Child of God, truth-seeker finder and sharer, patriot, inspired and fired up!
These look like streptococci and staphylococci🤔
Child of God, truth-seeker finder and sharer, patriot, inspired and fired up!
Bacteria
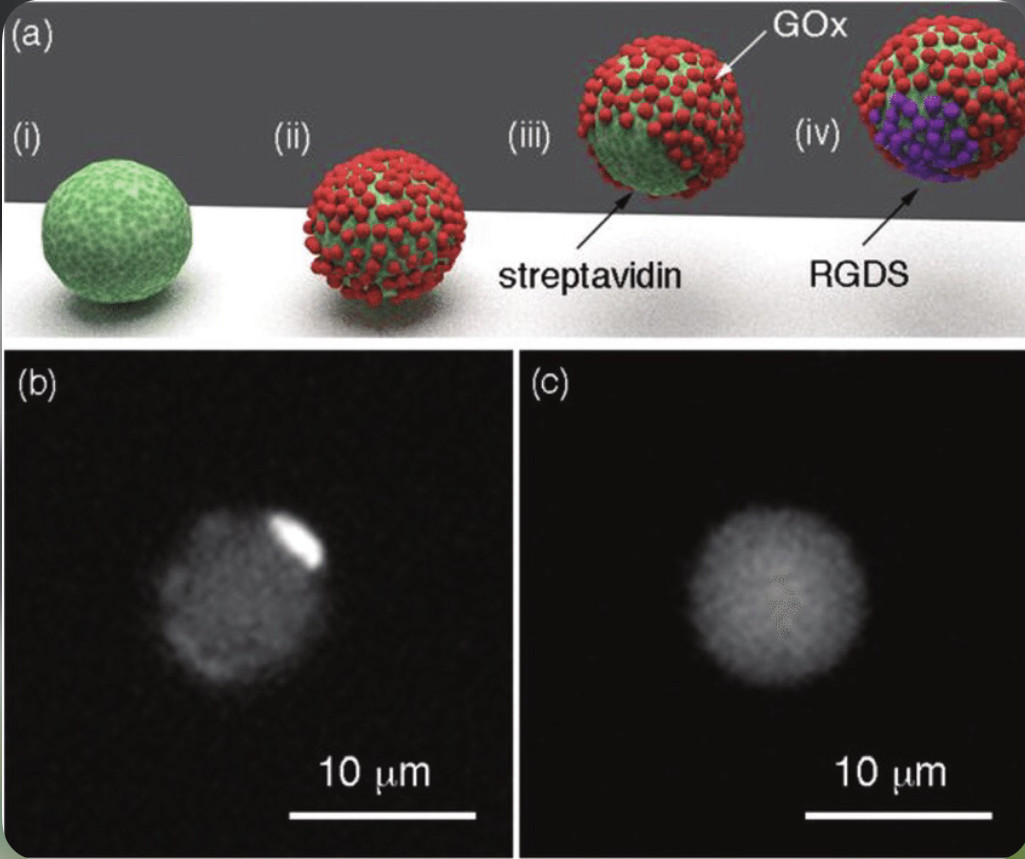
Here, we have investigated structural changes in mixed liposomes mimicking the lipid composition of Gram-positive bacteria membranes, in which the concentration of Bacillus Subtilis LTA was varied between 0–15 mol%. Small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) and dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurements indicated formation of mixed unilamellar vesicles, presumably stabilized by the negatively charged LTA polyphosphates.
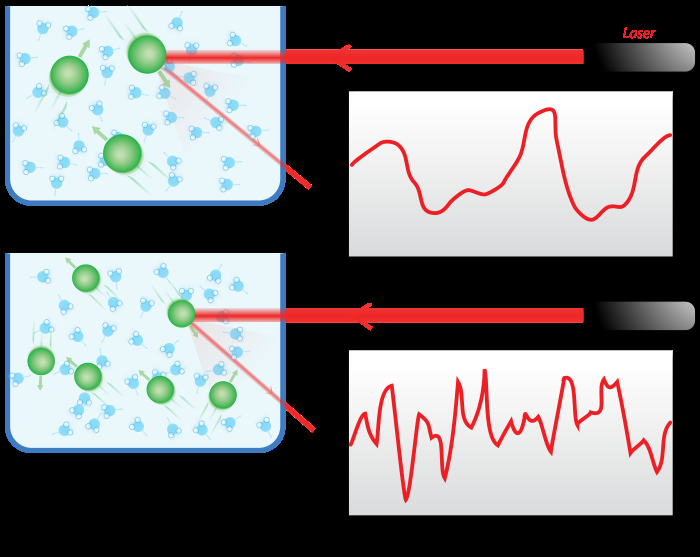
Dynamic light scattering (DLS) is a technique in physics that can be used to determine the size distribution profile of small particles in suspension or polymers in solution. In the scope of DLS, temporal fluctuations are usually analyzed by means of the intensity or photon auto-correlation function (also known as photon correlation spectroscopy or quasi-elastic light scattering).
🙂
NTA has been used by commercial, academic, and government laboratories working with nanoparticle toxicology, drug delivery, exosomes, microvesicles, bacterial membrane vesicles, and other small biological particles, virology and vaccine production, ecotoxicology, protein aggregation, orthopedic implants, inks and pigments, and nanobubbles.
Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) is a method for visualizing and analyzing particles in liquids that relates the rate of Brownian motion to particle size. The rate of movement is related only to the viscosity and temperature of the liquid; it is not influenced by particle density or refractive index. NTA allows the determination of a size distribution profile of small particles with a diameter of approximately 10-1000 nanometers (nm) in liquid suspension.
The technique is used in conjunction with an ultramicroscope and a laser illumination unit that together allow small particles in liquid suspension to be visualized moving under Brownian motion. The light scattered by the particles is captured using a CCD or EMCCD camera over multiple frames. Computer software is then used to track the motion of each particle from frame to frame.