It could just be me but ever since Joe Biden's sham inauguration... there seems to be this growing sense of relief for all these dirty scumbag perverts.
The Mac, it is not judt you whom feels their boldness.
Let them boast, the light of truth shall reveal them & their wickedness.
Samsung Asset Management is looking to learn from Rothschild via the agreement, too. Rothschild has been engaged in private banking for the super rich for over six decades and Samsung Asset Management is looking forward to being imparted with its portfolio organization know-how and financial product management expertise via its corporation in London.
Crap..Samsung too?? Well, guess I am saving for a different tablet...damn it.
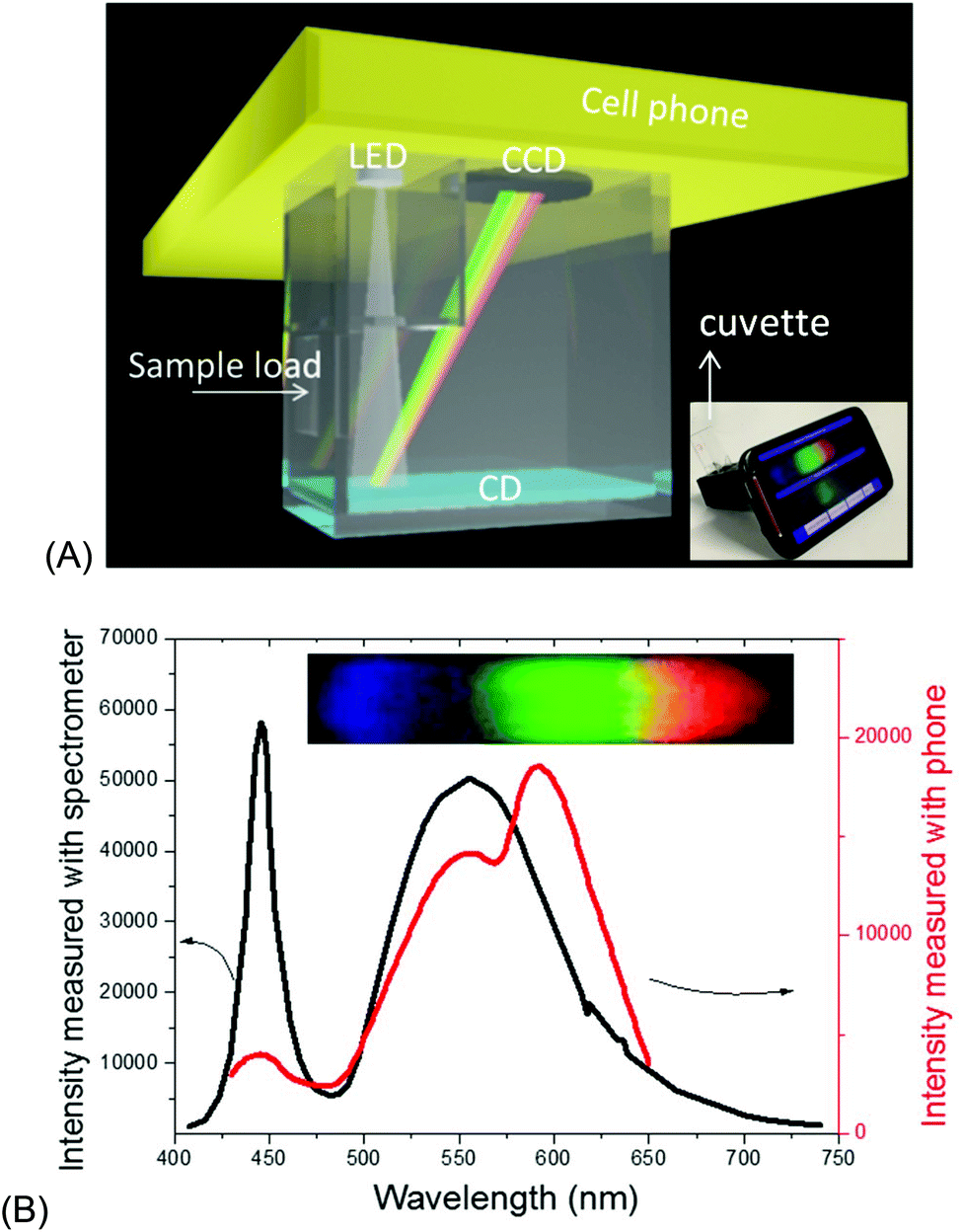
Cuvette 19 lol.
cuvette (French: cuvette = "little vessel") is a small tube-like container with straight sides and a circular or square cross section. It is sealed at one end, and made of a clear, transparent material such as plastic, glass, or fused quartz. Cuvettes are designed to hold samples for spectroscopic measurement, where a beam of light is passed through the sample within the cuvette to measure the absorbance, transmittance, fluorescence intensity, fluorescence polarization, or fluorescence lifetime of the sample. This measurement is done with a spectrophotometer.
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between matter and electromagnetic radiation as a function of the wavelength or frequency of the radiation.[1][2][3][4][5][6] In simpler terms, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum; indeed, historically, spectroscopy originated as the study of the wavelength dependence of the absorption by gas phase matter of visible light dispersed by a prism.
Matter waves and acoustic waves can also be considered forms of radiative energy, and recently gravitational waves have been associated with a spectral signature in the context of the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO).
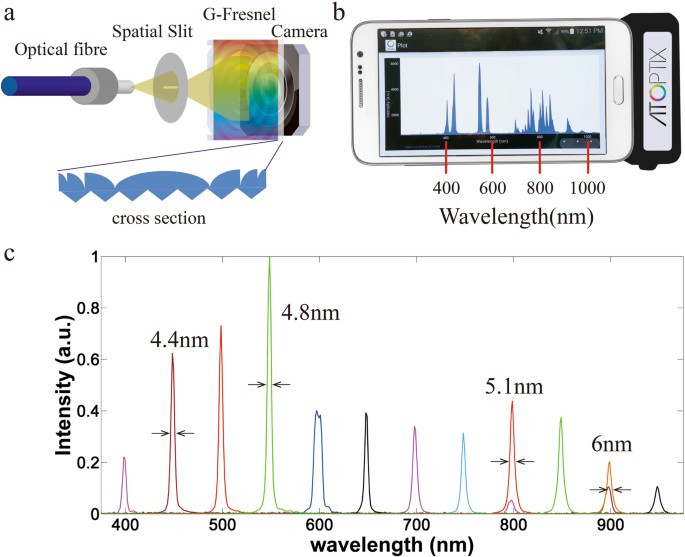
Galaxy S11 may be first Samsung with Spectrometer
By Chris Burns on Sep 30, 2019, 12:35pm CDT
An ideal probe would be local in its physical extent, minimize screening of local interactions and at the same time retain a parallel geometry to avoid non-homogeneous charging.
In addition, it should sustain a high bias without deforming local potentials. Here we show that these seemingly contradicting requirements are fulfilled by resonant tunneling through quantum dots (QDs) bound to atomic defects within van der Waals tunnel barriers.
Graphene-based tunnel junctions are highly parallel, and dot energies are capacitively tuned by the planar electrode, thus avoiding local charging effects due to applied bias. Barrier-embedded dots are nanometric—both in their physical dimensions, and in their proximity to the sample layer. Thus, they are sensitive to regions few nm large. Finally, defect dots lack any degree of freedom for charge rearrangement, they do not screen local interactions, and are hence less invasive than metallic probes.
When QDs couple weakly to the source and drain electrodes, they permit resonant charge transport through sharply peaked energy levels. In this regime, sample DOS is probed by the current through the dot, rather than differential current—avoiding large DC contributions.
QDs are utilized as local thermometers, where energy distribution is tracked using the energy-selective nature of injection and ejection of carriers through the QD. Alternatively, by electrostatic tuning of the QD level, sequential tunneling through the QD singles out the sample DOS in resonance with the dot—as seen in the gate-tunable dots used to probe the spectra of superconductor-proximitized nanowires
We demonstrate the utility of QD-assisted spectroscopy in a study of the graphene excitation spectrum. In the graphene quantum Hall regime, Landau levels are fourfold degenerate. This SU(4) symmetry allows for several distinct paths of symmetry breaking, driven by magnetic field, causing the emergence of ordered ground states which may break either spin or valley degeneracy. The order in which these symmetries should break is subject to debate: While the spin degeneracy is broken by the Zeeman effect, the breaking of valley degeneracy via magnetic field is not as straight-forward.
Coulomb blockade resonances in quantum dots are investigated as a function of magnetic fields applied in the plane of the electron gas. For weak coupling of the dot to the leads, where the Coulomb resonances are basically dominated by individual quantum states, we observe strongly fluctuating Coulomb peak positions, which can be qualitatively explained by linear Zeeman shifts.
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and their colleagues have for the first time created and imaged a novel pair of quantum dots -- tiny islands of confined electric charge that act like interacting artificial atoms. Such "coupled" quantum dots could serve as a robust quantum bit, or qubit, the fundamental unit of information for a quantum computer. Moreover, the patterns of electric charge in the island can't be fully explained by current models of quantum physics, offering an opportunity to investigate rich new physical phenomena in materials.
Here we show that many of these limitations can be overcome by replacing interferometric optics with a two-dimensional absorptive filter array composed of colloidal quantum dots14,15,16,17. Instead of measuring different bands of a spectrum individually after introducing temporal or spatial separations with gratings or interference-based narrowband filters, a colloidal quantum dot spectrometer measures a light spectrum based on the wavelength multiplexing principle18:
multiple spectral bands are encoded and detected simultaneously with one filter and one detector9,10,11,12, respectively, with the array format allowing the process to be efficiently repeated many times using different filters with different encoding so that sufficient information is obtained to enable computational reconstruction of the target spectrum.
We illustrate the performance of such a quantum dot microspectrometer, made from 195 different types of quantum dots with absorption features that cover a spectral range of 300 nanometres, by measuring shifts in spectral peak positions as small as one nanometre.
Given this performance, demonstrable avenues for further improvement, the ease with which quantum dots can be processed and integrated, and their numerous finely tuneable bandgaps that cover a broad spectral range, we expect that quantum dot microspectrometers will be useful in applications where minimizing size, weight, cost and complexity of the spectrometer are critical.
In vivo fluorescence imaging in near IR-IIb window (1,500–1,700 nm) can provide high spatial and temporal resolution and deep tissue penetration for fundamental research and potential translations. Herein, a bright fluorescent probe emitting at ∼1,600 nm based on lead sulfide (PbS)/CdS quantum dots was developed.
The CdS shell helped to chemically passivate and retain the high fluorescence of the PbS core after phase transfer to aqueous solutions for biocompatibility. The 1,600-nm emitting probe allowed noninvasive, millimeter-deep fluorescence imaging at high speeds up to 60 frames per second with micrometer-scale spatial resolution in 2D wide-field and 3D confocal modes. The probes were nontoxic and largely excreted over 1 month, providing a tool for in vivo research of preclinical animal models.
Light from electrons confined by quantum dots has been used to activate and control targeted brain neurons. It also offers an alternative to electrodes on the scalp or implanted within the brain that deliver zaps of electricity for cell stimulation. ...
The disadvantages of retinal implants include chronic damage from the implanted electrodes, insufficient current produced by microphotodiode (in case of subretinal implant) from the ambient light to stimulate adjacent neurons, cellular outgrowth due to surgical implantation and disordered stimulation patterns resulting from the electrical stimulation of both the axon and soma (in epiretinal implant).
Further, electrical stimulation-based implants are limited by poor resolution (higher electrode densities require more current, leading to heat production) and do not provide cell-specific activation.
Well that's that then. 🤷🏼♂️
...or is it?
Optogenetic sensitization (e.g. channelrhodopsin-2, ChR2; halorhodopsin, NpHR) of higher-order retinal neurons or residual receptors and cell-specific activation/inhibition with high temporal precision15,16,17,18,19 has potential as an alternative to electrical stimulation through implants. Optogenetics has advantages such as cellular specificity (e.g. residual cones, ganglion or bipolar cells), minimal invasiveness20,21 and elimination of intraocular surgery.
Optogenetic activation of ChR2 has been evaluated for vision restoration in mice models of retinal degeneration either by non-specific stimulation of retina22 or in a cell-specific manner for retinal ganglion cells23,24,25,26,27 and ON bipolar cells28,29. Further, use of such active light stimulation of chloride-channel opsin (NpHR) expressing in longer-persisting cone photoreceptor protein has shown promise for restoration of vision.
However, clinical translation of optogenetic activation for vision restoration has a major challenge: due to narrow spectral sensitivity of conventional opsins, the light levels needed to activate the cells are at least an order of magnitude higher than bright ambient white light levels (~0.01 mW/mm2). Thus, intense narrow-band light sources31 are being developed to activate opsin-sensitized cells in retina for restoring vision.
However, chronic stimulation of narrow-band opsin-expressing retinal cells at high light intensity may substantially damage the residual light-sensing function that might exist in the partially-degenerated retina.
Herein, we introduce an ambient white-light based cell stimulation paradigm employing a broad-band (400–700 nm) activatable white-opsin. Our results show that significant photocurrent with ms-channel kinetics can be reliably generated in white-opsin sensitized cells at white light intensity level close to ambient day-light condition.
The significantly reduced white light stimulation intensity required for activating white-opsin sensitized cells will lead to ambient white light based restoration of vision in case of retinal degenerative diseases. This will provide high resolution vision restoration and eliminate the requirement of active-stimulation device.
The retina is the back part of the eye that contains the cells that respond to light. These specialized cells are called photoreceptors. There are 2 types of photoreceptors in the retina: rods and cones. ... Signals from the cones are sent to the brain which then translates these messages into the perception of color.
An improved method for stimulating electrical activity in an eye is provided. Provided is a technique for implanting small, nanometer-sized photoactive devices into an eye to improve electrical activity within an eye or mitigate degradation of electrical response in damaged eyes.
photoactive (comparative more photoactive, superlative most photoactive)
Able to convert the energy of light into electricity via photoelectricity
Able to react chemically under the influence of light
God bless you. 🙏🏻❤️