Should we lock up the the culprits who pushed the vaccine until we get to the bottom of the truth?
They will only do it again given the opportunity.
They targetted the elderly people, soldiers, nurses, women... and innocent vulnerable children.
These are cold hearted bastards with no remorse or care for life... f amnesty forgiveness.
Never Forget Why This War Was Started It Is All About Saving The Children
When optics researchers get together over coffee to discuss their favorite cavities, attention turns to microtoroids, tiny glass spheres, and photonic crystals with defects. These cavities all have a few things in common: they are all really good at storing light, and they are high-precision devices.
Physicists use a number, called Q, to characterize how well an optical cavity stores light: the higher the Q, the longer light stays confined in the cavity. You do not, it turns out, go blithely into your local fab and turn out a high-Q cavity. It takes a lot of practice and trial and error to create a high-Q optical cavity.
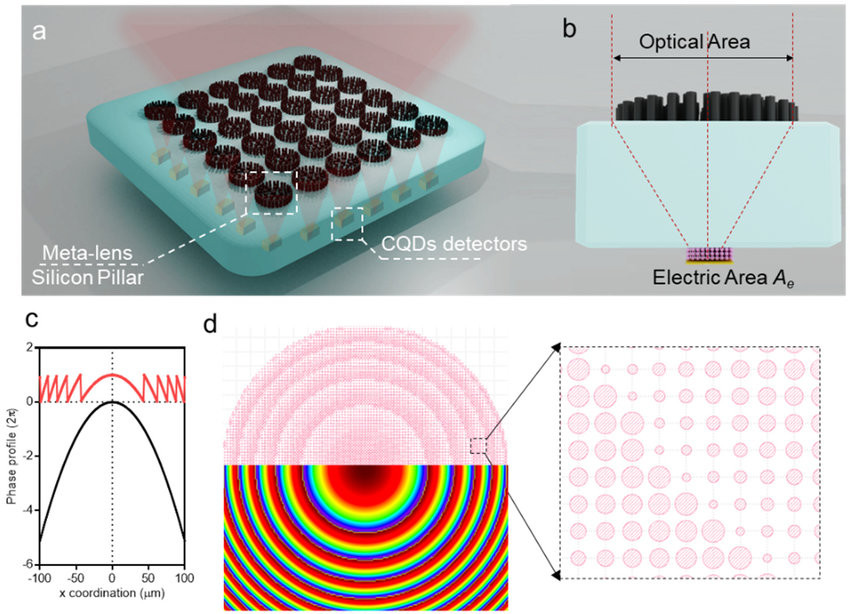
(a) Illustration of meta-lens integrated with CQD detectors. Incident light is collected and focused into CQD detectors with a small electric area. (b) Cross-sectional illustration of the meta-lens integrated with the CQD detector. Light illuminated onto the optical area is focused to the CQD detector with electric area A e . (c) Phase profile of a regular lens (black curve) and meta-lens (red). (d) Design of meta-lens using pillar structures. The diameter and focal length are 200 and 200 µm, respectively. Inset is a representative 2D phase mapping used to generate the meta-lens design.
We report on the spectroscopic investigation of quantum dot - micropillar cavities with unprecedented quality factors. We observe a pronounced dependency of the quality factor on the measurement scheme, and find that significantly larger quality factors can be extracted in photoreflectance compared to photoluminescence measurements. While the photoluminescence spectra of the microcavity resonances feature a Lorentzian lineshape and Q-factors up to 184,000, the reflectance spectra have a Fano-shaped asymmetry and feature significantly higher Q-factors in excess of 250,000 resulting from a full saturation of the embedded emitters. The very high quality factors in our cavities promote strong light-matter coupling with visibilities exceeding 0.5 for a single QD coupled to the cavity mode.
3D polymer/quantum dots (QDs) nanocomposite QD-lens is fabricated by stereolithography (SLA) 3D printer with in-situ UV curing system. Various UV-curable polymer precursors are mixed with QDs to investigate their printability and optical performance.
Optoelectronic modulation of neural activity is an emerging field for the investigation of neural circuits and the development of neural therapeutics. Among a wide variety of nanomaterials, colloidal quantum dots provide unique optoelectronic features for neural interfaces such as sensitive tuning of electron and hole energy levels via the quantum confinement effect, controlling the carrier localization via band alignment, and engineering the surface by shell growth and ligand engineering. Even though colloidal quantum dots have been frontier nanomaterials for solar energy harvesting and lighting, their application to optoelectronic neural interfaces has remained below their significant potential. However, this potential has recently gained attention with the rise of bioelectronic medicine.
As indicated, the BBB may restrict drug distribution into the brain and liposomal formulation is expected to overcome such restrictions.
Understanding Drug Delivery to the Brain Using Liposome-Based Strategies: Studies that Provide Mechanistic Insights Are Essential
Brain drug delivery may be restricted by the blood-brain barrier (BBB), and enhancement by liposome-based drug delivery strategies has been investigated. As access to the human brain is limited, many studies have been performed in experimental animals. ...
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8553706/Quantum dots increasingly gain popularity for in vivo applications. However, their delivery and accumulation into cells can be challenging and there is still lack of detailed information. Thereby, the application of advanced fluorescence techniques can expand the portfolio of useful parameters for a more comprehensive evaluation. Here, we encapsulated hydrophilic quantum dots into liposomes for studying cellular uptake of these so-called lipodots into living cells. First, we investigated photophysical properties of free quantum dots and lipodots observing changes in the fluorescence decay time and translational diffusion behaviour.
In comparison to empty liposomes, lipodots exhibited an altered zeta potential, whereas their hydrodynamic size did not change. Fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM) and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS), both combined with two-photon excitation (2P), were used to investigate the interaction behaviour of lipodots with an insect epithelial tissue.
In contrast to the application of free quantum dots, their successful delivery into the cytosol of salivary gland duct cells could be observed when applying lipodots. Lipodots with different lipid compositions and surface charges did not result in considerable differences in the intracellular labelling pattern, luminescence decay time and diffusion behaviour. However, quantum dot degradation after intracellular accumulation could be assumed from reduced luminescence decay times and blue-shifted luminescence signals. In addition to single diffusing quantum dots, possible intracellular clustering of quantum dots could be assumed from increased diffusion times. Thus, by using a simple and manageable liposome carrier system, 2P-FLIM and 2P-FCS recording protocols could be tested, which are promising for investigating the fate of quantum dots during cellular interaction.
Study on intracellular delivery of liposome encapsulated quantum dots using advanced fluorescence microscopy | Scientific Reports
Quantum dots increasingly gain popularity for in vivo applications. However, their delivery and accumulation into cells can be challenging and there is still lack of detailed information. Thereby, the application of advanced fluorescence techniques can expand the portfolio of useful parameters for a..
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-46732-5