So lets get this right here. The Covid-19 virus was a set up using a mixture of light activated semiconducting paramagnetic solar cell liposome nanoparticles (quantum dots) sprayed from the air (atomizer nozzle) and also pre-encapsulated in the flu vaccines.
The mRNA lipid nanoparticle vaccine is for mutating (DNA) neurons to express light activated opsin, that are coincidently activated by an incident of light emitted from the (quantum dot) nanoparticle.
The trick here using ultrasound phased array transducers/antennas to burst the lipid bilayer open and guide the particles as tweez
Child of God, truth-seeker finder and sharer, patriot, inspired and fired up!
And there you have it in a nutshell.
That is why you are "The Mac".
Awesome.
Now, how do we fix this?
verb: fix; 3rd person present: fixes; past tense: fixed; past participle: fixed; gerund or present participle: fixing
1.
fasten (something) securely in a particular place or position.
"they had candles fixed to their helmets"
fasten
attach
affix
secure
make fast
join
connect
couple
link
install
implant
plant
embed
anchor
stick
glue
bond
cement
pin
nail
screw
bolt
clamp
clip
bind
tie
lash
establish
position
station
situate
lodge
Opposite:
remove
direct one's eyes, mind, or attention steadily or unwaveringly towards.
"Ben nodded, his eyes fixed on the ground"
(of a person's eyes, attention, or mind) be directed steadily or unwaveringly towards.
focus
direct
level
point
rivet
train
turn
converge
zero in
attract
draw
hold
grip
engage
captivate
absorb
look at someone unwaveringly.
"Cowley fixed him with a cold stare"
2.
decide or settle on (a specific price, date, course of action, etc.).
"no date has yet been fixed for a hearing"
decide on
select
choose
resolve on
determine
arrive at
settle
set
finalize
arrange
prearrange
establish
allot
prescribe
designate
define
name
ordain
appoint
specify
stipulate
establish the exact location of (something) by using radar or visual bearings
or astronomical observation.
settle the form of (a language).
assign or determine (a person's liability or responsibility) for legal purposes.
"there are no facts which fix the defendant with liability"
mend or repair.
The word grim comes from the Proto-Indo-European root 'ghrem-' meaning 'angry'. Over time, the word was adapted into the Proto-Germanic 'grimmaz' meaning 'fierce, savage, painful'. Grim was first recorded in English sometime in the late 12th century.
(“to resound, thunder, grumble, roar”).
grim (comparative grimmer, superlative grimmest)
dismal and gloomy, cold and forbidding
Life was grim in many northern industrial towns.
rigid and unrelenting
His grim determination enabled him to win.
ghastly or sinister
disgusting; gross
grim (plural grims)
(obsolete) specter, ghost, haunting spirit
Verb
grim (third-person singular simple present grims, present participle grimming, simple past and past participle grimmed)
(transitive, rare) To make grim; to give a stern or forbidding aspect to.
grim (uncountable)
(archaic) Anger, wrath.
Perhaps related in Old Norse to veiled or hooded, Grim is also an alternate name for Odin, who often went around disguised; compare the hooded appearance of The Grim Reaper.
Anglicized form of Old Norse Óðinn, which was derived from óðr meaning "inspiration, rage, frenzy". It ultimately developed from the early Germanic *Woðanaz.
An odd number is an integer when divided by two, either leaves a remainder or the result is a fraction. One is the first odd positive number but it does not leave a remainder 1. Some examples of odd numbers are 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, and 11. ... Since odd numbers are integers, negative numbers can be odd.
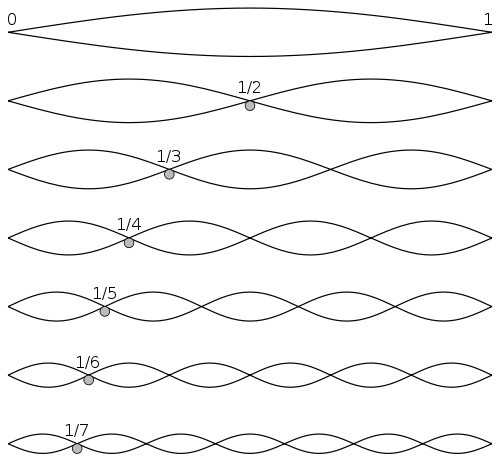
For all standing wave frequencies, the nodes and antinodes alternate with equal spacing.
This standing wave is called the fundamental frequency, with L = λ 2 L= dfrac{lambda}{2} L=2λL, equals, start fraction, lambda, divided by, 2, end fraction, and there are two nodes and one antinode.
The fundamental frequency, often referred to simply as the fundamental, is defined as the lowest frequency of a periodic waveform. In music, the fundamental is the musical pitch of a note that is perceived as the lowest partial present.
In terms of a superposition of sinusoids, the fundamental frequency is the lowest frequency sinusoidal in the sum of harmonically related frequencies, or the frequency of the difference between adjacent frequencies. In some contexts, the fundamental is usually abbreviated as f0, indicating the lowest frequency counting from zero. In other contexts, it is more common to abbreviate it as f1, the first harmonic.(The second harmonic is then f2 = 2⋅f1, etc. In this context, the zeroth harmonic would be 0 Hz.)
A harmonic spectrum is a spectrum containing only frequency components whose frequencies are whole number multiples of the fundamental frequency; such frequencies are known as harmonics.
harmonic is any member of the harmonic series. The term is employed in various disciplines, including music, physics, acoustics, electronic power transmission, radio technology, and other fields. It is typically applied to repeating signals, such as sinusoidal waves. A harmonic of such a wave is a wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the frequency of the original wave, known as the fundamental frequency.
The original wave is also called the 1st harmonic, the following harmonics are known as higher harmonics. As all harmonics are periodic at the fundamental frequency, the sum of harmonics is also periodic at that frequency. For example, if the fundamental frequency is 50 Hz, a common AC power supply frequency, the frequencies of the first three higher harmonics are 100 Hz (2nd harmonic), 150 Hz (3rd harmonic), 200 Hz (4th harmonic) and any addition of waves with these frequencies is periodic at 50 Hz.
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time.[1] It is also referred to as temporal frequency, which emphasizes the contrast to spatial frequency and angular frequency. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is equal to one occurrence of a repeating event per second.
The period is the duration of time of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency.[2] For example: if a newborn baby's heart beats at a frequency of 120 times a minute (2 hertz), its period, T, — the time interval between beats—is half a second (60 seconds divided by 120 beats). Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio signals (sound), radio waves, and light.
Alternating current describes the flow of charge that changes direction periodically.
The Finite element modeling (FEM) simulation and comparison of electroacoustic properties for alternating current poling (ACP) phased arrays and ...
Controlling particle size is essential for crystal quality in the chemical and pharmaceutical industry. Several articles illustrate the potential of ultrasound to tune this particle size during the crystallization process.
This paper investigates how ultrasound can control the particle size distribution (PSD) of acetaminophen crystals by continuous seed generation in a tubular crystallizer followed by batch growth. It is demonstrated that the supersaturation ratio at which ultrasound starts seed generation has a substantial effect on the final PSD while the applied power is insignificant in the studied conditions.
The higher the supersaturation ratio, the smaller the final crystals become up to a supersaturation ratio of 1.56. Furthermore, it was shown that ultrasound can also impact the final PSD when applied during the growth phase. Frequencies of 850 kHz or below reduce the final particle size; the lower the applied frequency, the smaller the crystals become. In conclusion, one could state that ultrasound is able to control the particle size during seed generation and subsequent growth until the final particle size.
Keywords: sonocrystallization; particle size control; acoustic cavitation; continuous seeding; semi-continuous crystallization; process intensification; cooling crystallization
Sonication is the act of applying sound energy to agitate particles in a sample, for various purposes such as the extraction of multiple compounds from plants, microalgae and seaweeds. Ultrasonic frequencies are usually used, leading to the process also being known as ultrasonication or ultra-sonication.
What does an ultrasound transducer do?
A device that produces sound waves that bounce off body tissues and make echoes. The transducer also receives the echoes and sends them to a computer that uses them to create a picture called a sonogram. Transducers (probes) come in different shapes and sizes for use in making pictures of different parts of the body.
Resonant ultrasound spectroscopy (RUS) is a laboratory technique used in geology and material science to measure fundamental material properties involving elasticity. This technique relies on the fact that solid objects have natural frequencies at which they vibrate when mechanically excited.