87,000 doctors and nurses suing those who are pushing this covid scam...
It's still me, following my heart 🙂❤️ and something else 👉 https://anonup.com/thread/13230439 💥
The Nuremberg Code
http://www.environmentandhumanrights.org/resources/Nuremberg%20Code.pdf
The Hippocratic Oath (Modern Version)
https://rjoy4u.org/modernhippocraticoath.pdf
Hippocratic Oath
https://tsmubioethics.weebly.com/uploads/5/0/1/7/5017099/hippocratic_oath.pdf
"To practice and prescribe to the best of my ability for the good of my patients, and to try to avoid harming them."
Oxidation is a normal and necessary process that takes place in your body. Oxidative stress, on the other hand, occurs when there’s an imbalance between free radical activity and antioxidant activity. When functioning properly, free radicals can help fight off pathogens. Pathogens lead to infections.
When there are more free radicals present than can be kept in balance by antioxidants, the free radicals can start doing damage to fatty tissue, DNA, and proteins in your body. Proteins, lipids, and DNA make up a large part of your body, so that damage can lead to a vast number of diseases over time.
diabetes
atherosclerosis, or the hardening of the blood vessels
inflammatory conditions
high blood pressure, which is also known as hypertension
heart disease
neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s
cancer
Oxidative stress can cause chronic inflammation. Infections and injuries trigger the body's immune response. Immune cells called macrophages produce free radicals while fighting off invading germs. These free radicals can damage healthy cells, leading to inflammation.
Oxidative stress can activate a variety of transcription factors, which lead to the differential expression of some genes involved in inflammatory pathways. The inflammation triggered by oxidative stress is the cause of many chronic diseases.
Oxidation happens under a number of circumstances including: when our cells use glucose to make energy. when the immune system is fighting off bacteria and creating inflammation.
Inflammation refers to your body's process of fighting against things that harm it, such as infections, injuries, and toxins, in an attempt to heal itself. When something damages your cells, your body releases chemicals that trigger a response from your immune system.
Inflammation happens when a physical factor triggers an immune reaction.
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is characterized by persistent deficits in social communication and interaction and restricted-repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities. Strong inflammation states are associated with ASD. This inflammatory condition is often linked to immune system dysfunction.
👉 find me here! https://linktr.ee/petahjane
I raised two kids with ASD
Bless your heart. 🙏🏻❤️
👉 find me here! https://linktr.ee/petahjane
and three stepchildren... hardest job ever
Cells produce glutathione as an antioxidant to help resist oxidative stress.
In a more recent study, coenzyme Q10 supplementation was shown to reduce oxidative stress and ASD-like symptoms in ASD children. Another promising molecule is N-acetylcysteine (NAC), a strong antioxidant that helps in boosting glutathione levels. 6 May 2020
During the earliest stages of a virus infection, cytokines are produced when innate immune defenses are activated. The rapid release of cytokines at the site of infection initiates new responses with far-reaching consequences that include inflammation.
Note: Many kinds of bacteria have developed a process called CRISPR that helps them remember viruses they have seen before.
the infected bacterial cell self-destructs to keep the infection from ...
ROS can kill pathogens directly by causing oxidative damage to biocompounds or indirectly by stimulating pathogen elimination by various nonoxidative mechanisms, including pattern recognition receptors signaling, autophagy, neutrophil extracellular trap formation, and T-lymphocyte responses.
Scientists have found that a virus can stimulate photosynthesis in bacterial hosts. ... Viruses that infect bacteria specifically are called bacteriophages. "They abuse the bacteria to produce new virus proteins," explained Microbiology Professor Nicole Frankenberg-Dinkel of the TU Kaiserslautern.
"a virus can stimulate photosynthesis in bacterial hosts."
Blue light can excite porphyrin-like derivatives generated within bacteria, leading to the production of cytotoxic reactive oxygen species (ROS) (7–10).6 Jan 2021
The purpose of artificial photosynthesis is to produce a fuel from sunlight that can be stored conveniently and used when sunlight is not available, by using direct processes, that is, to produce a solar fuel.
Note: The team's perovskite converts light instead of generating current, transforming blue photons to near-infrared (near-IR) photons, which the silicon cell below then turns into electricity. The researchers say the design could boost the efficiency of silicon solar cells by nearly 20%
A quantum dot solar cell (QDSC) is a solar cell design that uses quantum dots as the absorbing photovoltaic material.
Whereas photovoltaics can provide energy directly from sunlight, the inefficiency of fuel production from photovoltaic electricity (indirect process) and the fact that sunshine is not constant throughout the day sets a limit to its use.
Blue quantum dot light-emitting devices (QLEDs) are fabricated with solution process. Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) was doped into the ZnO nanoparticles electron transport layer. Electron injection is blocked and the electron mobility is reduced due to the presence of PVP.
Electron transport layer (ETL) is a layer which has high electron mobility and high electron affinity. Thus in this layer holes are blocked and cannot go through while electrons can flow through. Hole transport layer (HTL) do the opposite of (ETL) behavior it blocks electrons to fllow through .
Electron deficiency is a term describing atoms or molecules having fewer than the number of electrons required for maximum stability. For each atom in a molecule, main group atoms having less than 8 electrons or transition metal atoms having less than 18 electrons are described as electron-deficient.
Oxidation is the loss of electrons, gain of oxygen or loss of hydrogen. Reduction is the gain of electrons, loss of oxygen or gain or hydrogen. ... Often you can explain it in terms of change in oxygen content or hydrogen content but sometimes an explanation in terms of electrons is required.
A photon is produced whenever an electron in a higher-than-normal orbit falls back to its normal orbit. During the fall from high energy to normal energy, the electron emits a photon -- a packet of energy -- with very specific characteristics.
Photoreceptors: Cells in the retina that initially transduce light energy into neural energy. When light hits the eye, the process of photoactivation begins. Light is transduced by rod and cone photoreceptors. Cones: Photoreceptors that are specialized for daylight vision, fine visual acuity and color.
Quantum effect
While in the retina, the nanoparticles are stimulated by visible light entering the eye – and if a quantum dot is stimulated while it is in close proximity to a neural cell, it triggers an action potential in that cell which is interpreted as vision by the brain. 5 Dec 2019
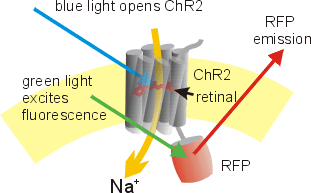
Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels.[1] They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light.[2] Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes (see optogenetics).
This change introduces a further one in the transmembrane protein, opening the pore to at least 6 Å. Within milliseconds, the retinal relaxes back to the all-trans form, closing the pore and stopping the flow of ions.[4] Most natural channelrhodopsins are nonspecific cation channels, conducting H+, Na+, K+, and Ca2+ ions. Recently, anion-conducting channelrhodopsins have been discovered.
Ultraviolet Radiation and HIV Infection: What Do We Know and Should ...
In these experiments, specific light sources were shown to activate the HIV gene and/or promote viral replication. UVC was the most potent activator. UVB, sunlight, and PUVA were also capable of activating HIV, albeit to lesser degrees (1–5).
We observed that oxidative stress positively affects viral RNA replication.
Note: A missense mRNA arises from a missense mutation, in the event of which a DNA nucleotide base pair in the coding region of a gene is changed such that it results in the substitution of one amino acid for another.
Virus mutation is mutation of viruses and may refer to: The feature of viruses to cause mutation in the human genome. The feature of viruses to perform viral genetic change in their own genome.
"to cause mutation in the human genome."
A genome is an organism's complete set of genetic instructions. Each genome contains all of the information needed to build that organism and allow it to grow and develop. ... The instructions in our genome are made up of DNA. Within DNA is a unique chemical code that guides our growth, development and health.
A major cause of DNA damage is oxidative stress, which is defined as an imbalance between an organism's ability to detoxify the reactive intermediates and the amount of reactive oxygen species (ROS) it faces.
Mechanisms of oxidative damage to DNA bases. Of the reactive oxygen species, the highly reactive hydroxyl radical (•OH) reacts with DNA by addition to double bonds of DNA bases and by abstraction of an H atom from the methyl group of thymine and each of the C‐H bonds of 2′‐deoxyribose (2).
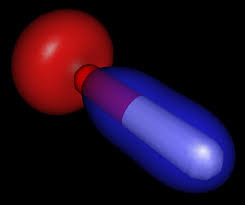
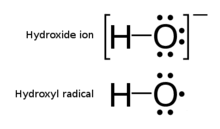
The hydroxyl radical, •OH, is the neutral form of the hydroxide ion (OH−). ... It is also an important radical formed in radiation chemistry, since it leads to the formation of hydrogen peroxide and oxygen, which can enhance corrosion and SCC in coolant systems subjected to radioactive environments.
In living organisms there are two major reactive oxygen species, superoxide radical and hydroxyl radical that are being continuously formed in a process of reduction of oxygen to water. In the Haber-Weiss reaction hydroxyl radicals are generated in the presence of hydrogen peroxide and iron ions.
In chemistry, iron(II) refers to the element iron in its +2 oxidation state. In ionic compounds, such an atom may occur as a separate cation denoted by Fe²⁺.