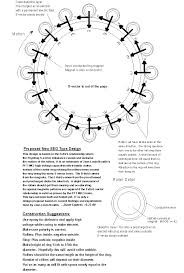
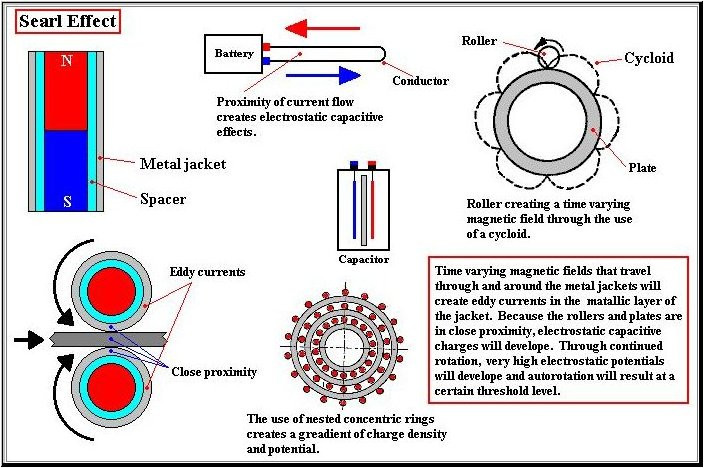
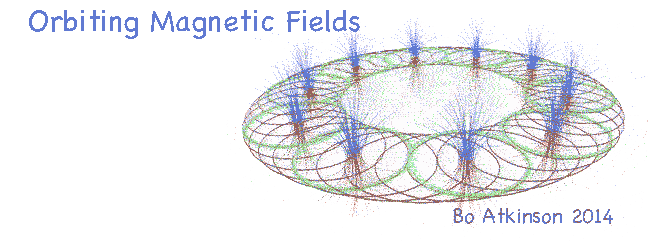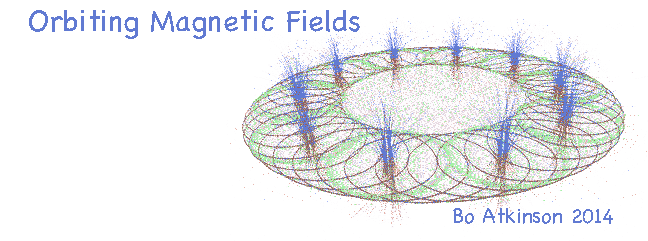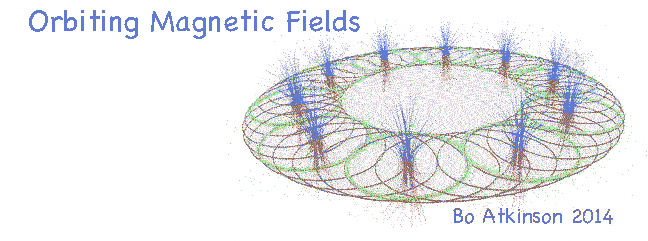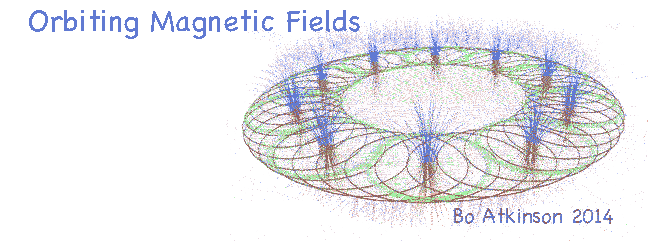
Оче наш, који си на небесима, да се свети име Твоје, да дође царство Твоје, да буде воља Твоја и на земљи као на небу
Frequency levitation. It's been here for a while, can't wait for it to be brought to commercial use. Don't know how they managed to keep it from us for so long, it's a simple concept in theory
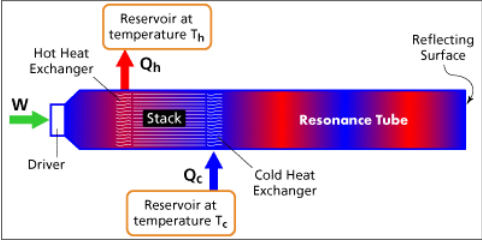
In many of the large scale applications of thermoacoustic engines, discussed by Swift [4] and Garrett and Hofler [5], a typical operating frequency has been around 500 Hz.
Its simple design and the fact that it is one of a few prime movers that do not require moving parts make such a device an attractive alternative for many practical applications. The acoustic power produced by the TAHE can be used to generate electricity, drive a heat pump or a refrigeration system.
Scientists have now found answers to central questions which had previously stood in the way of acoustic propulsion of nanoparticles.
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. was an American semiconductor manufacturer. It was created by the divestiture of the Semiconductor Products Sector of Motorola in 2004. Freescale focused their integrated circuit products on the automotive, embedded and communications markets. It was bought by a private investor group in 2006, and subsequently merged into NXP Semiconductors in 2015.
Loss of employees on Malaysia flight a blow, U.S. chipmaker says | Reuters
Employees of Freescale Semiconductor who were on a Malaysia Airlines flight presumed to have crashed were doing sophisticated work at the U.S. chipmaker, a company spokesman said on Sunday.
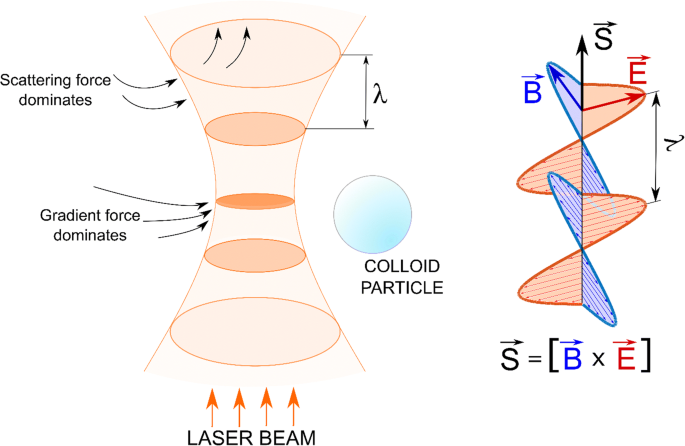
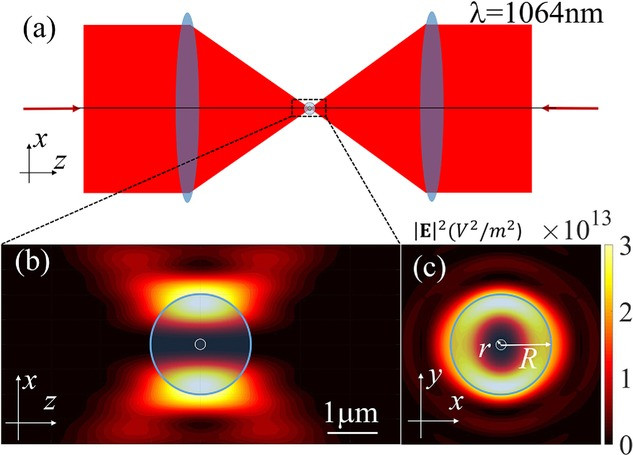
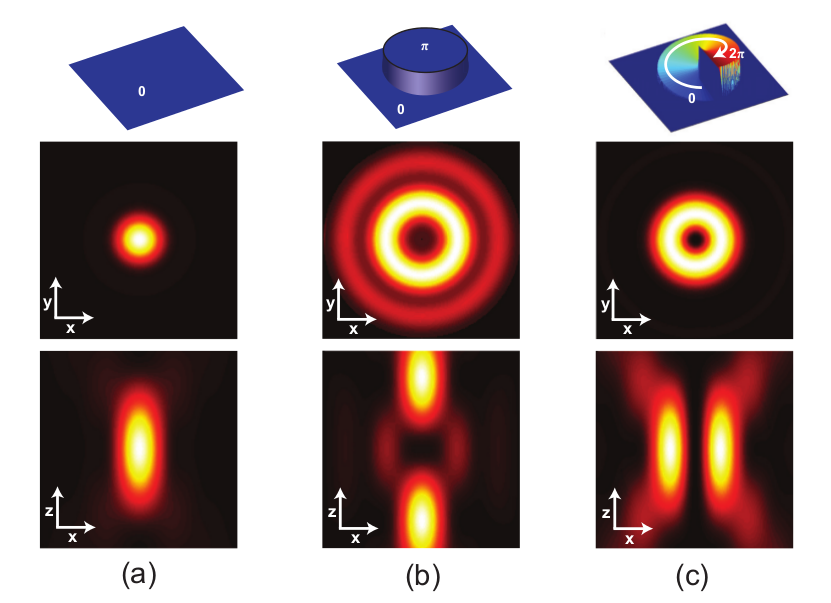
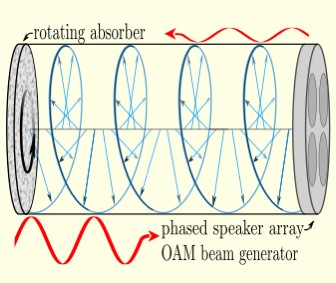
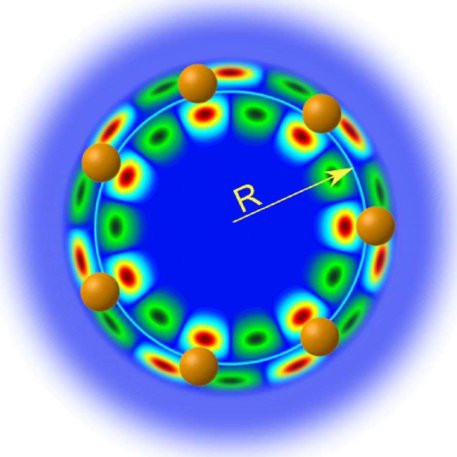
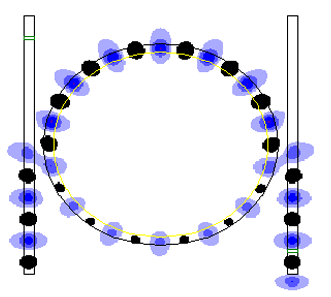
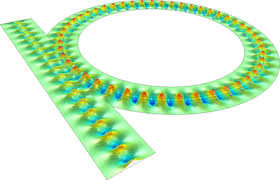
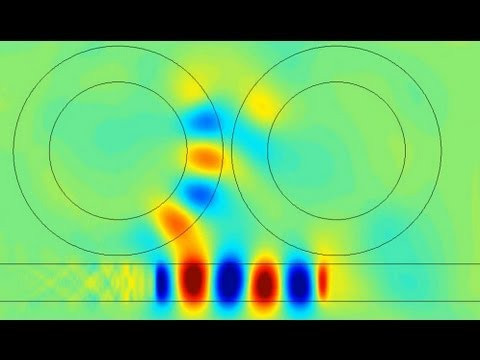
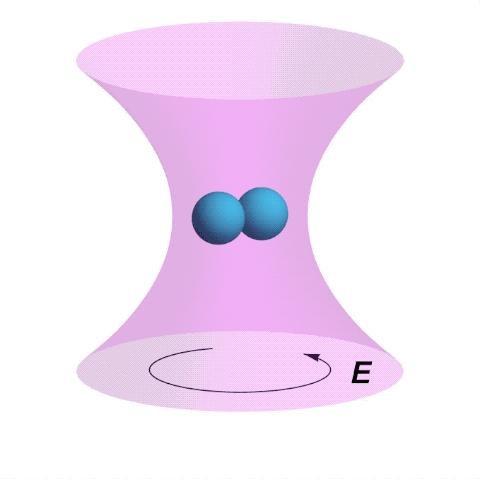
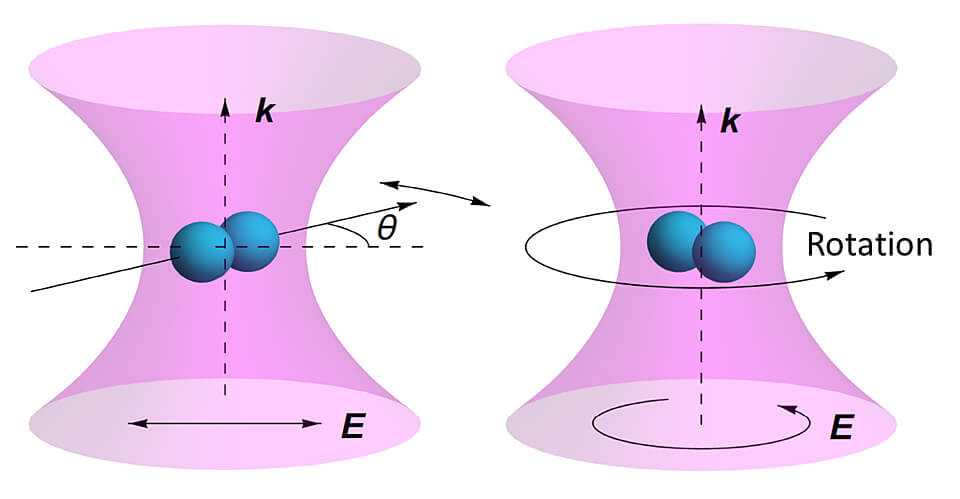
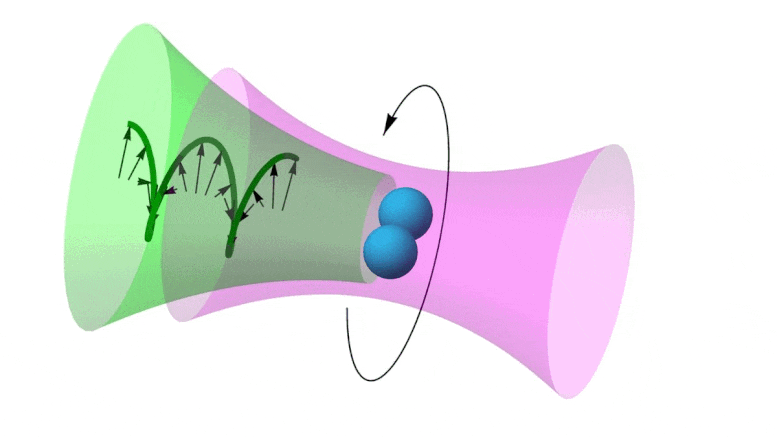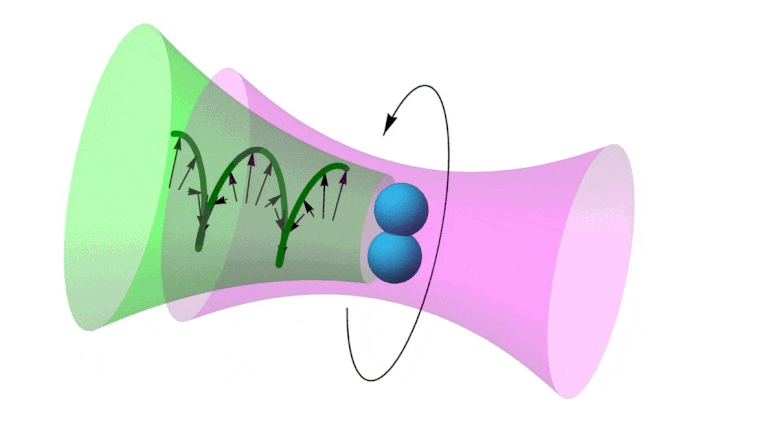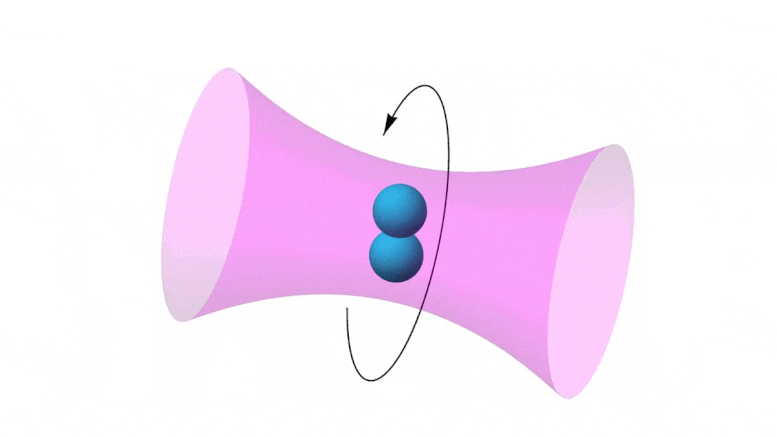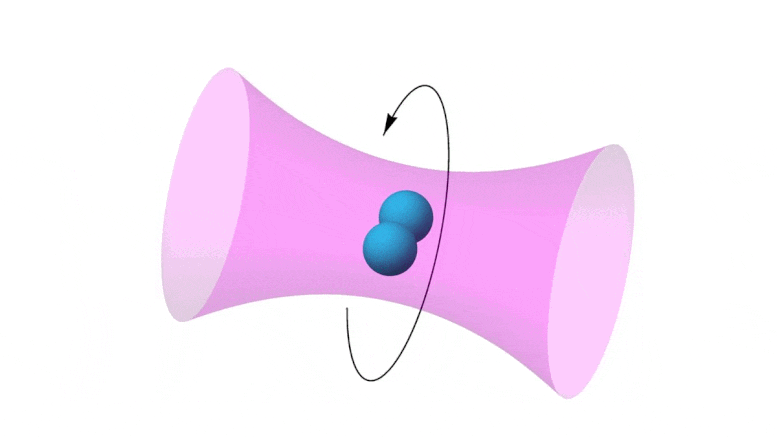
https://www.reuters.com/article/us-malaysia-airlines-freescale-idUSBREA280T020140309Acoustic levitation is a method for suspending matter in air against gravity using acoustic radiation pressure from high intensity sound waves. It works on the same principles as acoustic tweezers by harnessing acoustic radiation forces.
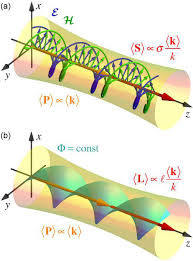
Radiation pressure is the mechanical pressure exerted upon any surface due to the exchange of momentum between the object and the electromagnetic field. This includes the momentum of light or electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength that is absorbed, reflected, or otherwise emitted (e.g. black-body radiation) by matter on any scale (from macroscopic objects to dust particles to gas molecules). The associated force is called the radiation pressure force, or sometimes just the force of light.
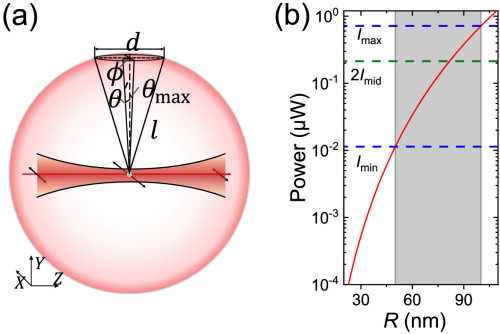
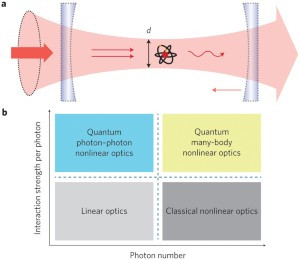
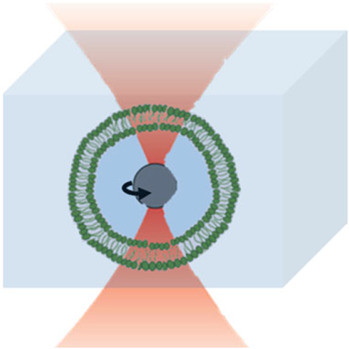
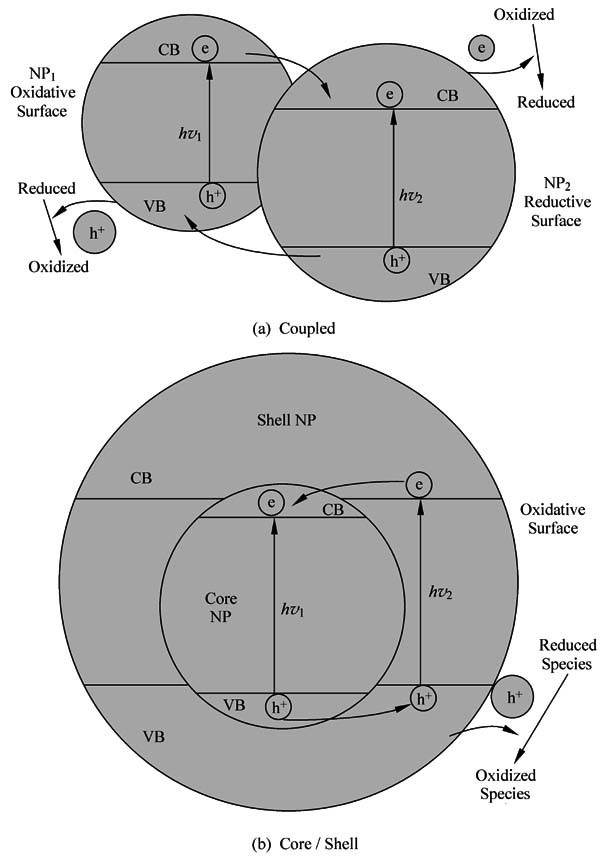
Semiconductor nanoparticles (NPs) are interesting materials because they have chemical and physical properties different from those of the bulk and isolated atoms or molecules with the same chemical composition (Henglein, 1989; Gratzel, 1989a; 1989b; Bawendi, et al., 1990a; 1990b; Wang, 1991a; 1991b; Schmid, 1994; Tolbert and Alivisatos, 1995; Miller, et al., 1995; Fendler and Meldrum, 1995; Alivisatos, 1996a; 1996b; Liu, et al., 1997; Kamat, 1997; Zhang, 1997; Collier, et al., 1998; Heath and Shiang, 1998). They provide opportunities to study the effect of spatial confinement and problems related to surfaces or interfaces. A typical nanoparticle has length of a few to a few tens of nanometers and contains atoms or molecules numbering from tens to tens of thousands. Nanoparticles may be fabricated in the form of quantum dots (QD), quantum particles (Q particles), nanocrystals, or nanophase materials.