Recap: Electrolytes for Your Brain
Electrolytes conduct nerve signals and regulate fluid balance in the brain. Sodium is critical for brain health. Hyponatremia (low serum sodium) symptoms include headaches, fatigue, lethargy, and seizures. When sodium is rapidly depleted from overwatering, it can cause brain swelling.
can is use regular old pink hymilayin salt deom the store?
This is the secret of life: Man lives in God and God lives in man.
This answers all questions.
question
/ˈkwɛstʃ(ə)n/
Origin
late Middle English: from Old French question (noun), questionner (verb), from Latin quaestio(n- ), from quaerere ‘ask, seek’.
inquiring (adj.)
"given to inquiry or investigation," 1590s, present-participle adjective from inquire (v.). Related: Inquiringly.
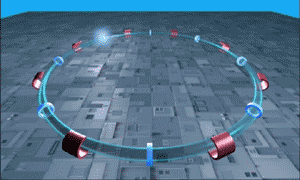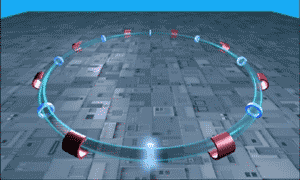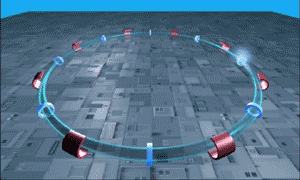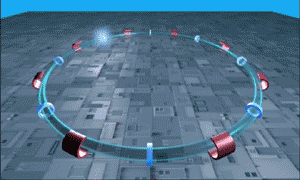
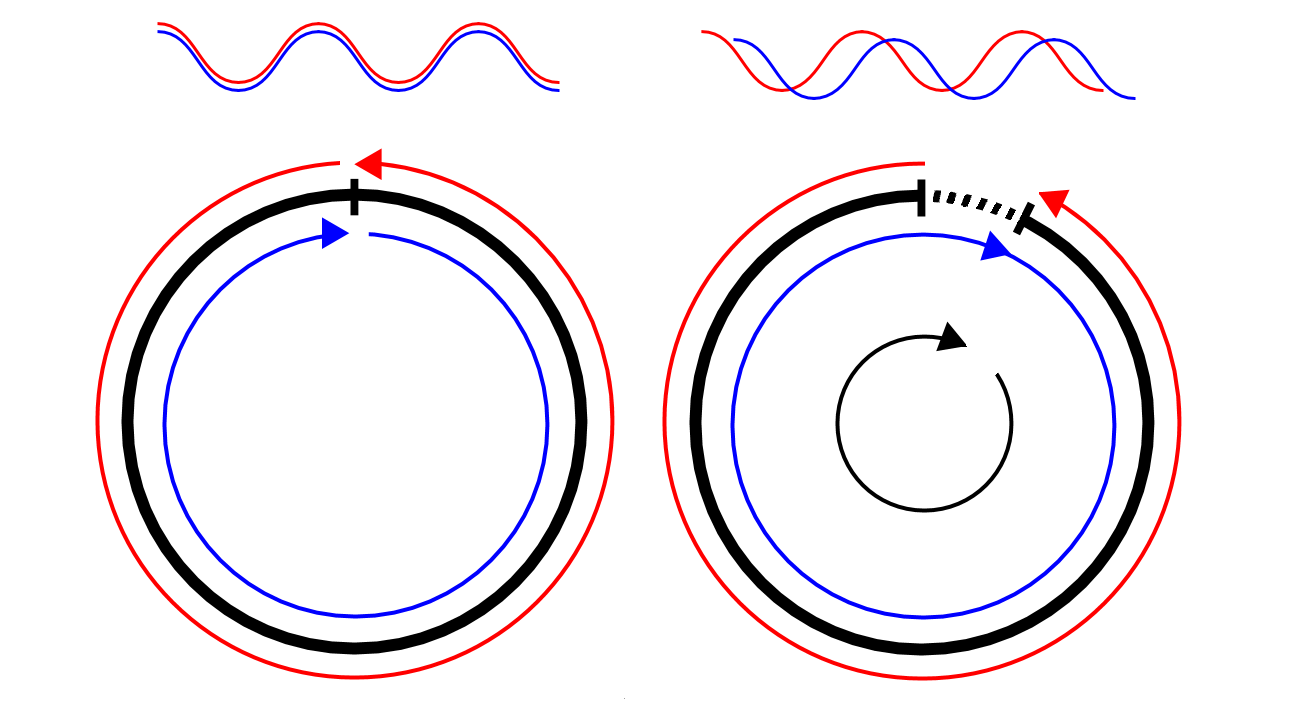
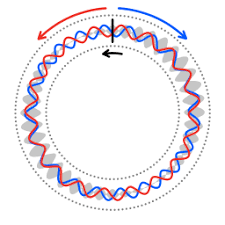
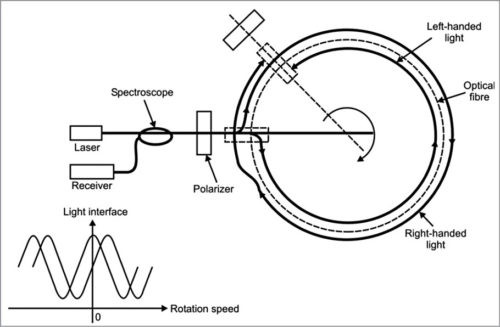
The Low Energy Ion Ring is a particle accelerator at CERN
Anolyte is the electrolyte on the anode side of an electrochemical cell that is divided into compartments.
that portion of the electrolyte in the immediate vicinity of the anode in an electrolytic cell —opposed to catholyte.
catholyte (plural catholytes)
The portion of an electrolyte near a cathode, especially in a cell in which the cathode and anode are in separate compartments
An anion is an ion that is negatively charged, and is attracted to the anode (positive electrode) in electrolysis. A cation has a net positive charge, and is attracted to the cathode (negative electrode) during electrolysis
An electrolytic cell is an electrochemical cell that utilizes an external source of electrical energy to drive a chemical reaction that would not otherwise occur.
Reported here is a preliminary assessment of the feasibility of catalyzing on-line derivatization reactions inside the inlet (i.e., the injection port) of a gas chromatograph (GC) with solid heterogeneous catalysts. The experiments described here entail the installation of candidate catalysts inside the GC inlet liner and the subsequent injection of analyte/reagent mixtures onto the catalyst beds. Two catalysts are identified, each of which clearly catalyzes one of the chosen model derivatization reactions in the inlet of a GC. This result supports our hypothesis that on-line derivatizations can, in principle, be reproducibly catalyzed inside the GC inlet by solid heterogeneous catalysts and that the presence of such catalysts in the inlet do not necessarily cause a serious loss of instrument performance or chromatographic efficiency.
Heterogeneous catalysis typically involves solid phase catalysts and gas phase reactants. In this case, there is a cycle of molecular adsorption, reaction, and desorption occurring at the catalyst surface. Thermodynamics, mass transfer, and heat transfer influence the rate (kinetics) of reaction.
The use of TiO2 as heterogeneous catalyst and/or active support for metals or other oxides is here reported.
A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction, or lowers the temperature or pressure needed to start one, without itself being consumed during the reaction. Catalysis is the process of adding a catalyst to facilitate a reaction.
Heterogeneous gold catalysis refers to the catalysis of chemical reactions by gold, typically supported on metal oxide substrates. Despite the well known inertness of bulk gold, decreasing the diameter of supported gold clusters to c. 2 to 5 nm result in high catalytic activities towards low-temperature carbon monoxide (CO) oxidation. Several other industrially relevant reactions are also observed such as H2 activation, water gas shift, and hydrogenation.[1][2][3]
conceptual
relating to or based on mental concepts.
"philosophy deals with conceptual difficulties"
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a promising antitumor treatment that is based on the photosensitizers that inhibit cancer cells by yielding reactive oxygen species (ROS) after irradiation of light with specific wavelengths. As a potential photosensitizer, titanium dioxide (TiO2) exhibits minimal dark cytotoxicity and excellent ultraviolet (UV) light triggered cytotoxicity, but is challenged by the limited tissue penetration of UV light. Herein, a novel near-infrared (NIR) light activated photosensitizer for PDT based on TiO2-coated upconversion nanoparticle (UCNP) core/shell nanocomposites (UCNPs@TiO2 NCs) is designed. NaYF4:Yb3+,Tm3+@NaGdF4:Yb3+ core/shell UCNPs can efficiently convert NIR light to UV emission that matches well with the absorption of TiO2 shells.
The UCNPs@TiO2 NCs endocytosed by cancer cells are able to generate intracellular ROS under NIR irradiation, decreasing the mitochondrial membrane potential to release cytochrome c into the cytosol and then activating caspase 3 to induce cancer cell apoptosis. NIR light triggered PDT of tumor-bearing mice with UCNPs@TiO2 as photosensitizers can suppress tumor growth efficiently due to the better tissue penetration than UV irradiation. On the basis of the evidence of in vitro and in vivo results, UCNPs@TiO2 NCs could serve as an effective photosensitizer for NIR light mediated PDT in antitumor therapy.