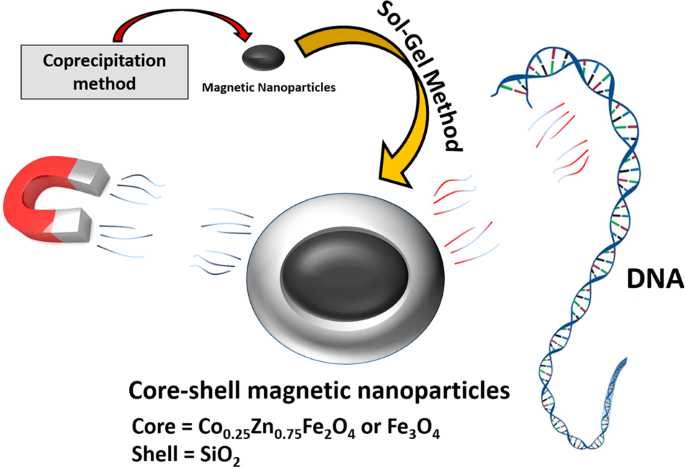
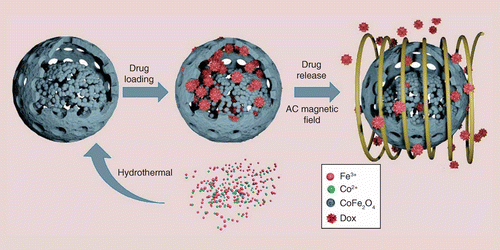
Applying ultrasound waves in the region where magnetic erythrocytes accumulate can induce vehicle destruction and the release of a drug at the organ or tissue level [24], [25].
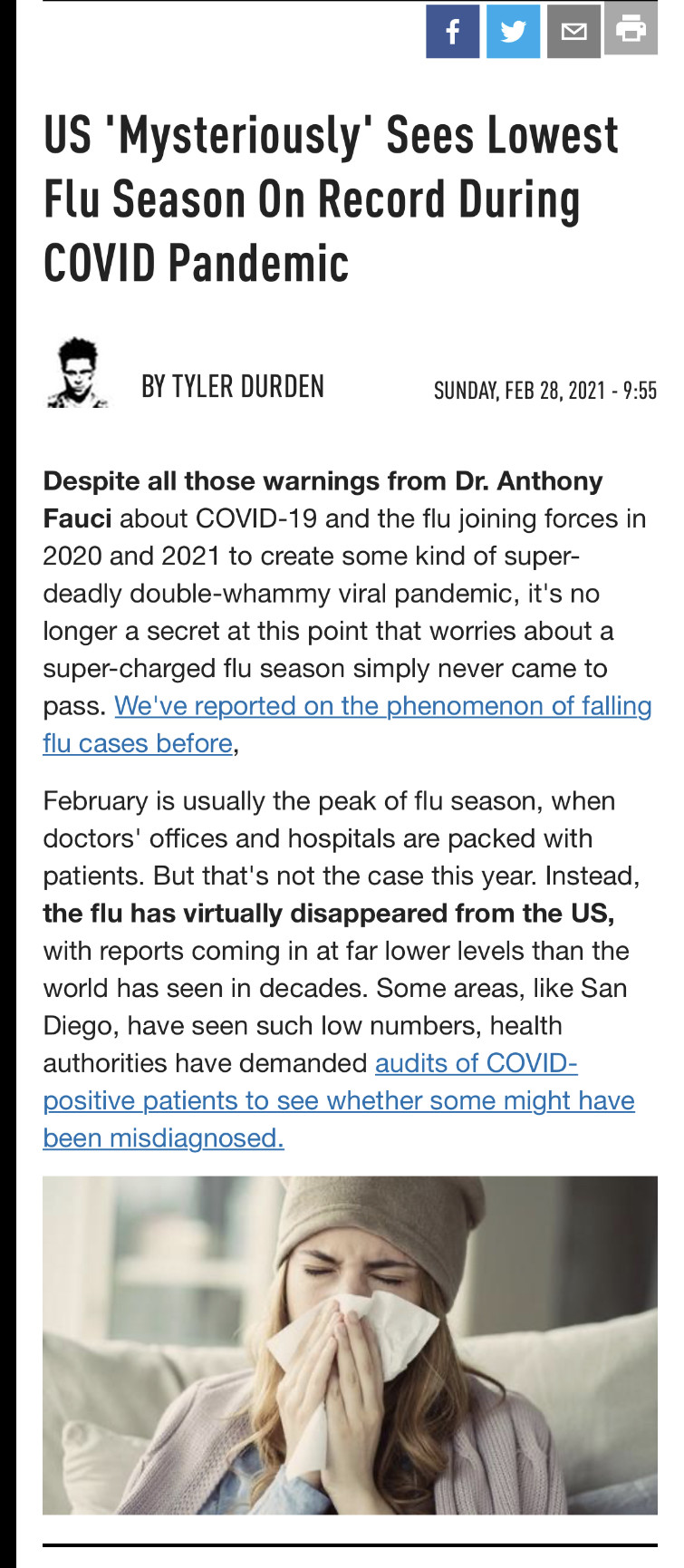
The magnetic erythrocytes, resulting from the co-encapsulation of the drugs with some ferrofluids such as cobalt–ferrite and magnetite, have been reported to direct the encapsulated drug predominantly to the desired sites of the body by means of an external magnetic field [21]–[23].
Magnetic nanoparticles are a class of nanoparticle that can be manipulated using magnetic fields. Such particles commonly consist of two components, a magnetic material, often iron, nickel and cobalt, and a chemical component that has functionality. While nanoparticles are smaller than 1 micrometer in diameter (typically 1–100 nanometers), the larger microbeads are 0.5–500 micrometer in diameter. Magnetic nanoparticle clusters that are composed of a number of individual magnetic nanoparticles are known as magnetic nanobeads with a diameter of 50–200 nanometers.
[1][2] Magnetic nanoparticle clusters are a basis for their further magnetic assembly into magnetic nanochains.